
Android ユーザーは、オーディオブック、音楽、ポッドキャスト、ラジオなどのさまざまなメディアタイプを利用しています。ユーザーがスマートウォッチでメディア コンテンツに簡単にアクセスできるアプリを設計することが重要です。スマートウォッチは、スマートフォンやタブレットと比べて操作時間がはるかに短いため、操作のしやすさと速さを重視する独自のサーフェスです。
詳しくは、GitHub のメディア ツールキットについての説明をご覧ください。
メディアアプリのアーキテクチャ
Wear OS の設計要件を満たすメディアアプリを作成します。多くの場合、メディアアプリには、参照ページとエンティティ ページがあります。
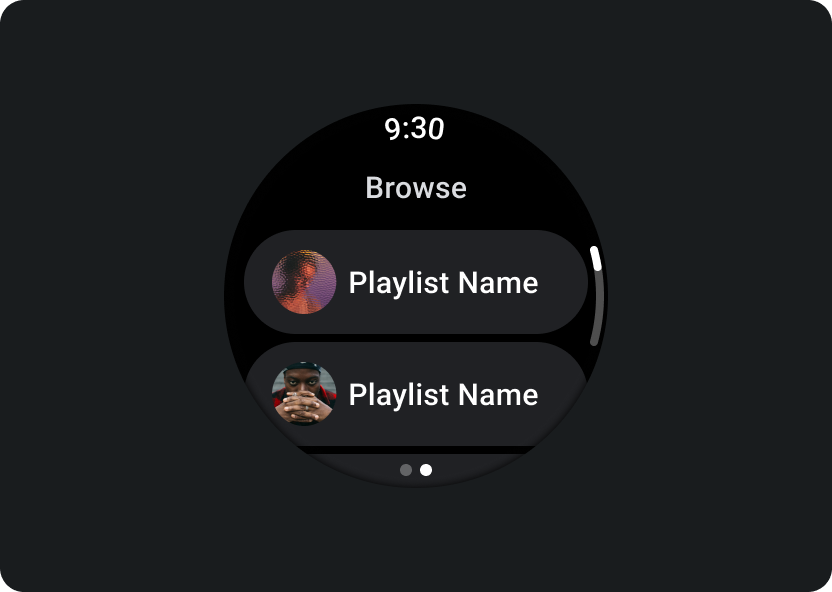
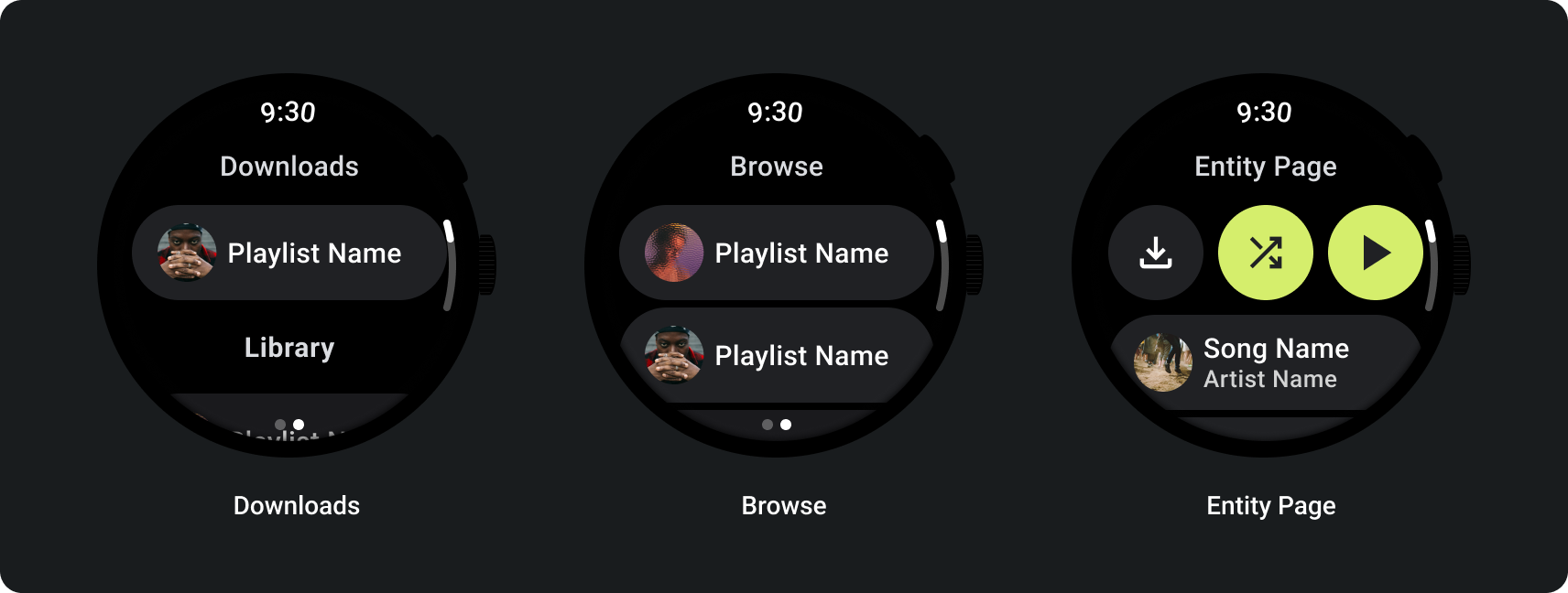
閲覧
ユーザーが再生するメディアを探すことができます。ダウンロードしたアイテムに優先順位を付け、ユーザーが再生をすばやく開始または再開できるようにします。
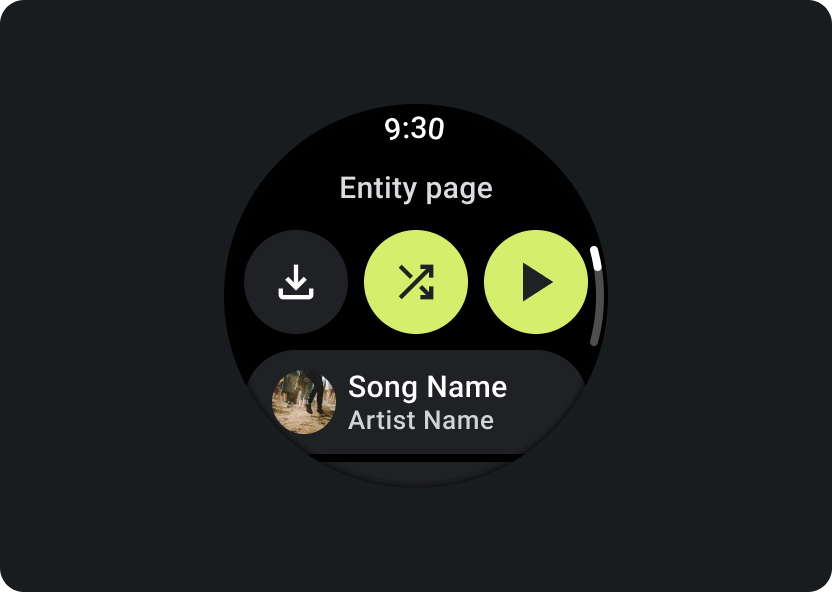
Entity(エンティティ)
特定のメディア アイテムに関する詳細情報をユーザーに提供します。重要なコンテキストと重要なアクション(ダウンロード、再生、シャッフルなど)をすぐに利用できるようにする必要があります。
アプリ階層を削減して、ユーザーにメディアを公開します。フラットな情報アーキテクチャを使って、ユーザーがすばやくリストにアクセスしてサムネイルを表示できるようにします。Wear OS にはカスタム デザイン コンポーネントの使用を検討してください。詳しくは、チップとカードについてのデザイン推奨事項をご覧ください。
メディア コントロール画面
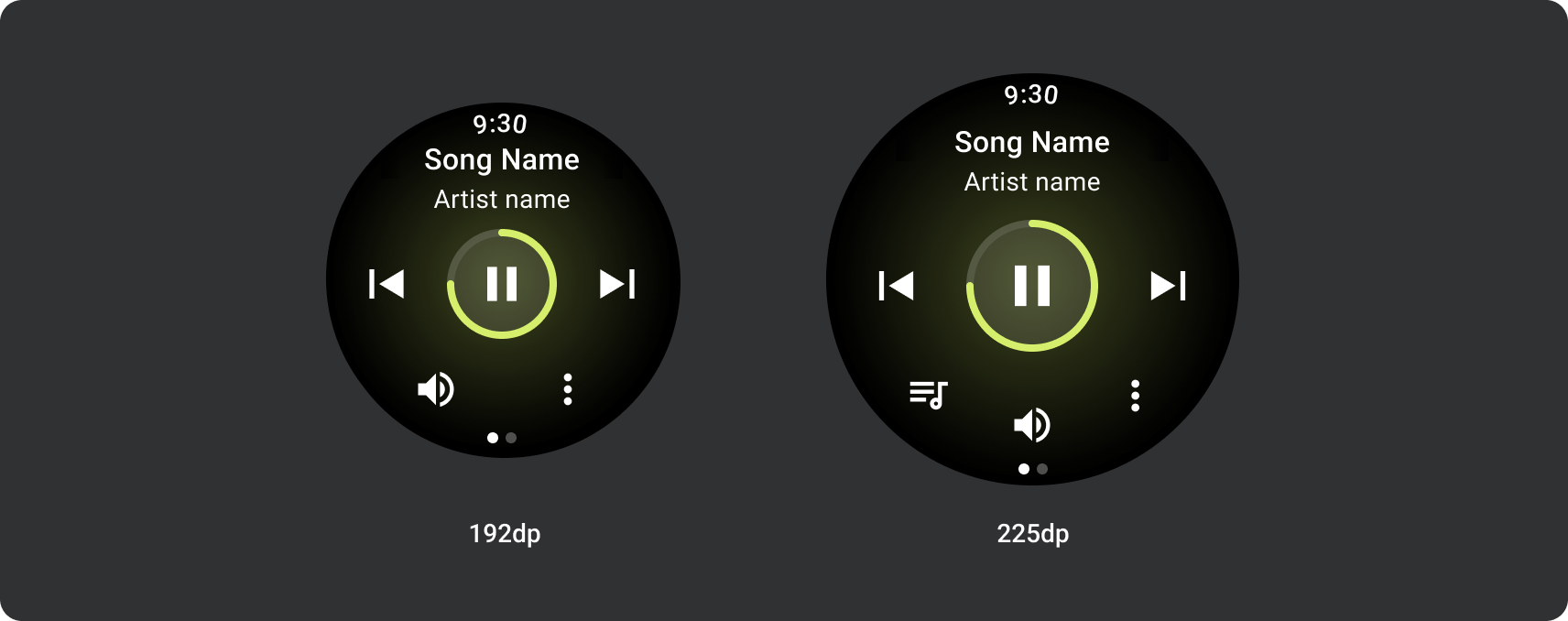
メディアアプリには、メディア コントロール用の画面も必要です。メディア コントロールの作成には 5 ボタン レイアウトを使用します。これで、最小タップ ターゲット数を満たすことができます。以下に、音楽アプリとポッドキャスト アプリのメディア コントロールの例を示します。
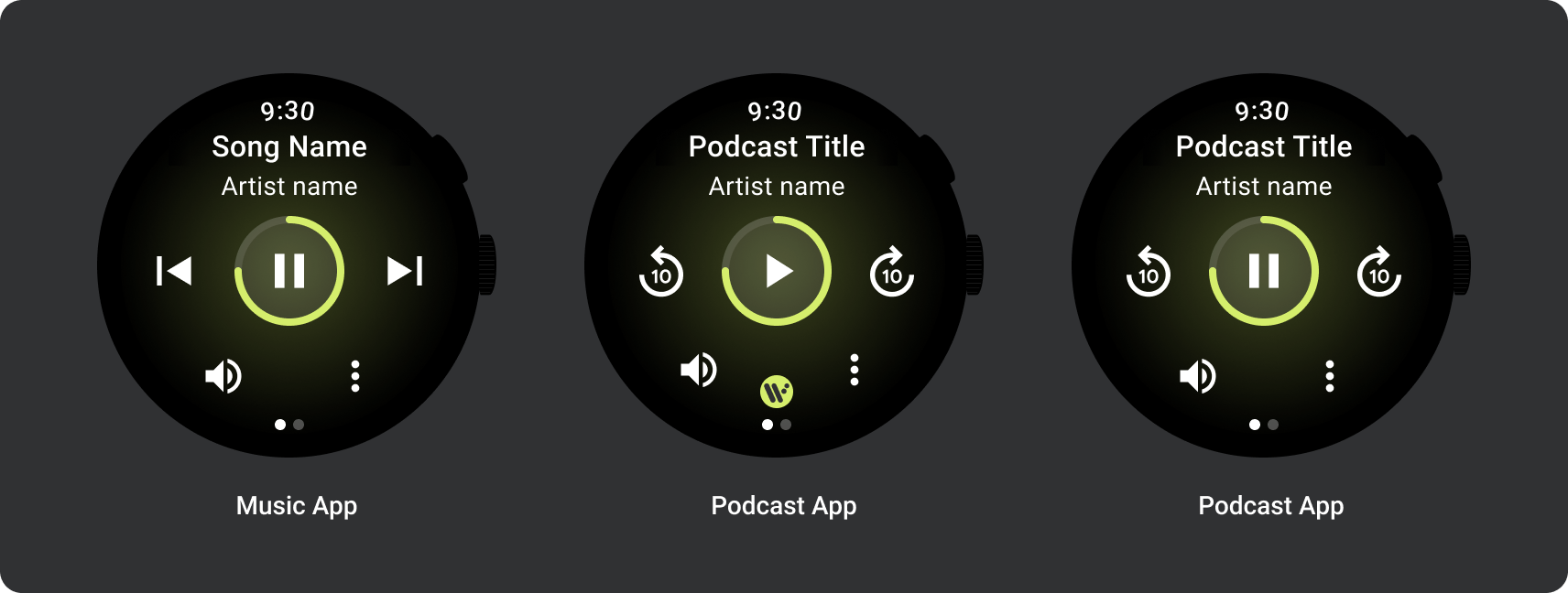
コンテンツの種類に応じて、表示するメディア コントロールを変更します。アクションの数が 5 つを超える場合は、追加ページにユーザーを誘導するオーバーフロー アイコン(3 つの点)を使用します。アプリにカスタムのアイコンやフォントを使用することもできます。
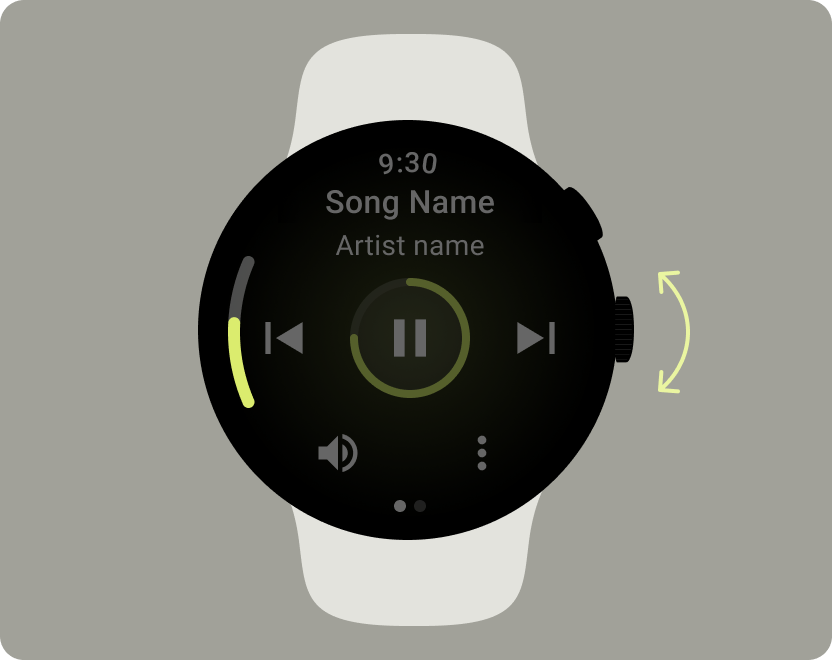
音量を調整する
音量コントロールは、スマートウォッチのユーザーにとって最も重要なメディア コントロールの一つです。メディア コントロールには、音量調節画面に移動するための音量ボタンが必要です。
ほとんどの Wear OS デバイスには、回転サイドボタン(RSB)またはベゼルが搭載されています。一部の Wear OS デバイスには、音量を調整するための追加ハードウェア ボタンも搭載されています。音量の調整には、RSB、ベゼル、または追加ボタンを使用します。例に示すように、RSB またはベゼルが回されたときのみインジケーターを表示します。
一般的なユースケース
メディアアプリを設計する際は、次の重要なユースケースを優先してください。
- ダウンロードしたメディアを聞く
- スマートウォッチから音楽をストリーミングする
ダウンロードしたメディアを聞く
ユーザーがエンティティ ページからメディア アイテムを手動でダウンロードできるようにする必要があります。
以下の例に示すように、コンテンツのダウンロード先、ダウンロードの進捗状況、ダウンロードの所要時間、ダウンロードのサイズをユーザーに伝えます。
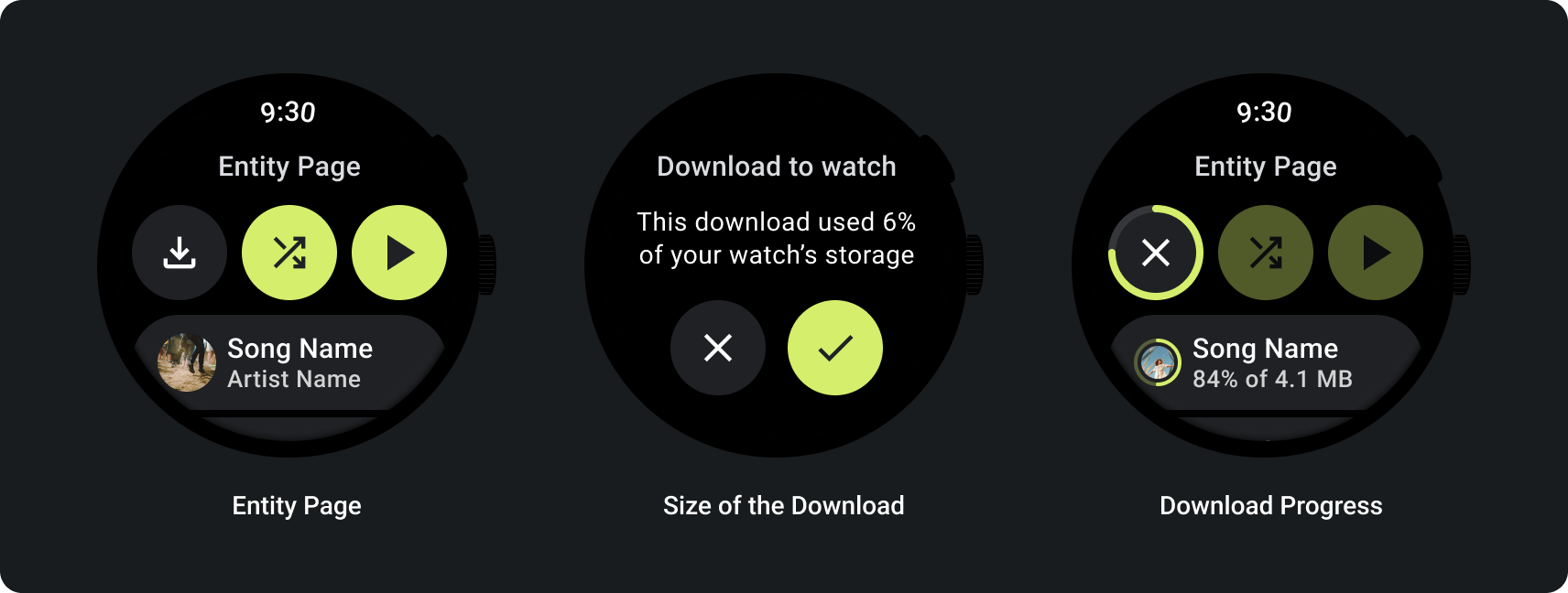
ユーザーがメディアをブラウジングした際は、最後にダウンロードしたメディアを表示します。
コンテンツがダウンロード済みの場合は、スマートウォッチからダウンロードを削除するアクションを表示することでダウンロード済みの状況を明確にします。この場合は、次の画像に示すように、そのダウンロードがスマートウォッチで占有しているサイズも示す必要があります。

ソースデバイスがスマートウォッチの場合は、音楽を聴き始める前にヘッドセットを接続するようユーザーに促します。ヘッドセットが接続されたら、メディアを再生し、メディア コントロールを開きます。
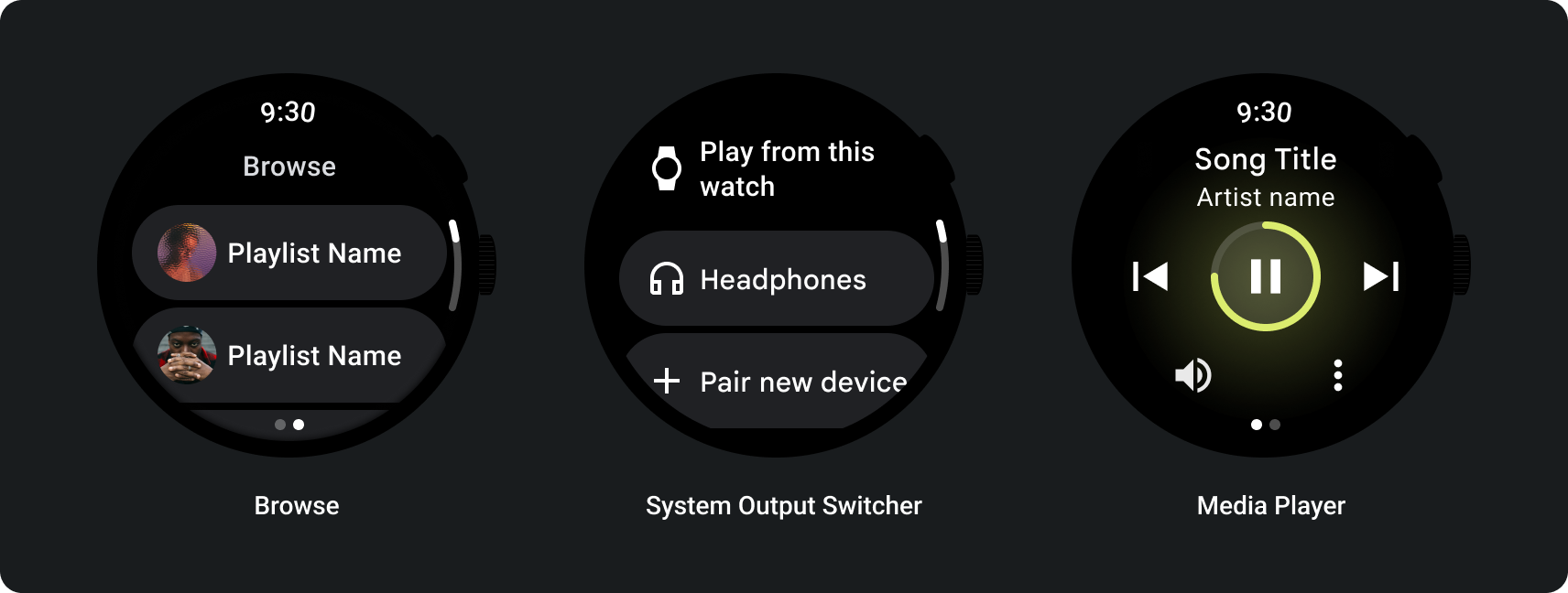
スマートウォッチから音楽をストリーミングする
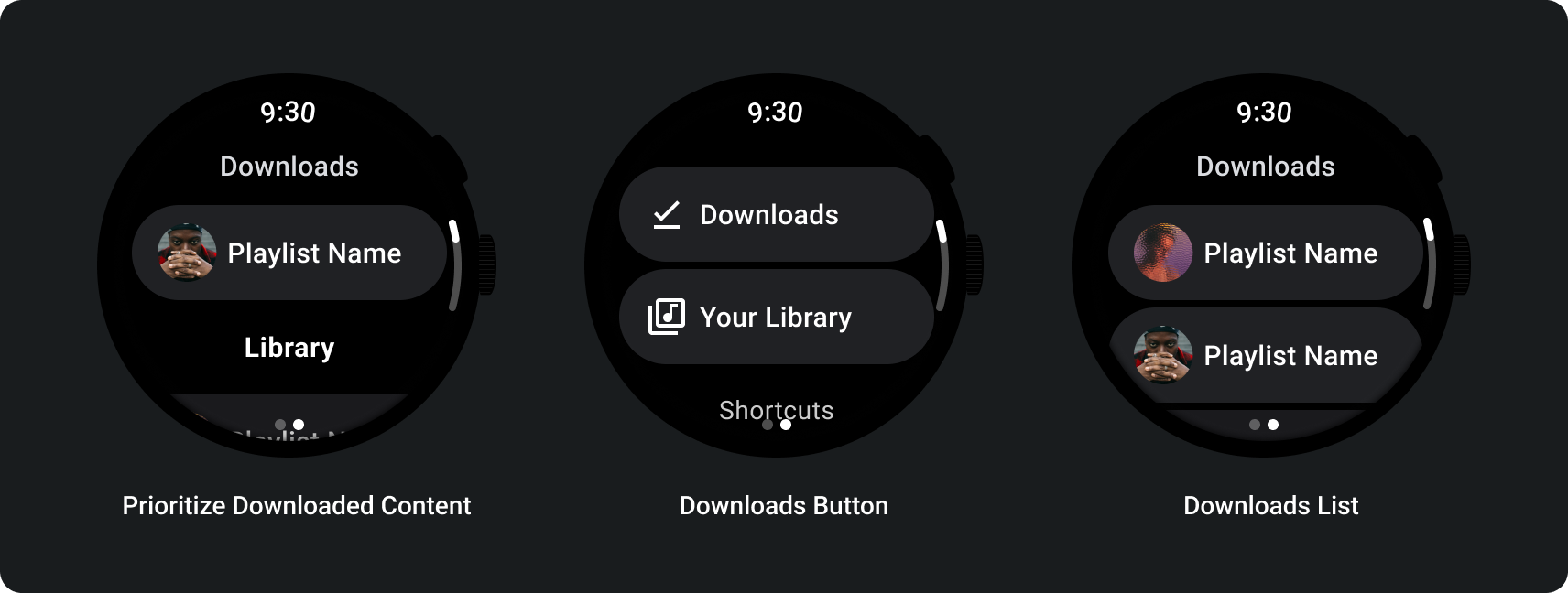
スマートウォッチからメディアをストリーミングすると、Wear OS デバイスのバッテリーに大きな影響があります。最近使用したダウンロードをブラウジング リストに表示することにより、ユーザーが Wear OS デバイスで聞く際にダウンロード済みのコンテンツを優先させます。次の画像に示すように、ダウンロードの全一覧にユーザーを誘導するボタンを追加することをご検討ください。
詳しくは、GitHub のメディア ツールキットをご覧ください。
アダプティブ レイアウト
メディアアプリの大画面への適応は、メディア プレーヤーのエクスペリエンスにのみ焦点を当てています。その他の要素はすべて、チップ、ボタン、ダイアログ、リストの各ページでキャプチャされ、大画面に対応するためのアプリの適切な動作について説明しています。
ボタンの構成
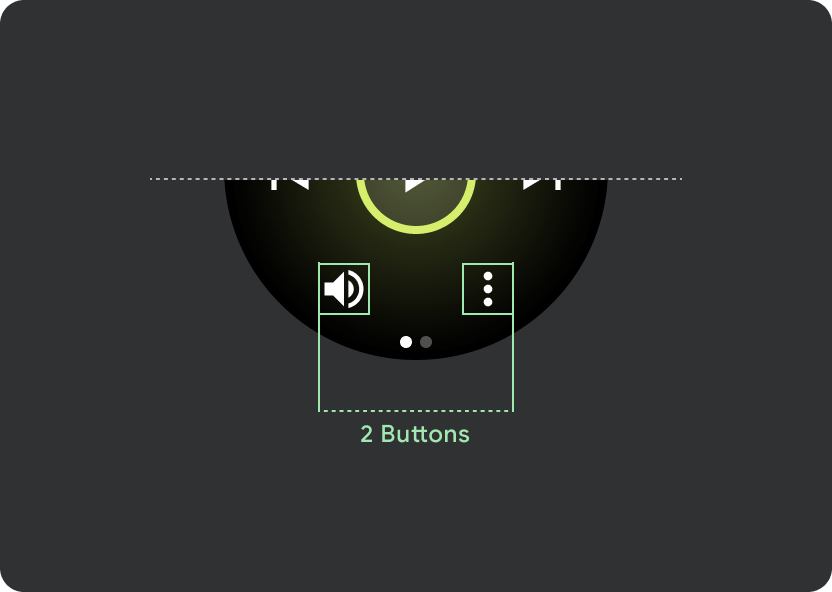
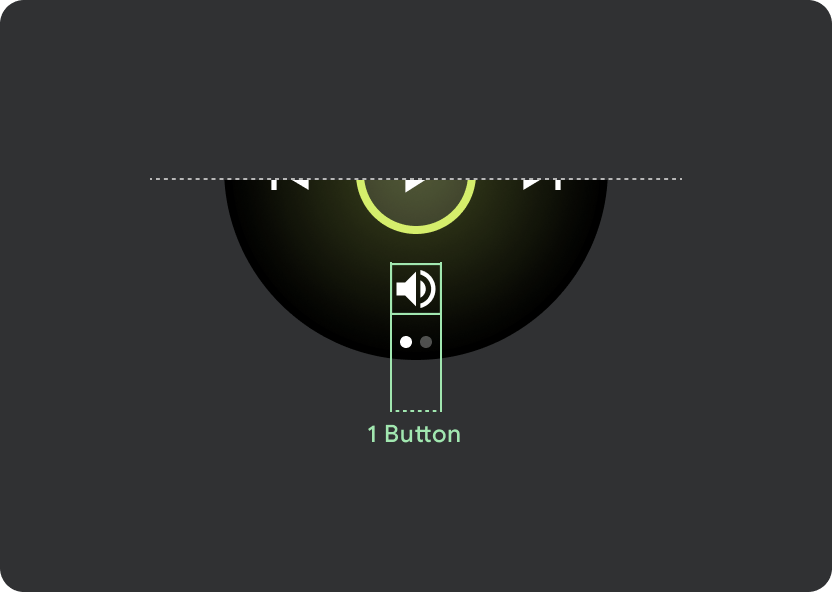
タップ ターゲットのサイズの原則に沿って、225 dp 未満の Wear OS デバイスでは 2 ボタン レイアウトを、画面の大きいデバイスでは 3 ボタン レイアウトを表示します。次の画像は、1 ボタン レイアウトやロゴ付きの 2 ボタン レイアウトなど、その他の例を示しています。

レスポンシブ コントロール ボタン
225 dp より大きい Wear OS デバイスでは、メイン コントロール(再生/一時停止)が 60 dp から 72 dp に拡大され、中央のセクションの高さが 72 dp になるため、その中のすべてのコントロールのタップ ターゲットが拡大されます。これは、メディア プレーヤー テンプレートから継承するレスポンシブな動作です。
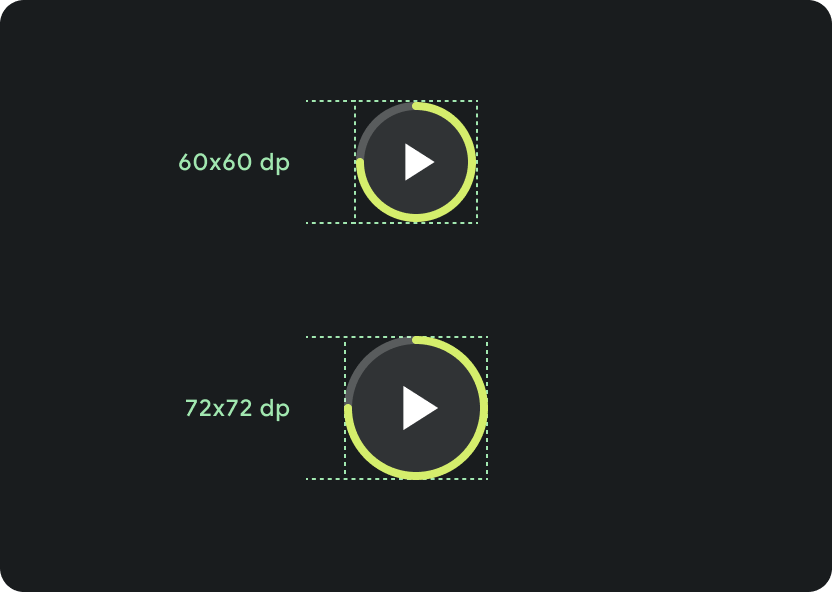
さまざまな画面サイズでのスケーリング:
225 dp 未満: 60 dp x 60 dp
225 dp 超: 72 dp x 72 dp
marquee の動作
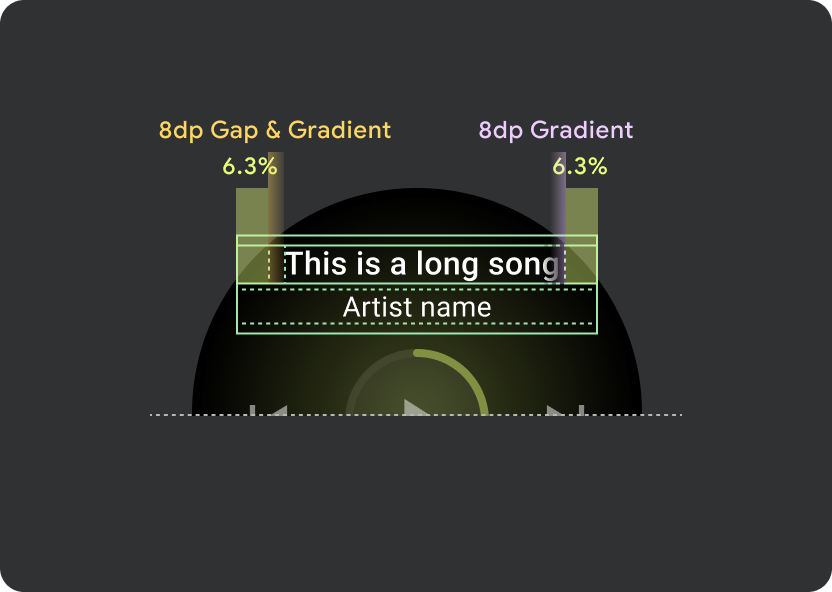
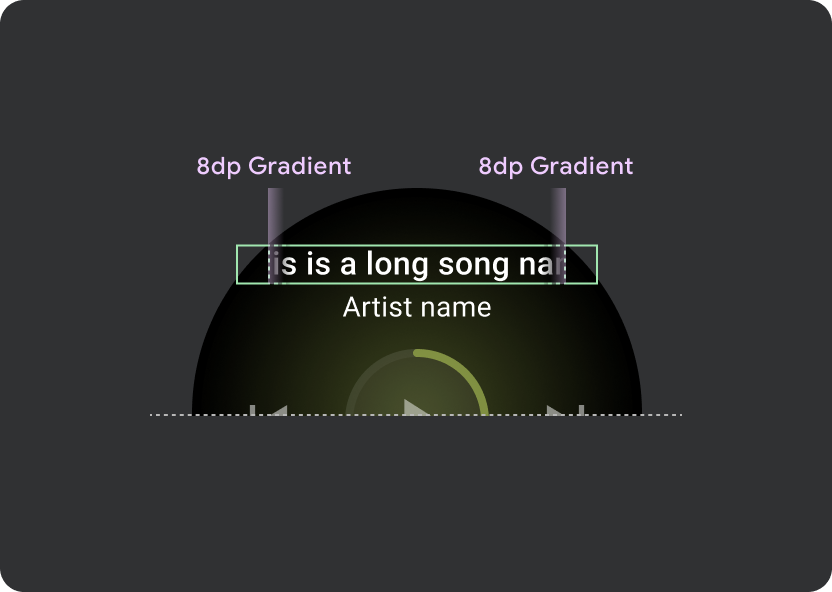
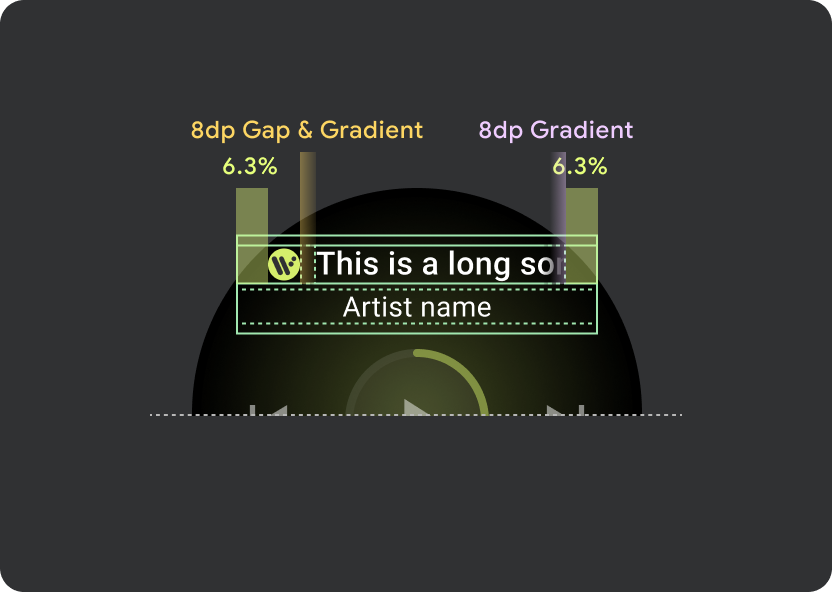
ヘッダー内では、9.38% のユニバーサル マージンを使用し、曲のタイトルには 6.3% の追加マージンを使用します。スクロールするタイトルには 8 dp のグラデーションを使用します。アイコンがある場合は、さらに 8 dp のギャップ(8 dp のグラデーションあり)を使用します。アイコンの下に、位置が固定されたマーキー スクロール アニメーションを含めます。

ヘッダー アトムの余白
9.38%
楽曲タイトルの内部マージン
6.3%
グラデーション
8 dp の余白
左に 8 dp の追加(アプリアイコンに対応するため)
アイコンの隙間
8 dp

ターゲットをタップする
画面が大きい Wear OS デバイスでは、中央セクションとフッター セクションのアイコンは、余分なスペースを利用してタップ ターゲットのサイズを大きくします。つまり、固定コントロール アトム以外では、アイコン コンテナに「空きスペースを埋める」プロパティが適用されます。
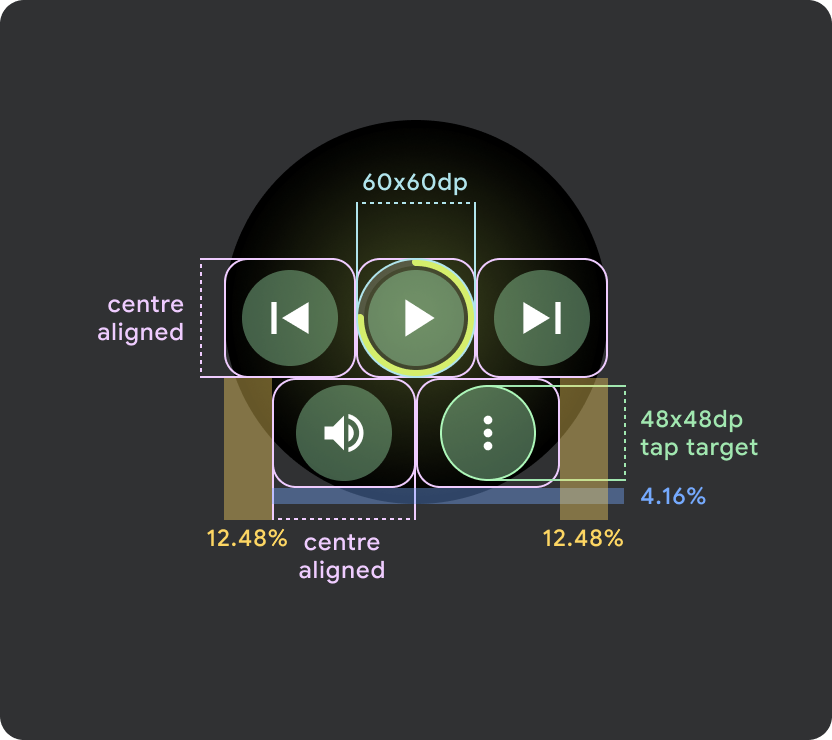
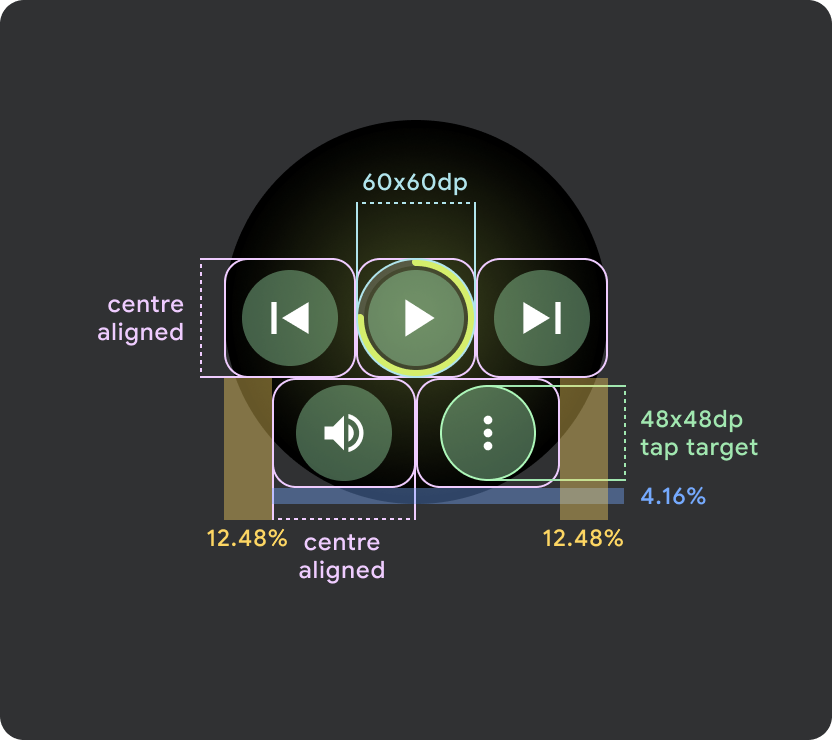
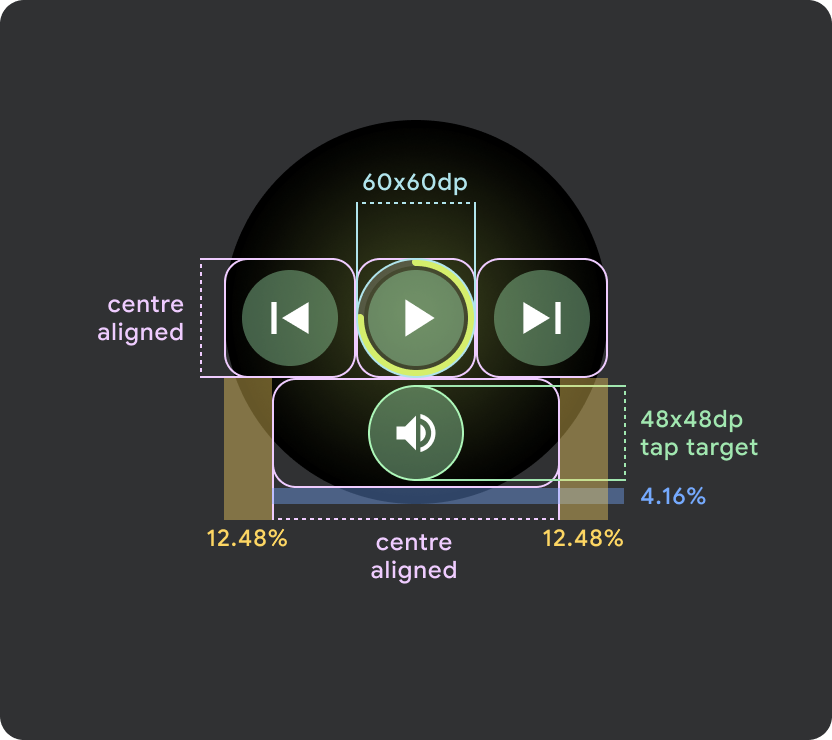
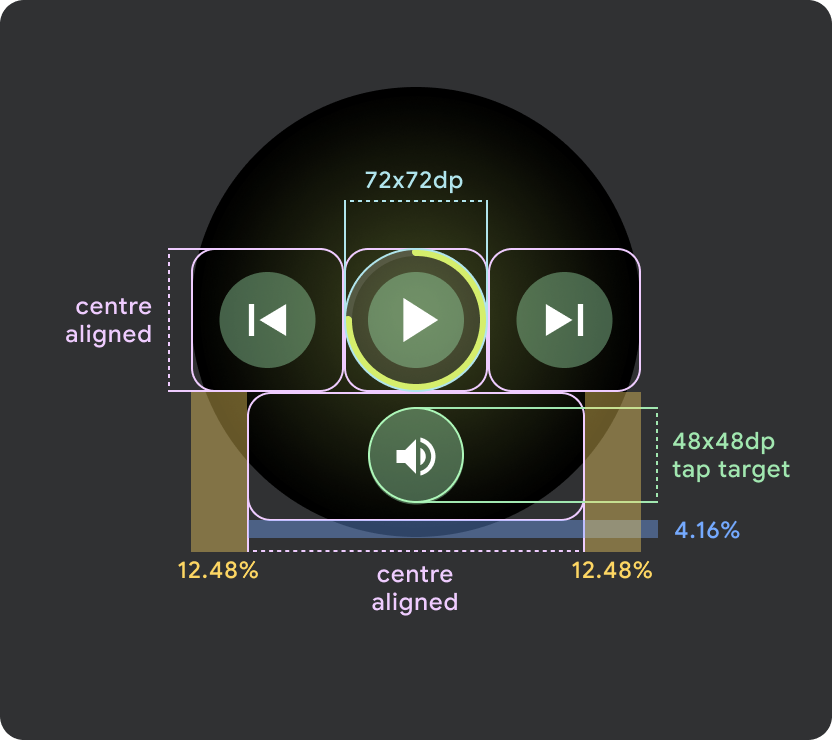
Wear OS の小さな画面(225 dp 未満)
- 小さい画面では最大 2 つのボタン、最小画面サイズでは 2 つのボタンを配置することをおすすめします。
- 下部のボタンの最小タップ ターゲットは 48 dp(H)x 48 dp(W)にする必要があります。
- アイコンはタップ ターゲットの中央に配置する必要があります
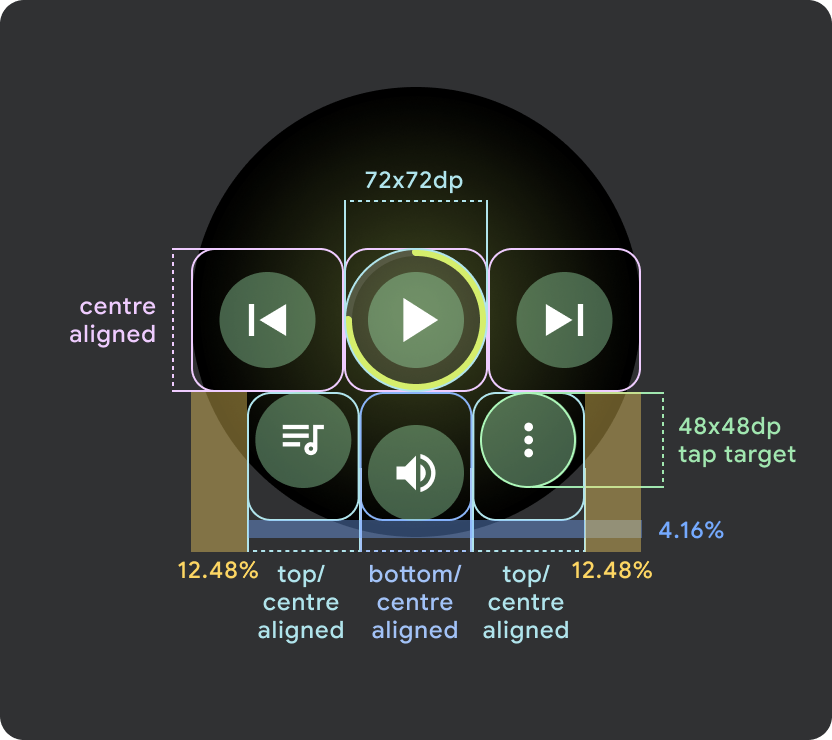
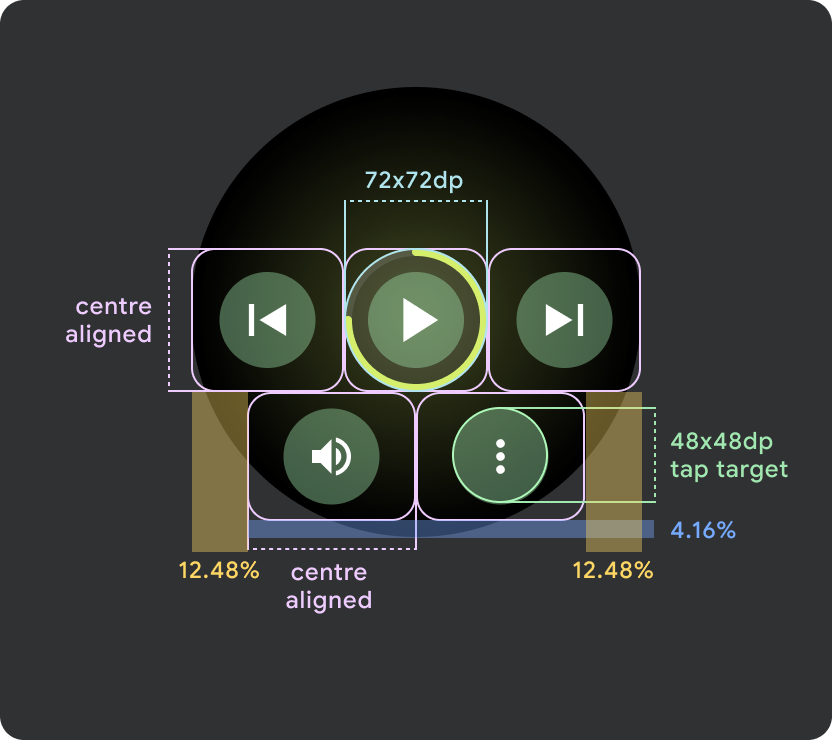
Wear OS の大画面 / ブレークポイント(225 dp 超)
- 大きな画面にはボタンを最大 3 つ配置し、これらの「大きな画面」のうち最も小さい画面にはボタンを 3 つ配置することが推奨されます。
- 下部のボタンの最小タップ ターゲットは 48 dp(H)x 48 dp(W)にする必要があります。
- アイコンはタップ ターゲットの中央に配置する必要があります(ただし、丸みを帯びた効果を作り出すために、上部と下部を揃え、内部にパディングを配置します)。
