רוחב הפס של הזיכרון של נתוני הטקסטורה יכול להיות צוואר בקבוק פוטנציאלי בביצועי ה-GPU של האפליקציה. יש כמה מדדים בפרופיל מערכת AGI שיכולים לעזור באבחון בעיות ברוחב הפס של זיכרון הטקסטורה.
מונים של Qualcomm Adreno
במכשירים עם מעבדי GPU מסוג Qualcomm Adreno, חלק מהמונים הבולטים כוללים:
| הגשת הצעה נגדית | תיאור |
|---|---|
| קצב העברת הנתונים של קריאת הזיכרון של הטקסטורה (בבייט לשנייה) | רוחב הפס של נתוני הטקסטורה שנקראים מזיכרון חיצוני. |
| % Texture L1 Miss | החמצה במטמון L1 בעקבות אחזור טקסטורות. |
| % של מרקמים שאינם ברמת הבסיס | אחוז האחזורים של טקסטורות שהם מפות MIP. |
| % Anisotropic Filtered | אחוז הטקסלים שעברו סינון אניסוטרופי. |
מונים של ARM Mali
במכשירים עם מעבדי ARM Mali GPU, חלק מהמונים הבולטים כוללים:
| הגשת הצעה נגדית | תיאור |
|---|---|
| קריאת טקסטורה מזיכרון חיצוני | נתונים שנקראים מזיכרון חיצוני על ידי יחידת הטקסטורה, בממוצע על ליבות ההצללה. |
| קריאת טקסטורה ממטמון L2 | נתונים שנקראים ממטמון L2 על ידי יחידת הטקסטורה, בממוצע על ליבות ההצללה. |
| [מידע נוסף] |
כדי לחשב את רוחב הפס הכולל מתוך ממוצע הפעימות של הקריאה, מכפילים את ערך הדלפק ברוחב האפיק (בדרך כלל 16 בייט) ובמספר הכולל של ליבות ההצללה.
ניתוח נגדי
כדי למדוד את ההתנהגות של המונים האלה, מודדים את רוחב הפס הממוצע והשיא במהלך פריים יחיד של GPU, ואז מתארים באמצעות בלוק רציף של ניצול ה-GPU.
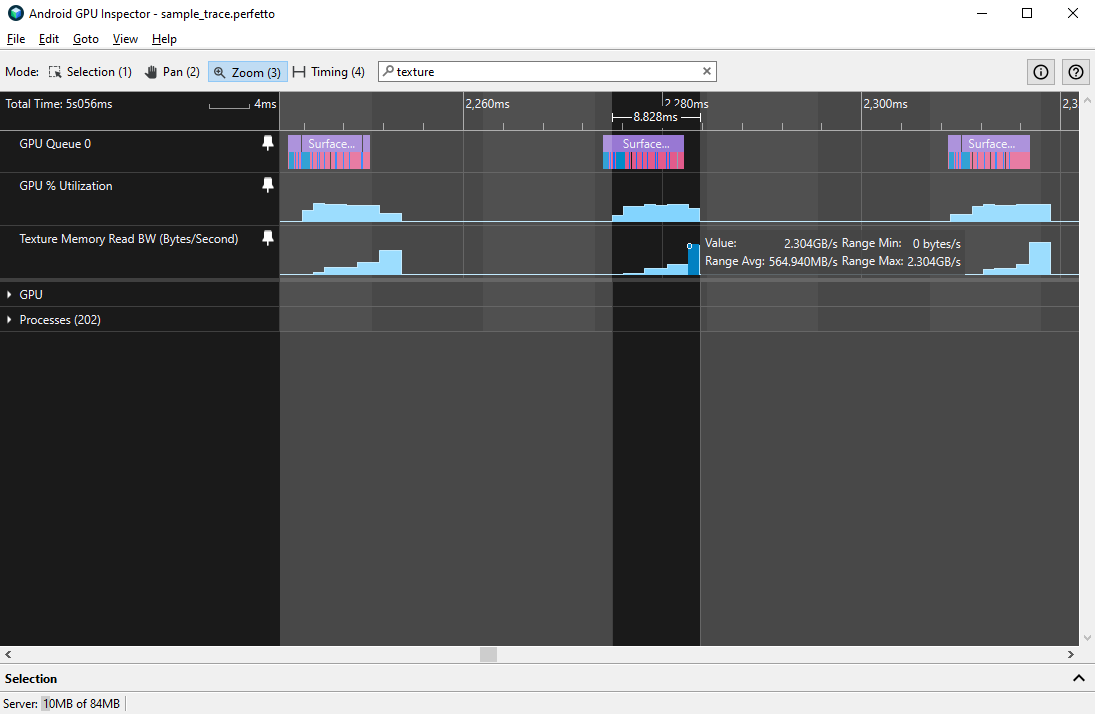
מומלץ להשתמש ברוחב פס ממוצע של זיכרון לקריאת טקסטורה שלא עולה על 1GBps, וברוחב פס מקסימלי שלא עולה על 3GBps. שיעור החמצת המטמון (cache miss) של Texture L1 צריך להיות גם הוא עד 10%. ערכים גבוהים יותר של רוחב פס או של מטמון L1 עשויים להצביע על בעיות עמוקות יותר בטקסטורה, כולל:
- הטקסטורות גדולות מדי: טקסטורות גדולות מגדילות את גודל החבילה, הן יקרות יותר ועשויות להקטין את יעילות המטמון.
- הטקסטורות לא דחוסות: כל הטלפונים עם Android תומכים בסוגים מסוימים של דחיסת טקסטורות, בין אם מדובר ב-ETC1 או ב-ASTC. כדי להקטין את גודל החבילה ואת רוחב הפס של הטקסטורות, צריך לדחוס את הטקסטורות.
- אחר: יש לקחת בחשבון מגוון בעיות אחרות שקשורות לטקסטורה, כולל טקסטורות של חזקות של 2, מיפמפינג, סינון אניסוטרופי ועוד. חלק מהבעיות האלה אפשר לזהות בפרופיל המערכת (כפי שמוסבר בהמשך), אבל כדי לזהות בעיות אחרות צריך לבצע בדיקה מעמיקה יותר.
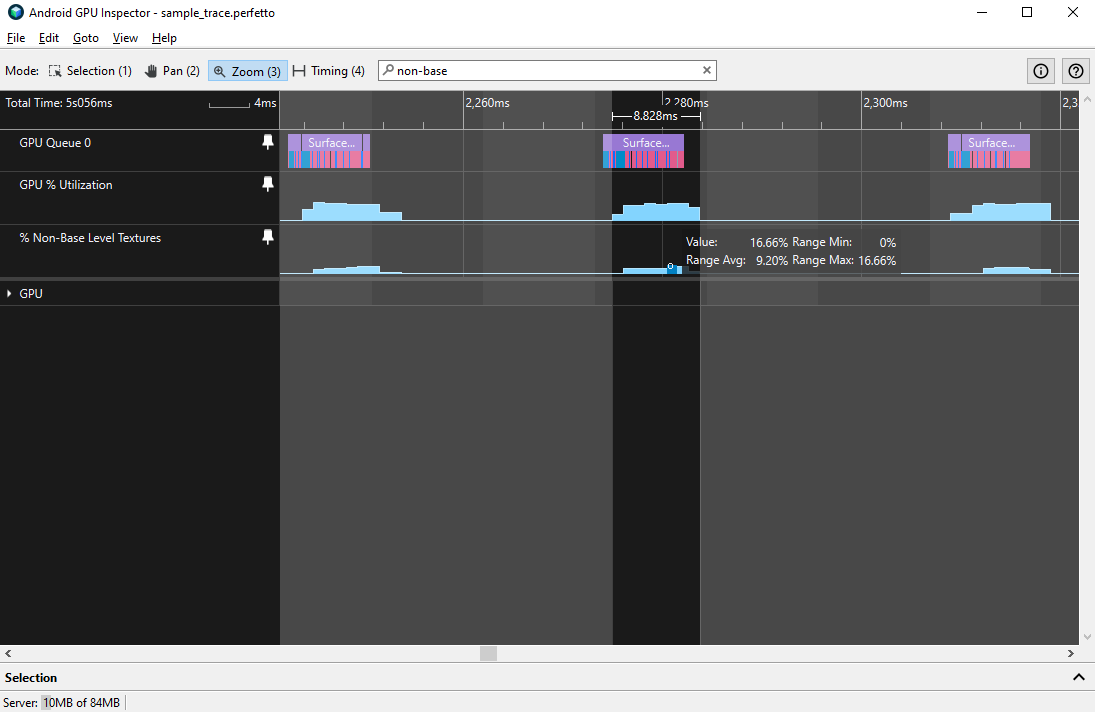
במשחקים תלת-ממדיים עם מצלמה חופשית, נכסי הטקסטורה צריכים להשתמש ב-mipmapping, כך שלאובייקטים שנמצאים במרחק מהמצלמה יהיה רוחב פס זיכרון מופחת, יעילות טובה יותר של מטמון הטקסטורה ואיכות תמונה טובה יותר. במכשירים עם מעבדי GPU מסוג Qualcomm Adreno, ערכי המונה Non-Base Level Textures (טקסטורות שאינן ברמת הבסיס) נמוכים מ-10% בממוצע עשויים להצביע על מיפוי MIP לא מספיק.
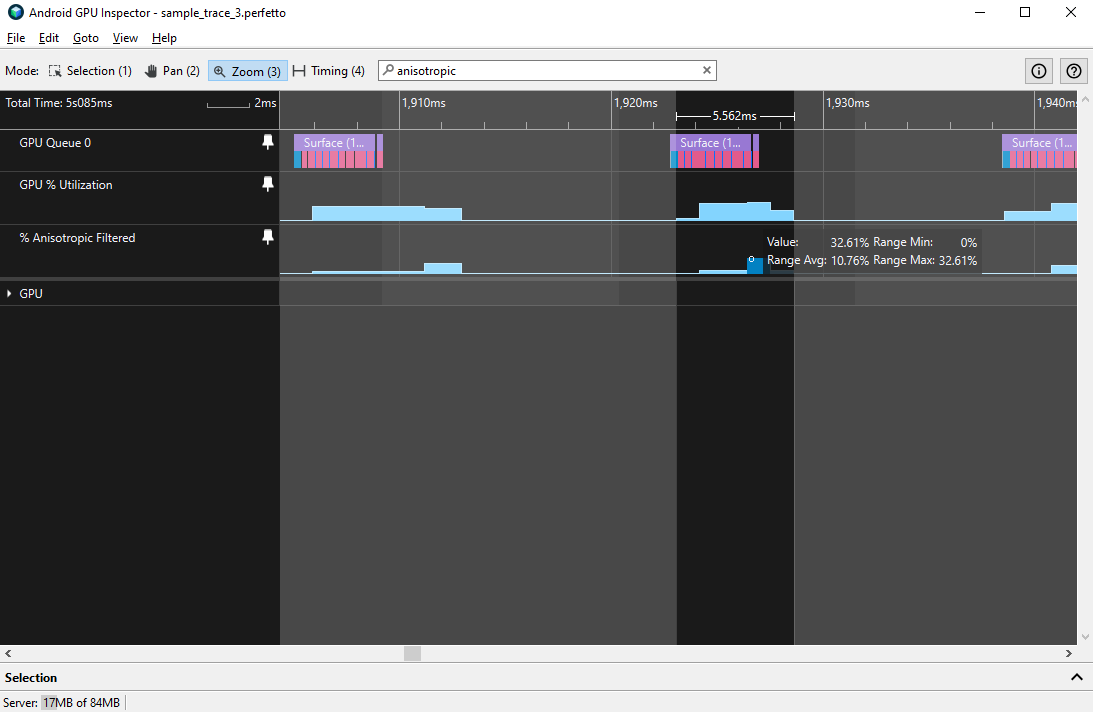
שיקול נוסף הוא השימוש בסינון אניזוטרופי, שמתואר על ידי מדד % Anisotropic Filtered עבור מעבדי Qualcomm Adreno, שמייצג את שיעור הטקסלים שעברו סינון אניזוטרופי. השימוש בטכנולוגיה הזו עשוי לשפר את איכות התצוגה של חלק מהמשחקים, אבל הוא גם עלול להיות יקר מאוד, ולכן צריך לשקול אותו מול העלות של ביצועי ה-GPU.
הדרך הכי טובה לאבחן בעיות ספציפיות יותר היא ליצור פרופיל של מסגרת כדי לנתח נכסי טקסטורה.
