Android 게임 개발 확장 프로그램을 사용하도록 프로젝트를 구성합니다.
Android 게임 개발 확장 프로그램은 MSBuild를 호출하여 공유 라이브러리(.so)와 정적 라이브러리(.a)에 C/C++ 소스 코드를 빌드합니다. 빌드 프로세스의 일부로 맞춤 MSBuild 작업에서는 Gradle을 호출하여 자바 및 Kotlin 소스 코드를 컴파일하고 애셋을 패키징하며 배포용 APK 파일을 생성합니다. 프로젝트를 구성할 때 MSBuild에 Android 플랫폼용으로 빌드하는 정보가 있는지 확인해야 합니다.
MSBuild로 C/C++ 빌드
일반적인 Android 프로젝트는 Gradle로 빌드됩니다. Gradle에서는 프로젝트 내부의 네이티브 코드가 CMake 또는 ndk-build를 실행하는 Gradle 패스를 통해 빌드됩니다. Visual Studio용 Android 게임 개발 확장 프로그램을 사용하면 빌드 프로세스는 반대가 됩니다. 이제는 MSBuild가 빌드 프로세스의 시작점이 됩니다. 먼저 MSBuild가 확장 프로그램의 일부로 시스템에 설치된 새 Android 플랫폼 (예: 'Android-x86_64')의 모든 C/C++ 소스 코드를 빌드합니다. 그런 다음 MSBuild가 Gradle을 호출하여 C/C++ 로직이 포함된 공유 라이브러리 파일을 APK에 패키징합니다.
먼저 개발자는 프로젝트의 기존 빌드 로직을 MSBuild의 CMake 또는 ndk-build에 복제해야 합니다. 타겟 플랫폼을 다음으로 설정합니다.
- Android-x86
- Android-x86_64
- Android-armeabi-v7a
- Android-arm64-v8a
이러한 플랫폼은 모두 Android 게임 개발 확장 프로그램에서 제공됩니다.
컴파일 및 연결 옵션 설정
AGDE는 선택한 NDK를 사용하여 앱의 C/C++ 부분을 빌드할 때 기본 컴파일 및 링크 옵션을 결정합니다.
이러한 컴파일 또는 링크 옵션을 맞춤설정해야 하는 경우 프로젝트 속성을 사용하여 설정할 수 있습니다. 가장 일반적인 옵션은 C/C++(컴파일용), 라이브러리 (정적 라이브러리 보관용) 및 링커 (동적 라이브러리 연결용) 그룹에서 찾을 수 있습니다. 다른 맞춤 옵션을 전달해야 하는 경우 명령줄 섹션에 추가하면 됩니다. 예를 들어 r28보다 오래된 NDK를 사용하는 경우 앱이 16KB 페이지 크기를 지원하도록 링커 플래그를 설정할 수 있습니다.
Android 플랫폼 추가
teapot 샘플 프로젝트에는 Android 플랫폼이 포함되어 있지만 기존 프로젝트에 Android 플랫폼을 수동으로 추가해야 합니다. 새 플랫폼을 추가하려면 Visual Studio에서 다음 작업을 수행하세요.
- Build > Configuration Manager를 선택합니다.
- Active solution platform에서 <New>를 선택합니다.
새 플랫폼과 관련해 다음 중 하나를 입력합니다.
- Android-armeabi-v7a
- Android-arm64-v8a
- Android-x86
- Android-x86_64
Copy settings from 상자에서 다른 기존 Android 플랫폼을 선택하거나 아직 Android 플랫폼이 없는 경우 <Empty>를 선택합니다. Create new project platforms를 사용 설정했는지 확인합니다.
Android APK 항목 추가
Add > New Item > Visual C++ > Android > Android APK를 선택하고 Add를 클릭합니다. 다음 대화상자에서 Android 애플리케이션을 구성합니다.
- Application Name: 사람이 읽을 수 있는 Android 애플리케이션 이름입니다.
- Application ID: Android 애플리케이션의 고유 식별자입니다.
- Solution Explorer Location: 추가된 Android 패키징 지원 파일이 포함된 가상 폴더의 위치입니다. 기본적으로 이러한 파일은 이름이 동일한 폴더의 프로젝트에도 있습니다. Put support files in a custom location 체크박스를 선택하고 맞춤 위치를 지정하여 위치를 맞춤설정할 수 있습니다. 가상 폴더는 계속해서 Solution Explorer의 현재 프로젝트 아래에 배치됩니다.
APK를 빌드할 Gradle을 호출하도록 MSBuild 설정
MSBuild는 Gradle 프로젝트의 위치를 모를 경우 Gradle을 호출할 수 없습니다. 그림 1에 나와 있는 것처럼, Gradle Build Directory 속성을 사용하여 이 위치를 설정합니다.
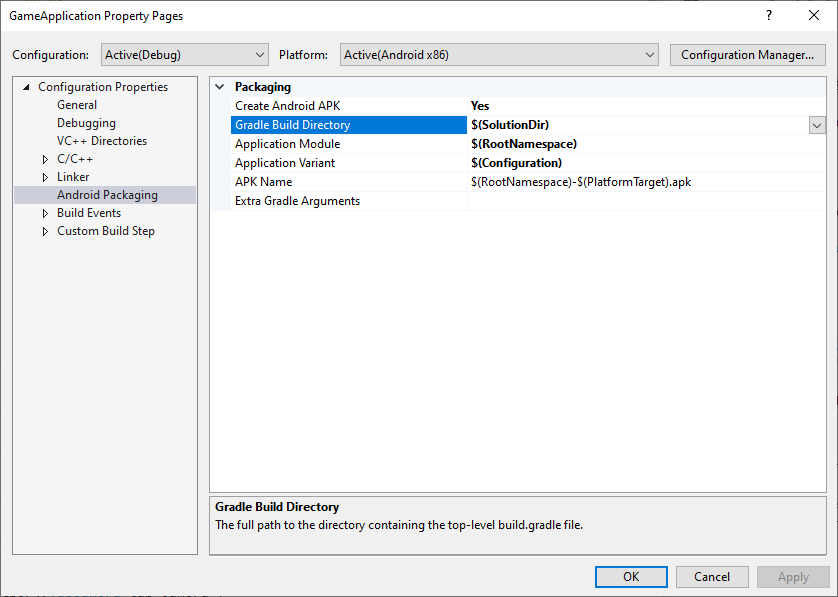
그림 1. Gradle Build Directory 속성
또한 MSBuild에서 빌드할 대상을 인식할 수 있도록, 이전 이미지에 나와 있는 것처럼 Application Module, Application Variant 및 APK Name 속성을 설정합니다.
- Application Module: Gradle 하위 프로젝트의 이름. 이는
settings.gradle파일에 설정된 기본 프로젝트입니다. Android 스튜디오를 사용하여 직접 만든 프로젝트에서는 대개app이라고 합니다. - Application Variant: 빌드할 Android 변형. 이 값은 MSBuild 구성에 따라 설정해야 합니다. 예를 들어 디버그 빌드의 값은 디버그 변형에 설정된 값이어야 합니다. 프로젝트의 MSBuild 구성 이름이 Gradle 변형 이름과 일치할 경우
$(Configuration)의 기본값을 사용하면 됩니다. - APK Name: 개발 컴퓨터에서 디버깅 및 프로파일링에 사용되는 생성된 APK 파일의 이름. 이 이름은 Gradle에 전달되며 Gradle 빌드 스크립트는 이를 준수해야 합니다(다음 섹션에서
MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAME속성 참고).
Gradle 빌드 스크립트 수정
빌드 중에 MSBuild가 다음 정보를 Gradle 스크립트에 프로젝트 속성으로 전달합니다. 이러한 속성을 읽어오도록 프로젝트의 기존 빌드 스크립트(일반적으로 build.gradle)를 변경합니다.
MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION: APK 빌드를 위한 최소 SDK 버전(문자열) 그림 2에 표시된 프로젝트 속성 페이지의 Minimum Android SDK Version 상자에 이 값을 설정합니다.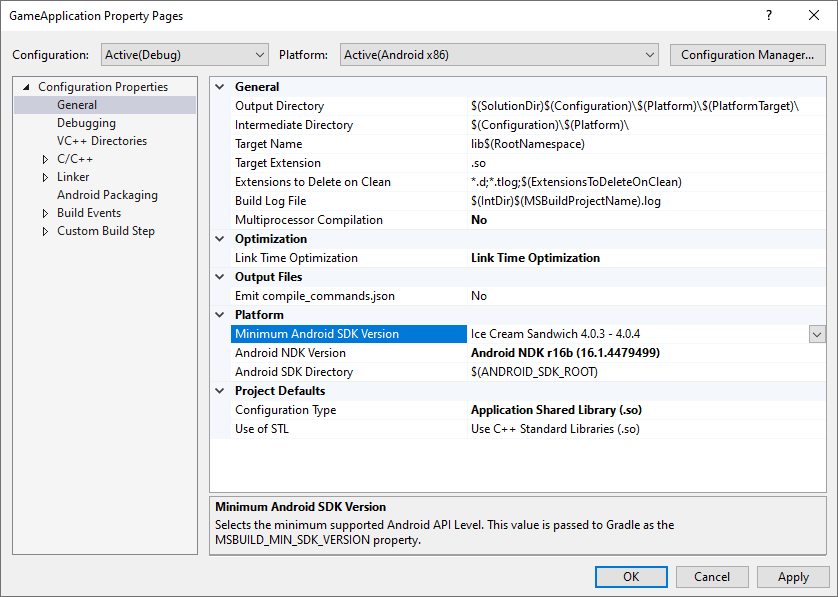
그림 2. Minimum Android SDK Version 속성Gradle 빌드 스크립트는 필요한 경우
toInteger()유형 변환을 사용하여minSdkVersion또는minSdk을 이 문자열 값으로 설정해야 합니다.Groovy
android { // ... defaultConfig { applicationId "com.yourcompany.yourapp" minSdkVersion MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION // Or: minSdk MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION.toInteger() // ... } // ... }
Kotlin
android { // ... defaultConfig { applicationId = "com.yourcompany.yourapp" minSdkVersion(MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION) // Or: minSdk = MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION.toInteger() // ... } // ... }
MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAME: Gradle이 빌드하는 APK의 예상 이름. Android 게임 개발 확장 프로그램이 이 이름과 일치하는 APK를 찾아 연결된 기기에 배포합니다(디버깅 및 프로파일링 목적). 그림 3에 표시된 프로젝트 속성 페이지의 APK Name 상자에 이 값을 설정합니다.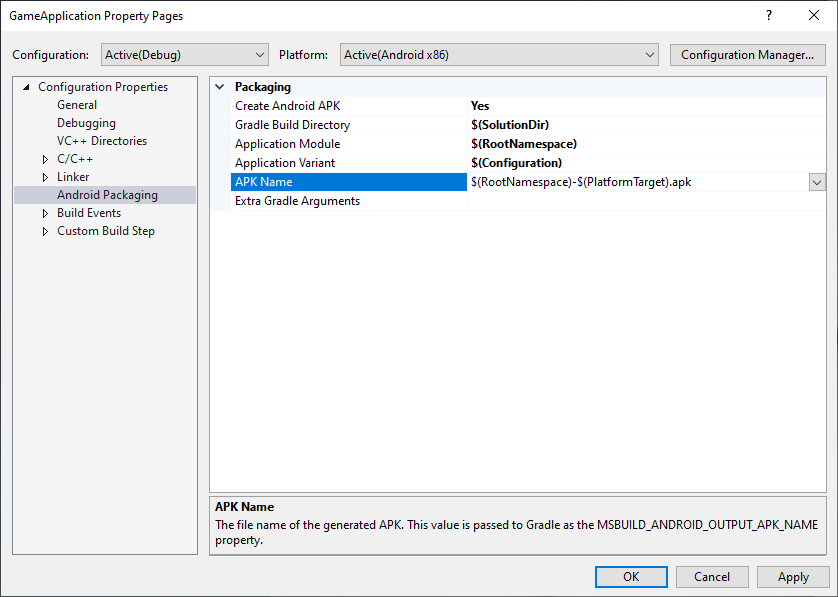
그림 3. APK Name 속성Gradle 빌드 스크립트는 이 속성을 준수해야 합니다. 예를 들어 다음 예제에서는 모든 변형의 출력 APK 이름이 MSBuild에서 선택한 이름으로 설정됩니다.
Groovy
android { // ... applicationVariants.all { variant -> variant.outputs.all { outputFileName = MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAME } } // ... }
Kotlin
android { // ... applicationVariants.all { variant -> variant.outputs.all { outputFileName = MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAME } } // ... }
MSBUILD_JNI_LIBS_SRC_DIR: MSBuild에 의해 빌드된 공유 라이브러리(.so파일)가 포함된 디렉터리. 아래 표시된 프로젝트 속성 페이지의 Output Directory 상자에 이 값을 설정합니다. 그림 4에 표시된 것처럼 기본적으로 이 값은 Visual Studio 프로젝트의 출력 디렉터리 속성입니다.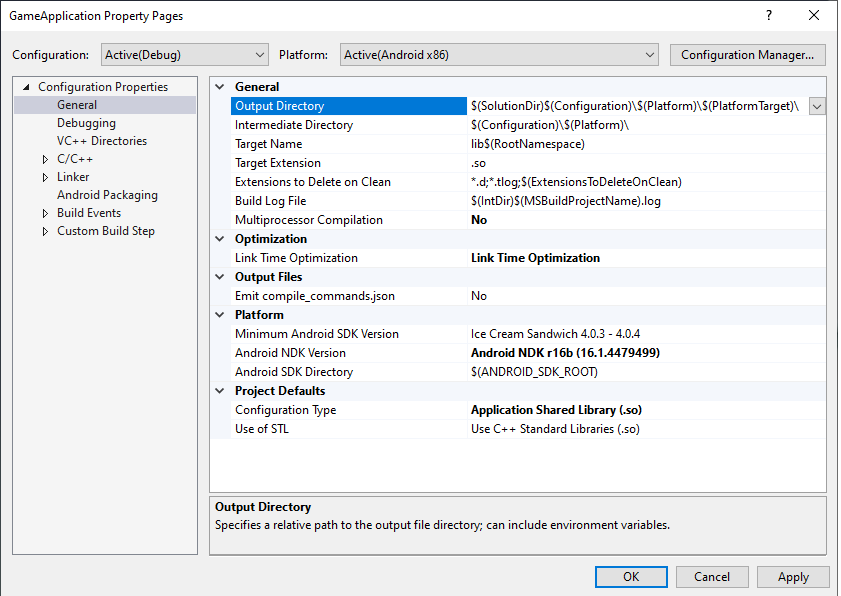
그림 4. Output Directory 속성Gradle에서 이 폴더의 공유 라이브러리 파일을 APK 내에 패키징해야 합니다. 그러면 Android 애플리케이션이 런타임 시 그 파일을 로드할 수 있습니다.
Groovy
android { // ... sourceSets { main { jniLibs.srcDirs += [MSBUILD_JNI_LIBS_SRC_DIR] } } // ... }
Kotlin
android { // ... sourceSets.getByName("main") { jniLibs.srcDir(MSBUILD_JNI_LIBS_SRC_DIR) } // ... }
또한 이제 모든 C/C++ 코드가 MSBuild에 의해 빌드되었으므로 Gradle 빌드 스크립트에서
externalNativeBuild섹션을 삭제합니다. 이러한 섹션은 CMake 또는 ndk-build를 호출하여 C/C++ 코드를 컴파일하는 데 사용되었지만 더 이상 필요하지 않습니다.MSBUILD_NDK_VERSION: 프로젝트를 빌드하는 데 사용할 NDK 버전. 그림 5에 표시된 프로젝트 속성 페이지의 Android NDK Version 상자에 이 값을 설정합니다.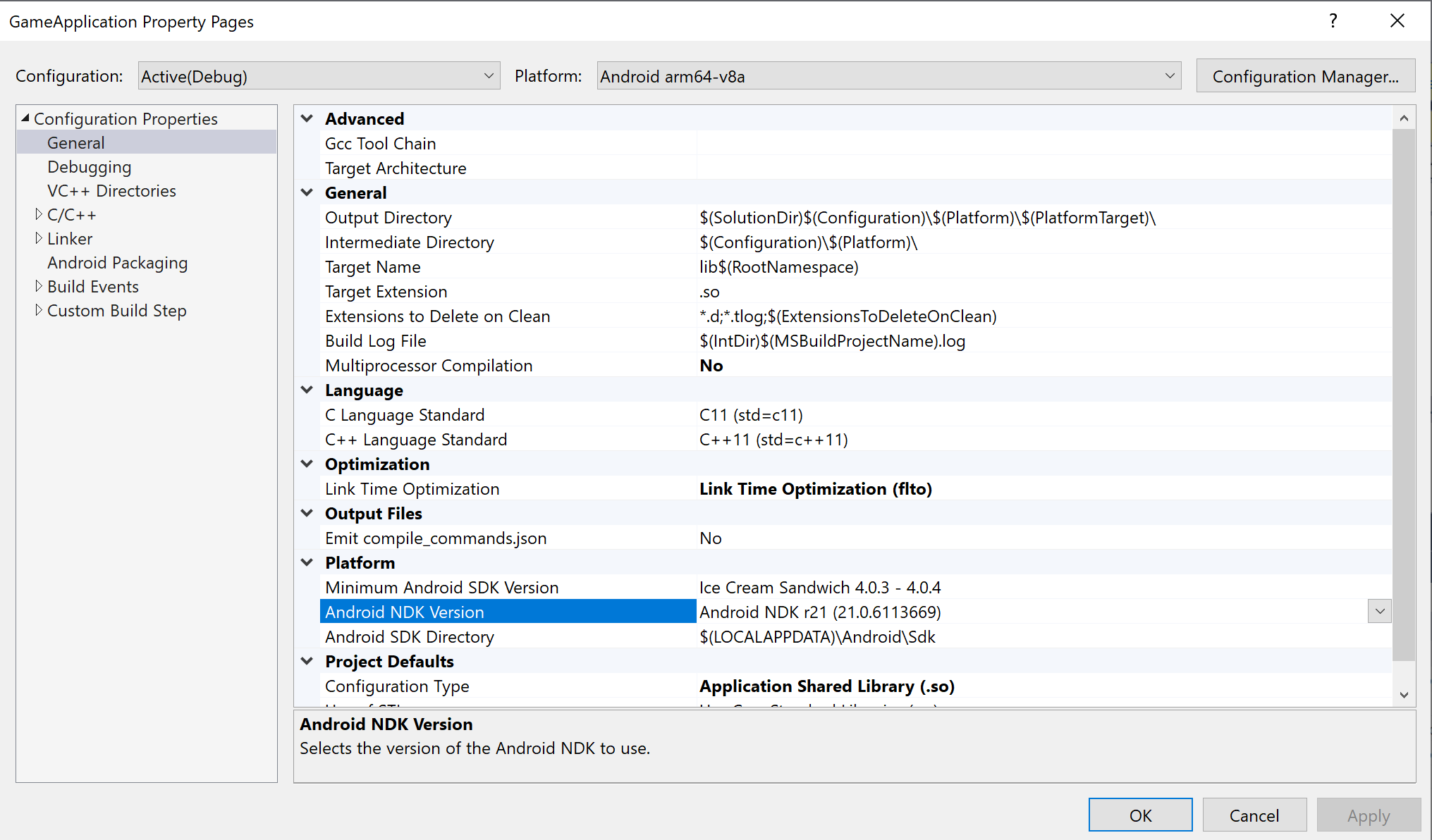
그림 5. Android NDK Version 속성Gradle 빌드 스크립트는 다음과 같이
ndkVersion을 이 값으로 설정해야 합니다.Groovy
android { // ... ndkVersion MSBUILD_NDK_VERSION // ... }
Kotlin
android { // ... ndkVersion = MSBUILD_NDK_VERSION // ... }
자세한 내용은 Android 스튜디오 주제 NDK 및 CMake 설치 및 구성을 참고하세요.
