Ce guide décrit les opérations suivantes :
- Sélectionner une version de Godot
- Télécharger et installer Godot
- Configurer Godot pour le développement Android
- Configurer votre système pour le développement et l'exportation C# (version Mono de Godot)
Sélectionner une version
Si possible, utilisez la dernière version stable de Godot. Pour le développement Android, utilisez la version 3.3 ou une version ultérieure.
Télécharger et exécuter Godot
Accédez à la page de téléchargement de Godot afin de télécharger le moteur de jeu correspondant à l'environnement de votre choix.
Godot propose deux versions sur sa page de téléchargement : Standard et Mono. Les deux peuvent être utilisées pour le développement Android. La version Mono est requise pour le développement en C#.
Godot est distribué en tant qu'application autonome. Aucun processus d'installation n'est nécessaire. Après avoir extrait l'archive de téléchargement, vous pouvez l'exécuter telle quelle.
Configurer la compatibilité avec Android
Configurer les paramètres du SDK Android Studio
- Si vous ne l'avez pas déjà fait, téléchargez et installez la dernière version stable d'Android Studio.
- Lancez Android Studio.
- Dans la fenêtre de bienvenue, ouvrez le menu déroulant Configure, puis sélectionnez SDK Manager.
- En haut de la fenêtre, notez l'emplacement du SDK Android sur votre ordinateur. Vous devrez spécifier cet emplacement dans l'éditeur Godot.
- Dans l'onglet SDK Platforms, recherchez l'entrée de liste pour Android 11.0 R. Cochez l'élément s'il n'est pas déjà coché.
- Dans l'onglet SDK Tools, recherchez les éléments de liste suivants : NDK (Side by side) (NDK (Côte à côte)), Command-line Tools (Outils de ligne de commande du SDK Android) et CMake. Cochez-les s'ils ne sont pas déjà cochés.
- Si l'état de certains éléments de la liste est défini sur Update Available (Mise à jour disponible), cochez leur case pour obtenir la dernière version.
- Cliquez sur le bouton OK. Confirmez le téléchargement et acceptez les contrats de licence pour terminer l'installation.
Créer un keystore de débogage
Les applications Android doivent être signées numériquement pour fonctionner sur un appareil. Pour les tests locaux, un fichier de keystore de débogage peut être utilisé pour signer des applications. Android Studio crée automatiquement un keystore de débogage par défaut. Si vous avez déjà créé des applications à l'aide d'une configuration de débogage avec Android Studio, un fichier debug.keystore doit se trouver dans le répertoire suivant :
- Microsoft Windows :
C:\Users\$username\.android\debug.keystore - Linux/macOS :
~\.android\debug.keystore
Si le fichier debug.keystore n'existe pas, créez-en un en procédant comme suit :
- Lancez Android Studio.
- Dans la fenêtre de bienvenue, sélectionnez l'option Import an Android Code Sample (Importer un exemple de code Android).
- Dans la liste, sélectionnez Ndk > Hello GL2, puis cliquez sur le bouton Next (Suivant).
- Choisissez un emplacement pour le projet, puis cliquez sur le bouton Finish (Terminer).
- Attendez que le projet soit chargé et synchronisé avec Gradle, puis sélectionnez Build > Make Project (Build > Créer un projet) dans la barre de menu d'Android Studio.
- Attendez la fin de la compilation, puis vérifiez qu'un fichier
debug.keystorea été créé dans le répertoire approprié.
Définir le SDK Android et l'emplacement du keystore de débogage dans l'éditeur Godot
- Lancez l'éditeur Godot.
- Créez ou ouvrez un projet.
- Sélectionnez Editor > Editor Settings… (Éditeur > Paramètres de l'éditeur) dans la barre de menu de l'éditeur.
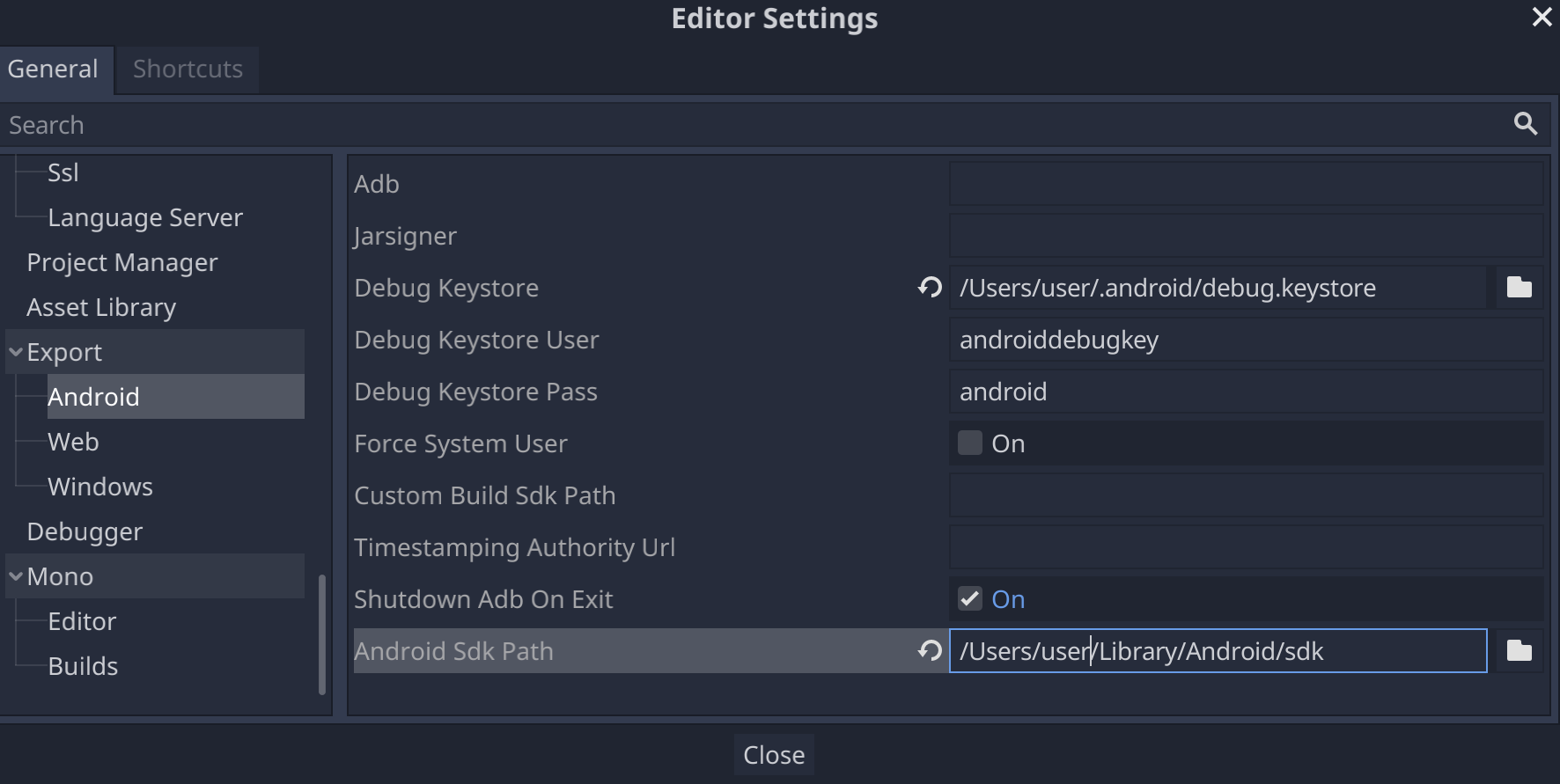
- Dans la fenêtre Editor Settings, sélectionnez l'élément Export > Android dans le panneau de gauche.
- Dans le panneau de droite, accédez à la zone de texte Android Sdk Path (Chemin d'accès du SDK Android), puis saisissez le chemin d'accès au SDK Android.
- Dans la zone de texte du keystore de débogage, saisissez le chemin d'accès au fichier
debug.keystore.
Configurer Mono
Installer MSBuild
La version Mono de Godot nécessite MSBuild pour créer et exporter des projets qui utilisent C#. Voici comment installer MSBuild :
Linux et macOS
- Téléchargez et installez la dernière version du SDK Mono.
Microsoft Windows
- Installez Microsoft Visual Studio ou les outils de création de Microsoft Visual Studio. Lorsque vous exécutez le programme d'installation, assurez-vous que le pack de ciblage .NET Framework 4.5 est sélectionné pour l'installation.
Configurer un éditeur C#
Godot ne permet de modifier du code C# que de façon très limitée. Il est vivement recommandé d'utiliser un éditeur externe pour les fichiers C#. Godot est compatible avec les éditeurs C# suivants :
- Microsoft Visual Studio/Visual Studio pour Mac
- Microsoft Visual Studio Code
- JetBrains Rider
- MonoDevelop
Pour configurer un éditeur C# externe, ouvrez un projet dans l'éditeur Godot, puis procédez comme suit :
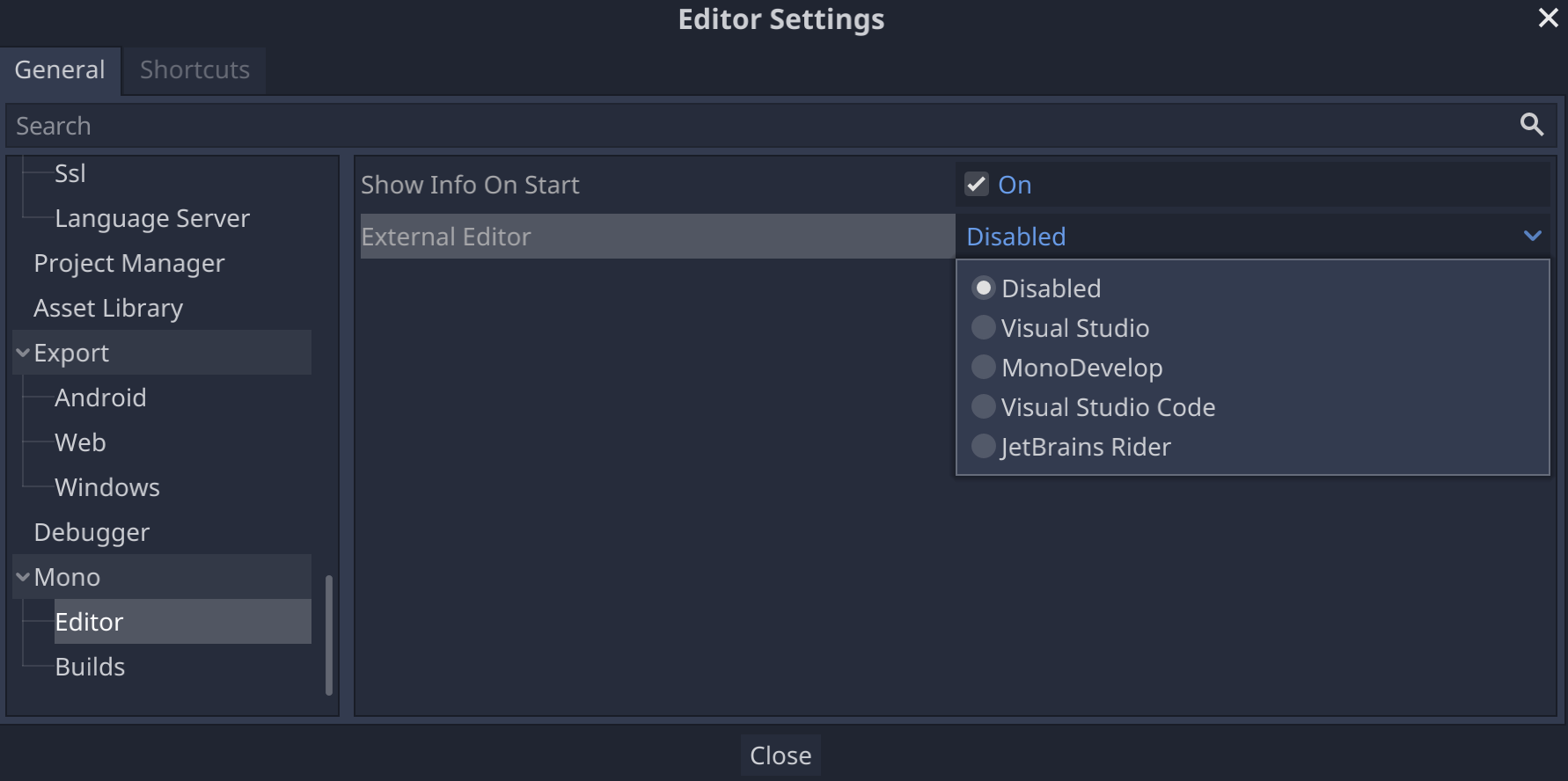
- Sélectionnez Editor > Editor Settings… (Éditeur > Paramètres de l'éditeur) dans la barre de menu de l'éditeur.
- Dans la fenêtre Editor Settings, sélectionnez l'élément Mono > Editor dans le panneau de gauche.
- Sélectionnez l'éditeur souhaité dans le menu déroulant Éditeur externe.
Plug-ins d'éditeur C# pour Godot
- Outils C# pour Godot : plug-in pour Microsoft Visual Studio Code qui dispose d'une assistance au débogage C# et d'une fonctionnalité de remplissage partiel de code.
- Plug-in JetBrains Rider : ajoute une assistance au débogage C#.

