如果您正在編寫原生程式碼,且擔心記憶體用量,建議您分析應用程式的原生配置,找出是否有可進行最佳化的部分。
為什麼您必須分析應用程式記憶體
Android 提供受管記憶體環境;當 Android 判定應用程式不再使用部分物件時,垃圾收集器就會將未使用的記憶體釋放回堆積中。我們正持續改善 Android 尋找未使用記憶體的運作機制,不過在所有 Android 版本中,系統有時會暫停執行您的程式碼。在多數情況下,這類暫停情形不易察覺。不過,如果應用程式配置記憶體的速度勝過於系統收集記憶體的速度,即使收集器釋出足以滿足配置需求的記憶體,應用程式仍可能會發生延遲情形。這類延遲可能會導致應用程式略過畫格,並讓顯示畫面變慢。
如要進一步瞭解可減少應用程式記憶體用量的程式設計做法,請參閱「管理應用程式的記憶體」。
原生配置總覽
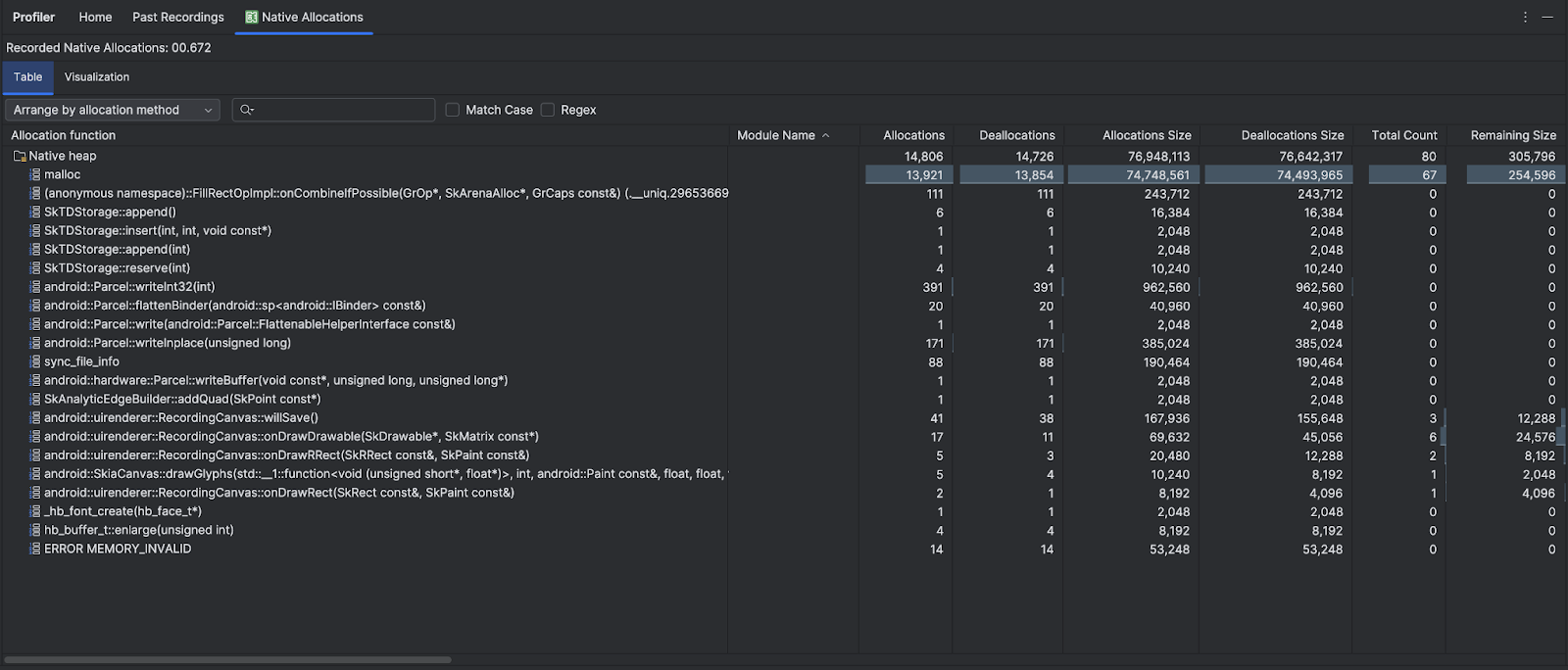
執行「追蹤記憶體用量 (原生配置)」工作時,Android Studio 分析器會在您指定的時間範圍內,追蹤原生程式碼中物件的配置和取消配置情形,並提供下列資訊:
- Allocations:在所選時間範圍內,使用
malloc()或new運算子配置的物件數量。 - Deallocations:在所選時間範圍內,使用
free()或delete運算子取消配置的物件數量。 - Allocations Size:在所選時間範圍內,所有配置的匯總大小 (以位元組為單位)。
- Deallocations Size:在所選時間範圍內,所有已釋放記憶體的匯總大小 (以位元組為單位)。
- Total Count:Allocations 欄中的值減去 Deallocations 欄中的值所得的結果。
- Remaining Size:Allocations Size 欄中的值減去 Deallocations Size 欄中的值所得的結果。
「Visualization」分頁會顯示所選時間範圍內,與呼叫堆疊中原生程式碼相關的所有物件的匯總檢視畫面。它基本上會顯示呼叫堆疊與顯示的例項所需的記憶體總量。第一個資料列會顯示執行緒名稱。根據預設,系統會根據分配大小,將物件從左至右堆疊;使用下拉式選單變更排序。
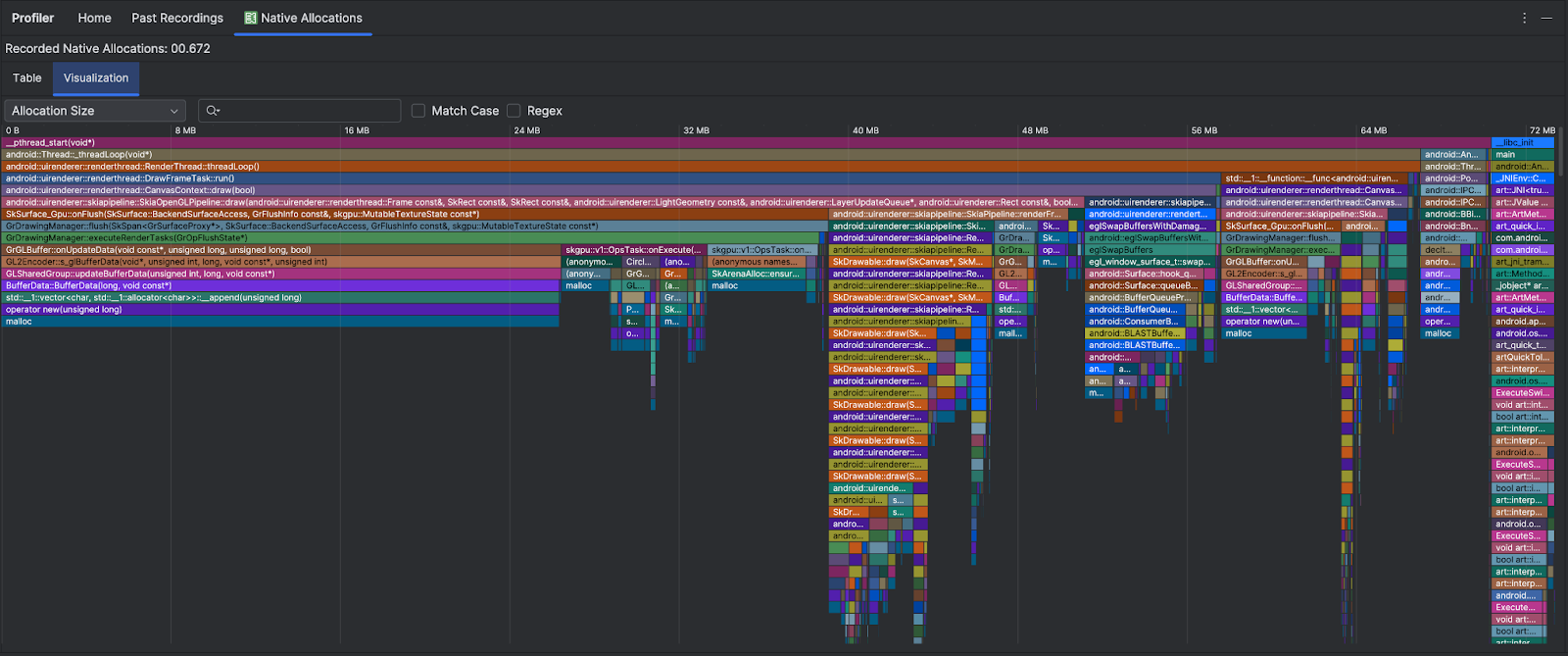
根據預設,分析器使用的樣本大小為 2048 位元組;意即每配置 2048 位元組的記憶體時,系統就會建立記憶體快照。樣本大小越小,快照擷取頻率就越高,進而產生更準確的記憶體用量資料。樣本大小越大,資料準確度就越低,但消耗的系統資源較少,並且能提升分析作業期間的效能。如要變更取樣大小,請參閱「編輯錄製設定」。
