Dengan AGI Frame Profiler, Anda dapat menyelidiki shader dengan memilih panggilan gambar dari salah satu penerusan render kami, dan melalui bagian Vertex Shader atau bagian Fragment Shader pada panel Pipeline.
Di sini Anda akan menemukan statistik berguna yang berasal dari analisis statis kode shader, serta assembly Standard Portable Intermediate Representation (SPIR-V) yang menjadi tujuan kompilasi GLSL kami. Ada juga tab untuk melihat representasi GLSL asli (dengan nama yang dihasilkan compiler untuk variabel, fungsi, dan lainnya) yang didekompilasi dengan SPIR-V Cross, untuk memberikan konteks tambahan bagi SPIR-V.
Analisis statis
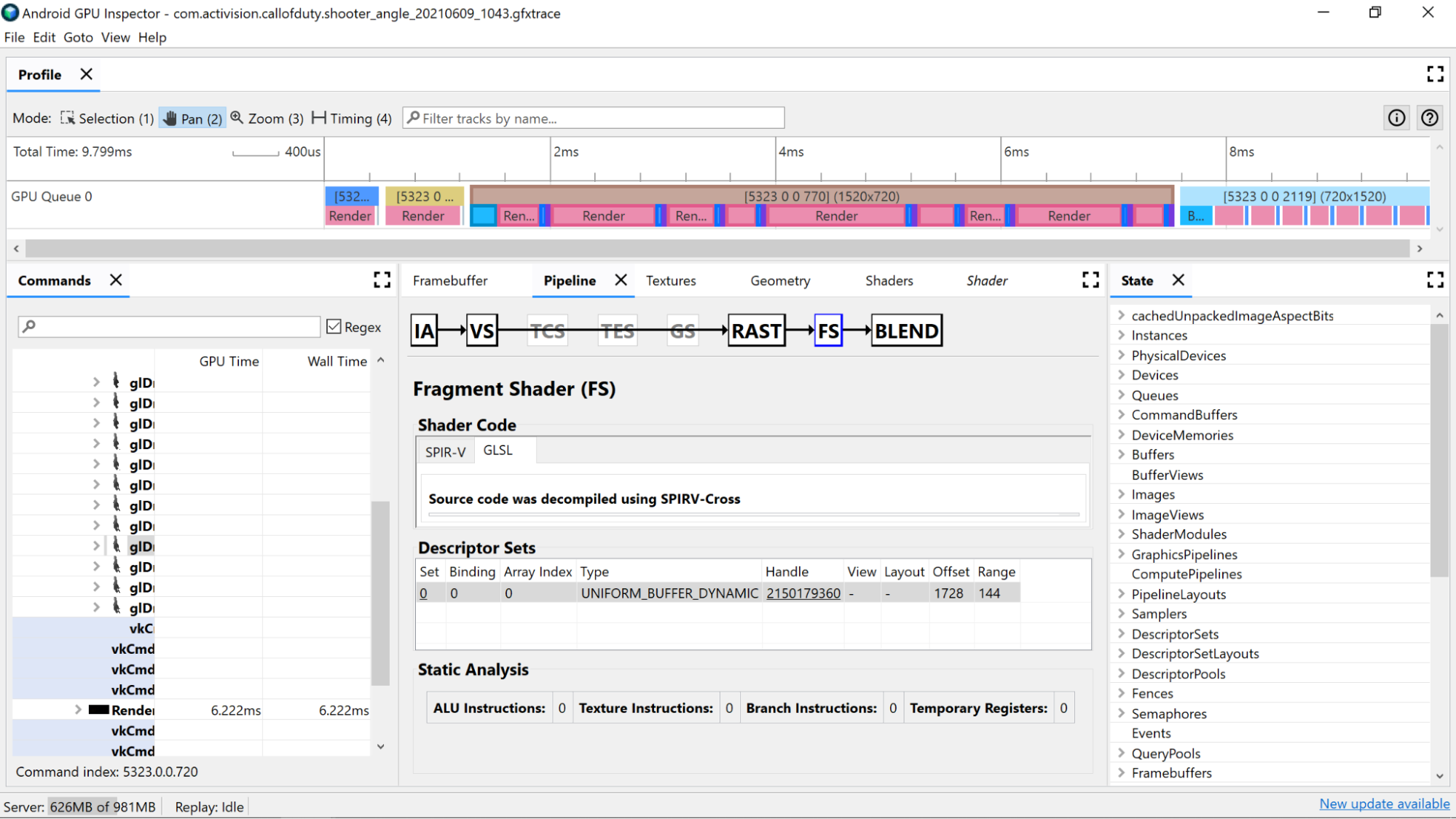
Gunakan penghitung analisis statis untuk melihat operasi tingkat rendah di shader.
Petunjuk ALU: Jumlah ini menunjukkan jumlah operasi ALU (penambahan, perkalian, pembagian, dan sebagainya) yang dijalankan dalam shader, dan merupakan proxy yang baik untuk tingkat kerumitan shader. Cobalah untuk meminimalkan nilai ini.
Memfaktorkan ulang komputasi umum atau menyederhanakan komputasi yang dilakukan di shader dapat membantu mengurangi jumlah petunjuk yang diperlukan.
Petunjuk Tekstur: Jumlah ini menunjukkan frekuensi terjadinya pengambilan sampel tekstur di shader.
- Pengambilan sampel tekstur bisa mahal bergantung pada jenis tekstur yang diambil sampelnya. Jadi, melakukan referensi silang kode shader dengan tekstur terikat yang ditemukan di bagian Kumpulan Deskripsi dapat memberikan informasi selengkapnya tentang jenis tekstur yang digunakan.
- Hindari akses acak saat mengambil sampel tekstur karena perilaku ini tidak ideal untuk penyimpanan tekstur ke cache.
Petunjuk Cabang: Jumlah ini menunjukkan jumlah operasi cabang di shader. Meminimalkan pencabangan sangat ideal pada prosesor paralel seperti GPU, dan bahkan dapat membantu compiler menemukan pengoptimalan tambahan:
- Gunakan fungsi seperti
min,max, danclampagar tidak perlu mencabangkan nilai numerik. - Menguji biaya komputasi melalui percabangan. Karena kedua jalur cabang dieksekusi di banyak arsitektur, ada banyak skenario di mana selalu melakukan komputasi lebih cepat daripada melewatkan komputasi dengan cabang.
- Gunakan fungsi seperti
Register Sementara: Register ini adalah register on-core yang cepat yang digunakan untuk menyimpan hasil operasi perantara yang diperlukan oleh komputasi pada GPU. Ada batasan jumlah register yang tersedia untuk komputasi sebelum GPU harus menggunakan memori luar inti lainnya untuk menyimpan nilai menengah, sehingga mengurangi performa keseluruhan. (Batas ini bervariasi bergantung pada model GPU.)
Jumlah register sementara yang digunakan mungkin lebih tinggi daripada yang diharapkan jika compiler shader menjalankan operasi seperti unrolling loop, jadi sebaiknya referensikan silang nilai ini dengan SPIR-V atau GLSL yang didekompilasi untuk melihat fungsi kode.
Analisis kode shader
Selidiki kode shader yang didekompilasi untuk menentukan apakah ada potensi peningkatan yang dapat dilakukan.
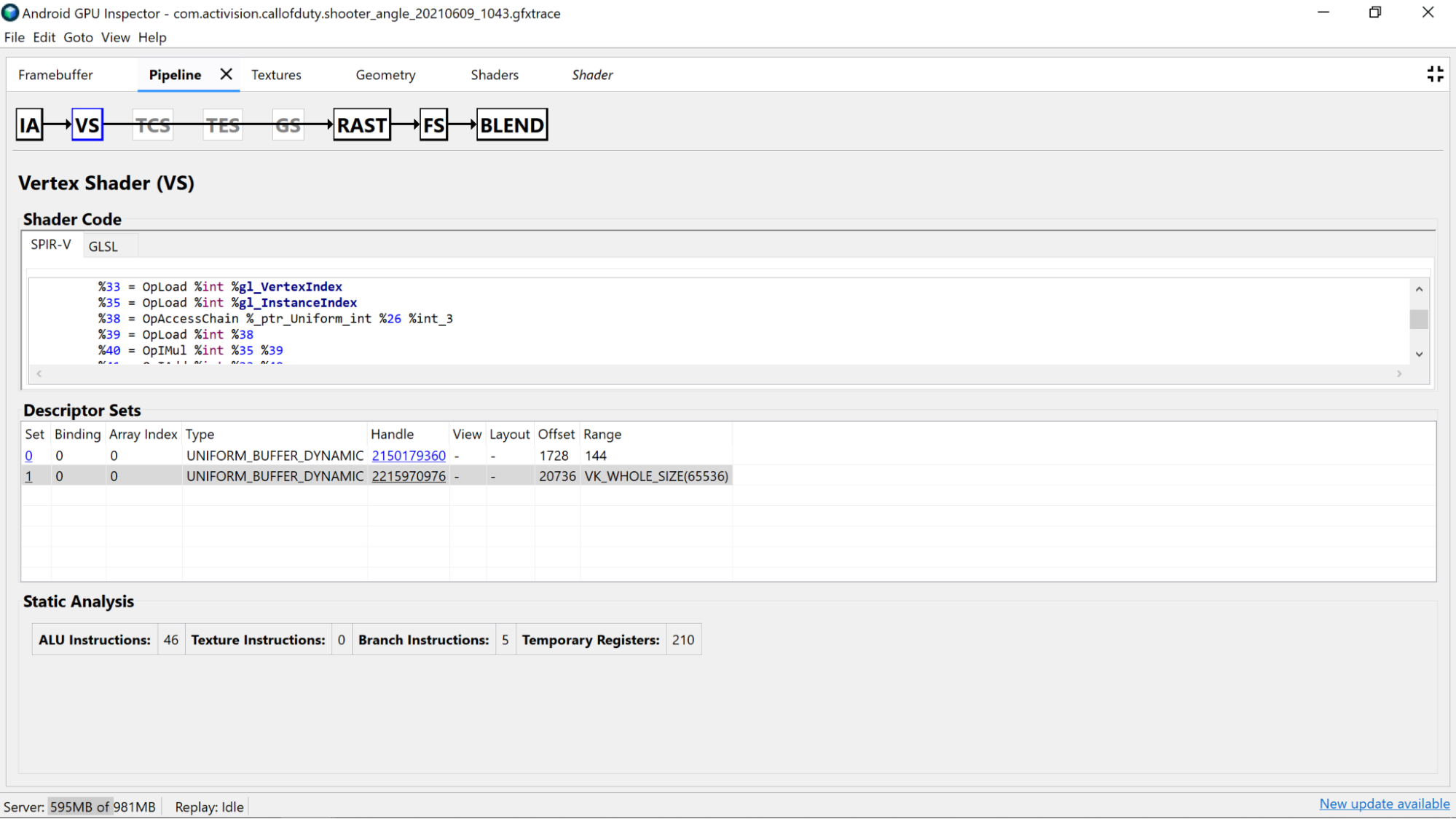
- Presisi: Presisi variabel shader dapat memengaruhi performa
GPU aplikasi Anda.
- Coba gunakan pengubah presisi
mediumppada variabel jika memungkinkan, karena variabel 16-bit presisi sedang (mediump) biasanya lebih cepat dan lebih hemat daya daripada variabel presisi penuh (highp) 32-bit. - Jika Anda tidak melihat penentu presisi di shader pada deklarasi
variabel, atau di bagian atas shader dengan
precision precision-qualifier type, default-nya adalah presisi penuh (highp). Pastikan Anda juga melihat deklarasi variabel. - Penggunaan
mediumpuntuk output shader vertex juga lebih disarankan untuk alasan yang sama seperti dijelaskan di atas, dan juga bermanfaat untuk mengurangi bandwidth memori serta penggunaan register sementara yang mungkin diperlukan untuk melakukan interpolasi.
- Coba gunakan pengubah presisi
- Uniform Buffers: Cobalah untuk mempertahankan ukuran Uniform Buffers sekecil mungkin (sambil mempertahankan aturan penyelarasan). Hal ini membantu membuat komputasi lebih kompatibel dengan caching dan berpotensi memungkinkan data seragam dipromosikan ke register on-core yang lebih cepat.
Menghapus Output Vertex Shader yang tidak digunakan: Jika Anda mendapati output shader vertex tidak digunakan dalam shader fragmen, hapus output tersebut dari shader untuk mengosongkan bandwidth memori dan register sementara.
Memindahkan komputasi dari Fragment Shader ke Vertex Shader: Jika kode shader fragmen melakukan komputasi yang tidak bergantung pada status khusus fragmen yang diarsir (atau dapat diinterpolasi dengan benar), sebaiknya pindahkan ke shader vertex. Alasannya karena di sebagian besar aplikasi, shader vertex dijalankan jauh lebih jarang dibandingkan dengan shader fragmen.
