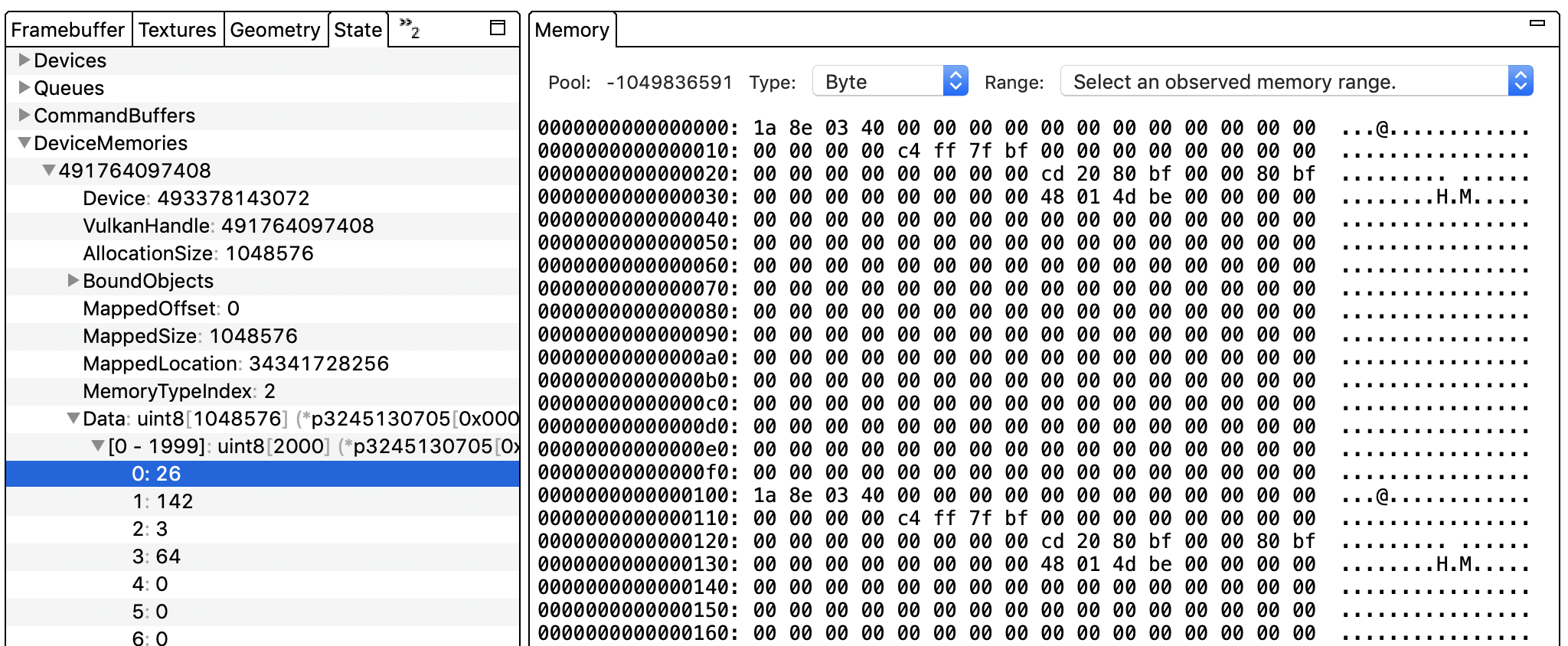
मेमोरी पैन में, चुनी गई कमांड के लिए RAM या GPU मेमोरी में मौजूद वैल्यू दिखती हैं.
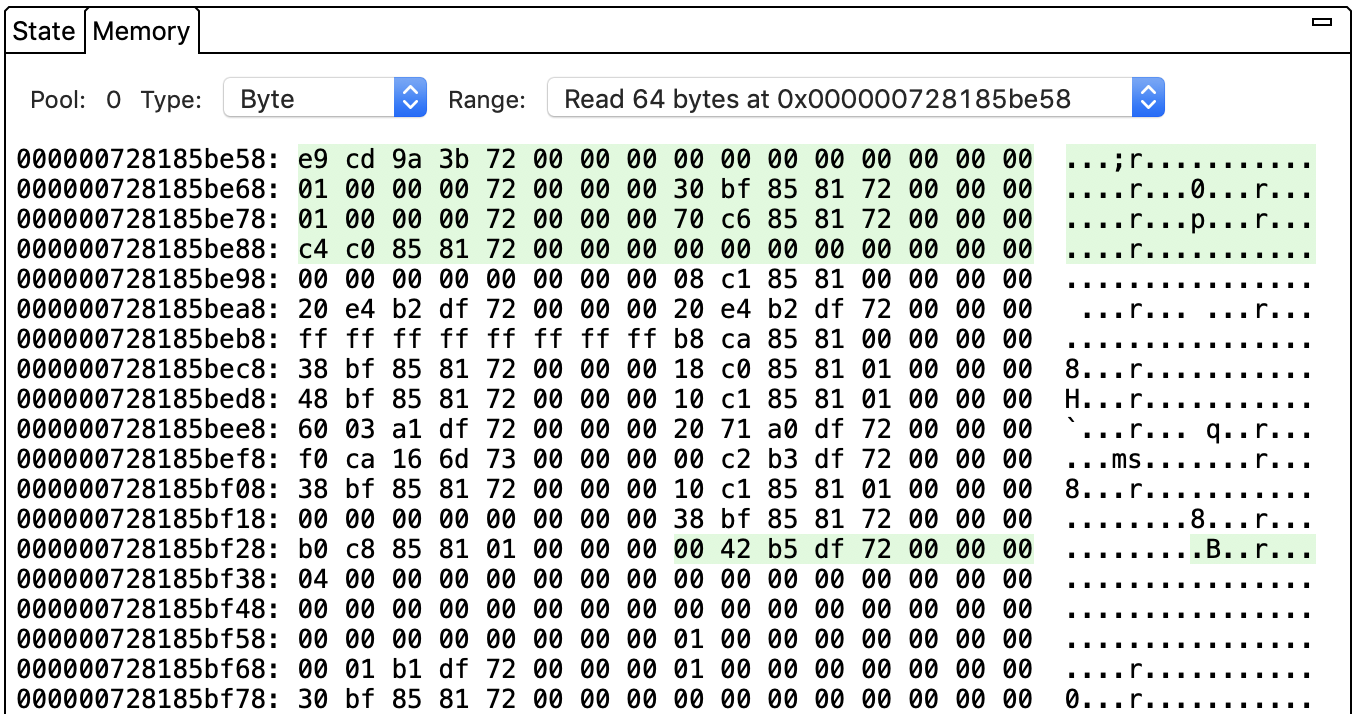
इस पैनल में यह दिखता है कि चुनी गई कमांड ने किन मेमोरी लोकेशन से डेटा पढ़ा और/या उनमें डेटा लिखा. आम तौर पर, हर कमांड में पढ़ने या लिखने की कई कार्रवाइयां होती हैं;
रेंज सूची से कोई एक चुनें. व्यू अपडेट हो जाता है और ऑपरेशन के लिए शुरुआती मेमोरी पता दिखता है. हरा रंग, पढ़ने की कार्रवाई को दिखाता है, जबकि लाल रंग लिखने की कार्रवाई को दिखाता है. उदाहरण के लिए, ऊपर दी गई इमेज में मौजूद कमांड में, मेमोरी पते 0x000000728185be58 से शुरू होने वाले 64 बाइट का रीड ऑपरेशन शामिल है. टाइप सूची से कोई दूसरा डेटा टाइप चुनकर, डेटा को दिखाने का तरीका बदला जा सकता है.
ऐप्लिकेशन की मेमोरी से जुड़ी वैल्यू दिखाने के लिए, पूल फ़ील्ड को 0 पर सेट किया जाता है. अगर पूल को किसी अन्य नंबर पर सेट किया जाता है, तो पैनल में GPU को असाइन की गई मेमोरी की वैल्यू दिखती हैं. ऐप्लिकेशन मेमोरी, रैम का इस्तेमाल करती है. वहीं, GPU को असाइन की गई मेमोरी, रैम या GPU मेमोरी का इस्तेमाल कर सकती है.
कमांड पैन में किसी पॉइंटर वैल्यू पर क्लिक करके, सीधे मेमोरी पैन में उस पते पर जाएं.
इस पैनल में, सिर्फ़ कुछ पतों की रेंज देखने की सुविधा नहीं मिलती है. कोई कमांड और फिर स्टेट पैनल चुनें. DeviceMemories को चुनें. (यह सेक्शन, Vulkan ट्रेस के लिए Vulkan हैंडल के हिसाब से व्यवस्थित किया गया है.) हैंडल को बड़ा करें और डेटा चुनें. व्यू में किसी पते को दिखाने के लिए, उस पर क्लिक करें.