Skonfiguruj rozszerzenie do tworzenia gier na Androida na komputerze z systemem Windows i uruchom przykładowy projekt Visual Studio C++ na urządzeniu z Androidem lub w emulatorze.
Wymagania wstępne
Aby przygotować komputer z systemem Windows do instalacji rozszerzenia, wykonaj czynności opisane w tej sekcji:
Pobierz i zainstaluj jedną z obsługiwanych wersji Visual Studio:
Android Studio w wersji 3.5 lub nowszej jest opcjonalne, ale można go używać zamiast rozszerzenia Android Game Development Extension do instalowania pakietów Android SDK i NDK.
Pobierz i zainstaluj JDK 17 w przypadku AGDE w wersji 23.1.82 lub nowszej albo JDK 11 w przypadku AGDE w wersji 22.2.71 lub starszej i ustaw zmienną środowiskową
JAVA_HOME.
Instalowanie rozszerzenia
Aby pobrać i zainstalować rozszerzenie Android Game Development Extension:
Zamknij wszystkie instancje programu Visual Studio.
Pobierz najnowszy instalator rozszerzenia i przykłady ze strony Pobieranie.
W miejscu pobierania kliknij dwukrotnie instalator. Instalatorowi zajmie to kilka minut.
Jeśli masz zainstalowanych więcej wersji Visual Studio, wybierz te, w których chcesz zainstalować rozszerzenie.
Aby zakończyć instalację, kliknij Zakończ.
Instalowanie pakietów SDK i NDK na Androida
Pakiet Android SDK i pakiet Native Development Kit (NDK) na Androida możesz zainstalować za pomocą Android Studio lub rozszerzenia Android Game Development Extension. Aby zainstalować pakiet SDK i NDK z poziomu rozszerzenia, użyj Menedżera SDK, który znajduje się na pasku narzędzi rozszerzenia w Visual Studio.
Podczas instalowania NDK zaznacz pole wyboru NDK (obok siebie), aby rozszerzenie mogło go znaleźć. Musisz zainstalować wersję NDK obsługiwaną przez rozszerzenie (patrz Historia wersji NDK).
Aby zainstalować pakiet SDK w innym miejscu niż domyślne, ustaw zmienną środowiskową ANDROID_SDK_ROOT na komputerze:
- Upewnij się, że program Visual Studio jest zamknięty.
- W wyszukiwarce Windows wyszukaj
Environment Variables. - Kliknij Edytuj systemowe zmienne środowiskowe.
- Kliknij Zmienne środowiskowe.
- W sekcji Zmienne użytkownika kliknij Nowa.
- W polu Nazwa zmiennej wpisz
ANDROID_SDK_ROOT. - W polu Wartość zmiennej wpisz ścieżkę do pakietu Android SDK.
- Uruchom ponownie komputer.
Lokalizacji pakietu SDK nie można modyfikować w oknie Menedżera SDK, ponieważ ta zmienna środowiskowa jest jedynym źródłem informacji o lokalizacji pakietu SDK.
Uruchamianie przykładu
Aby uruchomić podany przykład na emulatorze, a potem na fizycznym urządzeniu z Androidem, wykonaj czynności opisane w tej sekcji.
Konfigurowanie platformy
Rozpakuj plik ZIP z przykładowymi plikami do wybranego katalogu. Obejmuje to te przykłady:
- endless-tunnel
- HelloJNI
- Czajniczek
Uruchom Visual Studio, jeśli nie jest jeszcze uruchomione.
Otwórz katalog z przykładami. Wybierz Plik > Otwórz > Projekt/Rozwiązanie i przejdź do pliku
.sln.Wybierz platformę Androida:
- Wybierz Build > Configuration Manager (Kompilacja > Menedżer konfiguracji).
- W sekcji Aktywna platforma rozwiązania wybierz Android-x86_64.
Platformy Androida są już skonfigurowane w przykładach (informacje o dodawaniu platform znajdziesz w artykule Dodawanie kolejnych platform Androida).
Sprawdź, czy w przykładzie projektu skonfigurowano właściwości pakietów Android SDK i NDK:
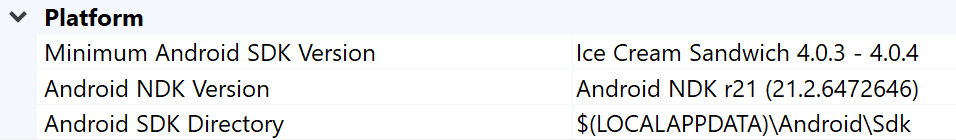
Rysunek 1. Właściwości platformy Android W Eksploratorze rozwiązań kliknij projekt prawym przyciskiem myszy i wybierz Właściwości.
Wybierz kartę właściwości Ogólne i znajdź właściwości Platforma dla Androida.
Wybierz kartę właściwości Pakowanie na Androida.
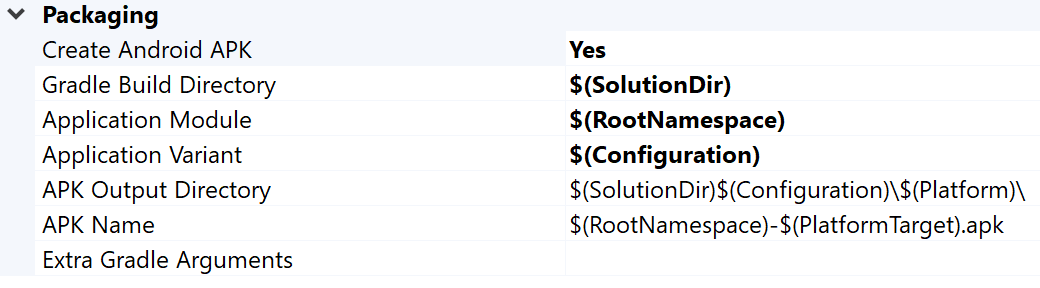
Rysunek 2. Właściwości pakowania na Androida Na tej karcie możesz zmienić nazwę i katalog wyjściowego pliku APK. Pamiętaj, że niektóre właściwości konfiguracji Androida są zdefiniowane na stronach właściwości i przekazywane do Gradle. Na przykład właściwość nazwy pliku APK
MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAMEprzekazuje tę nazwę do pliku aplikacjibuild.gradle.
Konfigurowanie emulatora
Uruchom AVD Manager z paska narzędzi rozszerzenia w Visual Studio. Skonfiguruj urządzenie wirtualne, a następnie uruchom je w emulatorze Androida.
- W Menedżerze urządzeń wirtualnych z Androidem kliknij Create Virtual Device (Utwórz urządzenie wirtualne).
- Wybierz definicję urządzenia (np. Pixel 2).
- Wybierz obraz systemu. Wybierz interfejs ABI x86_64, ponieważ ta architektura działa szybciej w emulatorze.
- Sprawdź konfigurację i kliknij Zakończ.
Uruchom wirtualne urządzenie, klikając przycisk Uruchom
 w Menedżerze wirtualnych urządzeń z Androidem.
w Menedżerze wirtualnych urządzeń z Androidem.W Visual Studio urządzenie wirtualne powinno pojawić się obok przycisku na pasku narzędzi Rozpocznij debugowanie. Kliknij Start Debugging (Rozpocznij debugowanie), aby uruchomić aplikację przykładową na urządzeniu. Podłączenie debugera do aplikacji może zająć kilka sekund. Jeśli uruchomisz przykład Teapot, możesz obracać czajnik, przeciągając po nim kursor myszy.

Rysunek 3. Przykładowa aplikacja Teapot uruchomiona w emulatorze Androida
Konfigurowanie urządzenia
Aby uruchomić przykład na fizycznym urządzeniu z Androidem, może być konieczne utworzenie w projekcie nowej platformy Androida. Ta platforma musi być zgodna z architekturą urządzenia. Aby utworzyć nową platformę w Visual Studio:
- Wybierz Build > Configuration Manager (Kompilacja > Menedżer konfiguracji).
- W sekcji Aktywna platforma rozwiązania kliknij <Nowa>.
Wpisz jedną z tych wartości dla nowej platformy:
- Android-armeabi-v7a
- Android-arm64-v8a
- Android-x86
- Android-x86_64
W polu Skopiuj ustawienia z wybierz inną istniejącą platformę Android (lub Brak, jeśli nie masz jeszcze żadnych platform Android). Sprawdź, czy masz włączoną opcję Twórz nowe platformy projektu.
Podłącz urządzenie z Androidem do komputera za pomocą kabla USB. Typ urządzenia powinien być widoczny obok przycisku paska narzędzi Rozpocznij debugowanie.

Rysunek 4. Połączone urządzenie z Androidem widoczne obok przycisku na pasku narzędzi Rozpocznij debugowanieJeśli urządzenia nie widać, sprawdź, czy:
- Wybrana platforma jest zgodna z interfejsem ABI urządzenia.
- Na urządzeniu są włączone opcje programisty i debugowanie USB.
- Kabel USB jest podłączony do urządzenia i komputera.
- Kabel USB obsługuje połączenie do transmisji danych (a nie tylko zasilanie).
Kliknij przycisk Rozpocznij debugowanie na pasku narzędzi, aby uruchomić przykładową aplikację na urządzeniu. Podłączenie debugera do aplikacji może potrwać kilka chwil. Po podłączeniu debugera możesz korzystać z aplikacji na urządzeniu.
Najczęstsze pytania
Poniżej znajdziesz odpowiedzi na najczęstsze pytania dotyczące rozszerzenia do tworzenia gier na Androida.
Gdzie znajdują się dzienniki wtyczki?
Plik dziennika wtyczki możesz otworzyć za pomocą ikony Open Logs (Otwórz dzienniki) na pasku narzędzi Android Game Development Extension.
Jakich zmiennych środowiskowych używa wtyczka?
Wtyczka korzysta z tych zmiennych środowiskowych:
ANDROID_SDK_ROOTANDROID_SDK_HOMETEMPGOOGLE_ANDROID_LOG_DIR
Co dalej
Aby używać własnego projektu z rozszerzeniem, musisz go skonfigurować zgodnie z przewodnikiem konfiguracji projektu.
