רוחב הפס של הזיכרון של נתוני הקודקודים יכול להיות צוואר בקבוק פוטנציאלי בביצועי מעבד ה-GPU של המשחק. יש כמה מוני נתונים בפרופיל של מערכת AGI שיכולים לעזור באבחון בעיות ברוחב הפס של זיכרון הקודקוד.
מונים של Qualcomm Adreno
במכשירים עם מעבדי GPU מסוג Qualcomm Adreno, חלק מהמונים הבולטים כוללים:
| הגשת הצעה נגדית | תיאור |
|---|---|
| קריאת זיכרון ב-Vertex | רוחב הפס של נתוני הקודקודים שנקראים מזיכרון חיצוני. |
| ממוצע בייטים לקודקוד | הגודל הממוצע של נתוני הקודקוד, בבייטים. |
| % Vertex Fetch Stall | אחוז מחזורי השעון שבהם ה-GPU חסום בנתוני קודקוד. |
מונים של ARM Mali (בשלבי פיתוח)
במכשירים עם מעבדי ARM Mali GPU, חלק מהמונים הבולטים כוללים:
| הגשת הצעה נגדית | תיאור |
|---|---|
| טעינה/אחסון של ביטים לקריאה מזיכרון חיצוני | הנתונים שנקראים מהזיכרון החיצוני על ידי יחידת הטעינה/האחסון, בממוצע על ליבות ההצללה. |
| טעינה/אחסון של פעימות קריאה ממטמון L2 | נתונים שנקראים ממטמון L2 על ידי יחידת הטעינה/האחסון, בממוצע על ליבות ההצללה. |
| [מידע נוסף] |
כדי לחשב את רוחב הפס הכולל מתוך ממוצע הפעימות של הקריאה, מכפילים את ערך הדלפק ברוחב האפיק (בדרך כלל 16 בייט) ובמספר הכולל של ליבות ההצללה. [מידע נוסף]
ניתוח נגדי
כדי למדוד את ההתנהגות של המונים האלה, אפשר למדוד את רוחב הפס הממוצע והשיא במהלך פריים יחיד של GPU, שאפשר לתחום אותו באמצעות בלוק רציף של ניצול GPU.
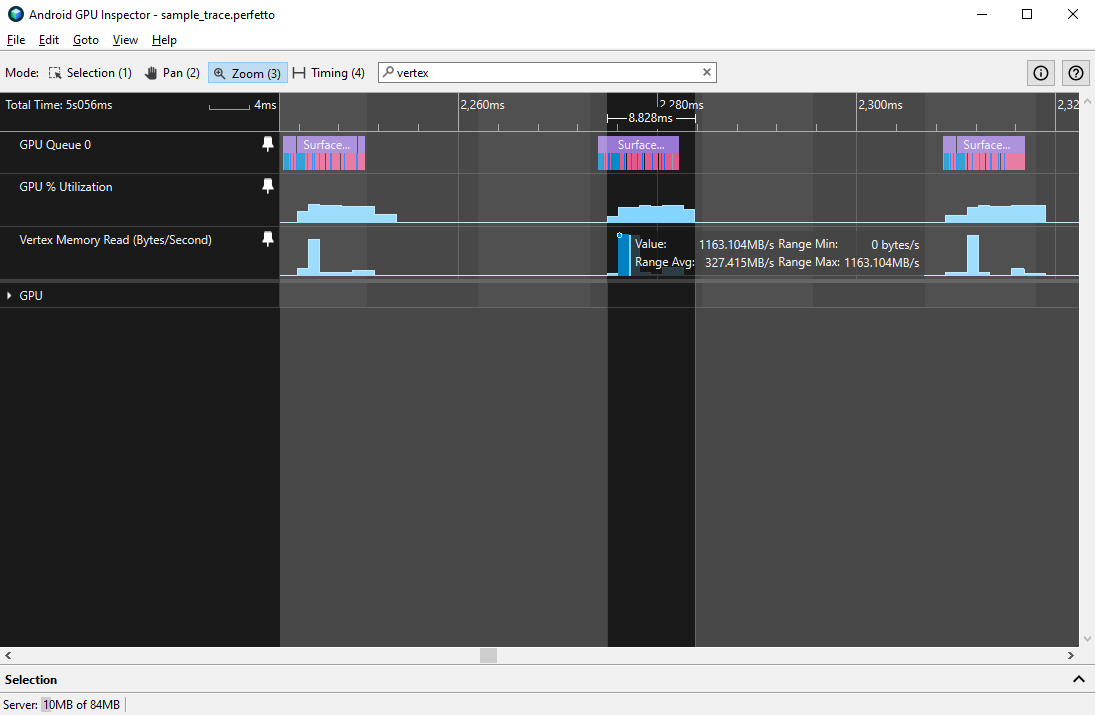
מומלץ להגדיר רוחב פס מקסימלי לקריאת זיכרון של קודקוד שלא יעלה על 1.5GBps, ורוחב פס ממוצע שלא יעלה על 500MBps. ערכים גבוהים יותר מצביעים על אחת מכמה בעיות נפוצות:
- גודל הקודקוד גדול מדי: יכול להיות שלקודקודים יש מאפייני קודקוד גדולים או מספר גדול של מאפייני קודקוד, מה שמשפיע על זמן ההצללה של הקודקודים.
- אין פיצול של זרמי מאפייני הקודקוד: מאפייני הקודקוד משולבים במאגר יחיד, וכך יעילות המטמון יורדת.
- יותר מדי קודקודים נשלחו לכל פריים: מודלים מורכבים או מספר גדול של מודלים עשויים לתפוס רוחב פס גדול יותר ולדרוש יותר זמן להצללה.
אפשר גם לאבחן בעיות בגודל הקודקוד באמצעות המדד Average Bytes / Vertex, שאנחנו ממליצים שלא יהיה גבוה מ-32 בייטים או קודקודים.
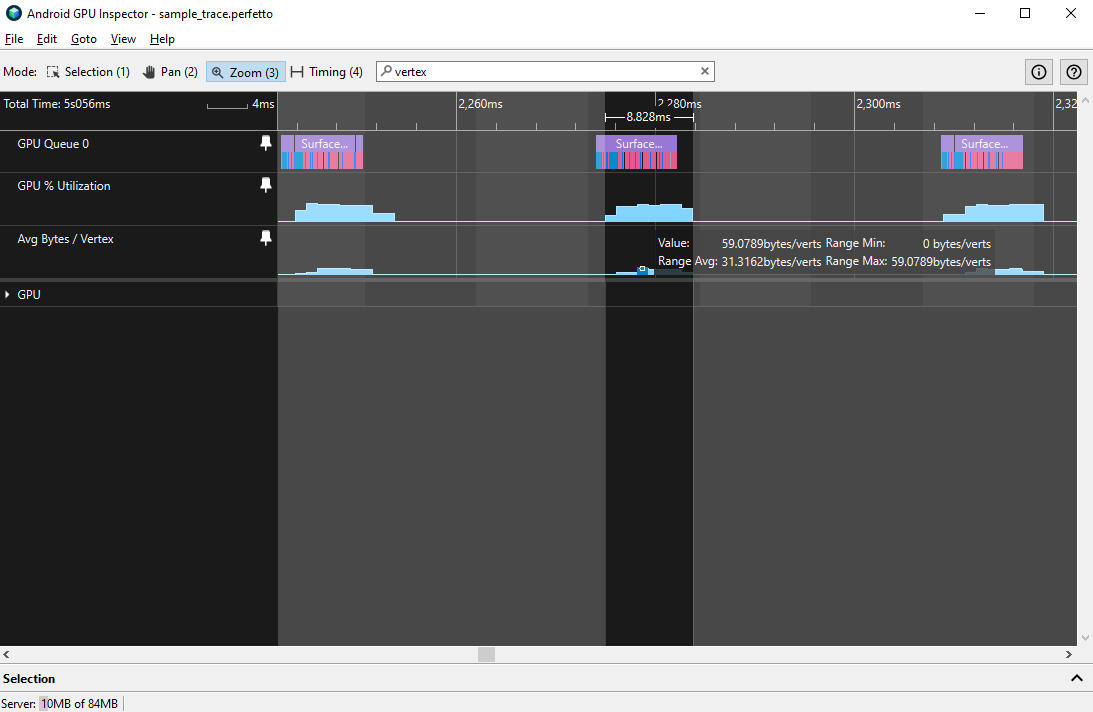
הדרך הכי טובה לאבחן איזו מהבעיות האלה מתרחשת היא ליצור מעקב אחר פרופיל של פריים כדי לנתח פורמטים של קודקסי צלעות.
