Wear OS 向けにアプリを設計する場合は、アプリのレイアウトを意識的に設計してください おすすめしますWear OS は円形ディスプレイで実行され、クリッピングがより効果的であるため 一般的ですが、2 つのカテゴリの正規レイアウトがあります。 考慮すべき点を紹介します
スクロールしないアプリ レイアウト
スクロールしないレイアウトは、ひと目でわかる情報を重視し、ユーザーに価値を提供します。 やり取りがほとんどないか まったくないかを確認しますそのため、インフラストラクチャの構築は 次のレイアウトに変更できます。
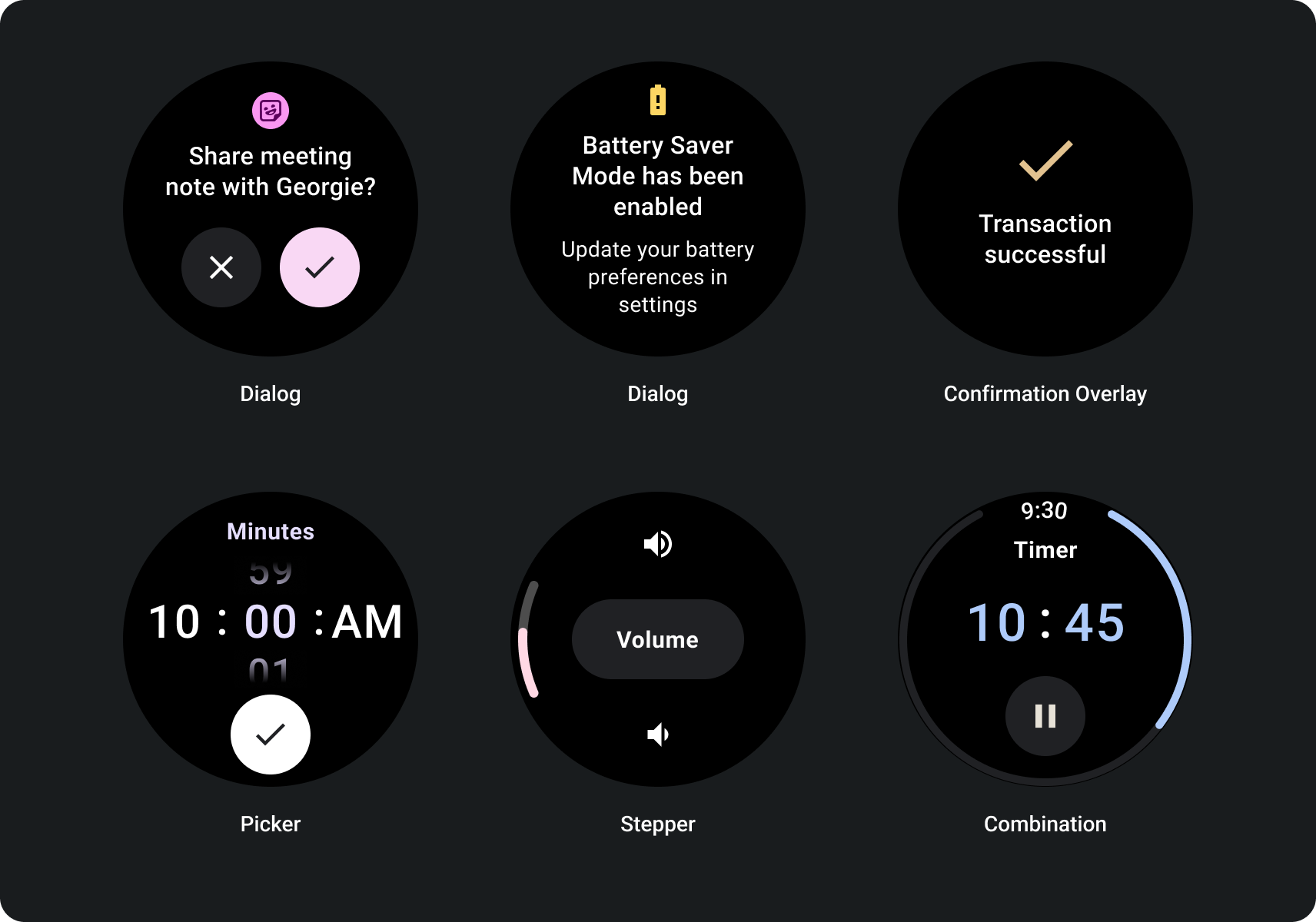
レスポンシブ非スクロール ビュー向けに作成する
- 言語、フォント スケーリング、デバイス、変数を組み合わせてテストする 説明します。
- スクロールできないレイアウトは、コンテンツが把握または管理されている場合にのみ使用する 特定のデザインを使用する必要がある場合に 最適です
- レイアウトに推奨される上部余白、下部余白、推奨余白を適用します。
- コンテンツが表示されない場所に余白をパーセンテージ値で定義する クリップされます。
- スペースを最大限に活用するように、 さまざまなサイズのデバイス間でバランスが維持されます。
アプリ レイアウトのスクロール
1 画面に収まらない情報を含むページ より長く没入感のあるジャーニーをサポートするために必要となる、 表示されます。
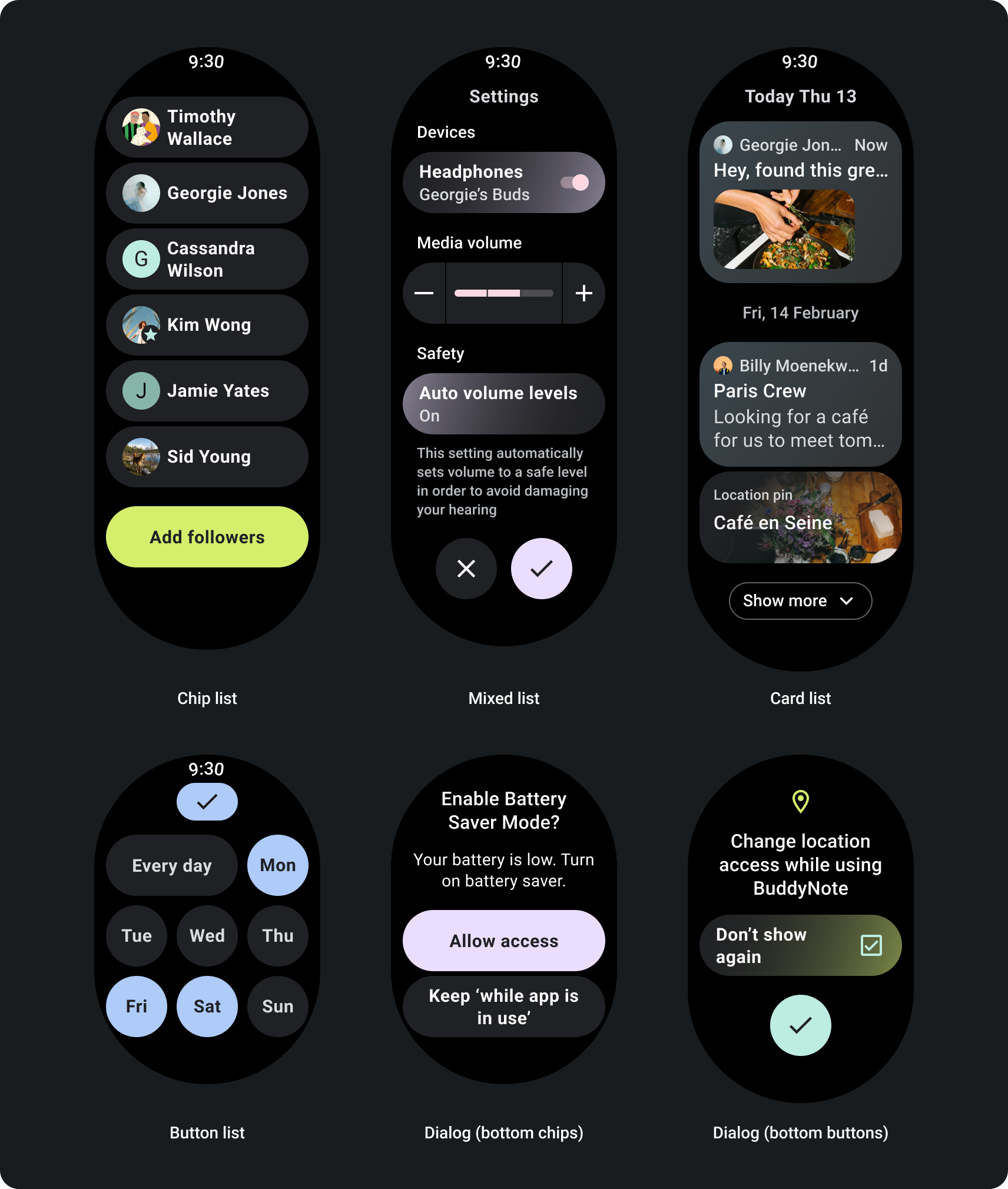
レスポンシブ スクロール ビューに対応する
- 推奨される上余白、下余白、余白を適用します。
- 位置でクリッピングしないように、外側の余白をパーセント値で定義します。 コンテナの先頭と末尾。
- UI 要素間に固定 DP 値でマージンを適用します。
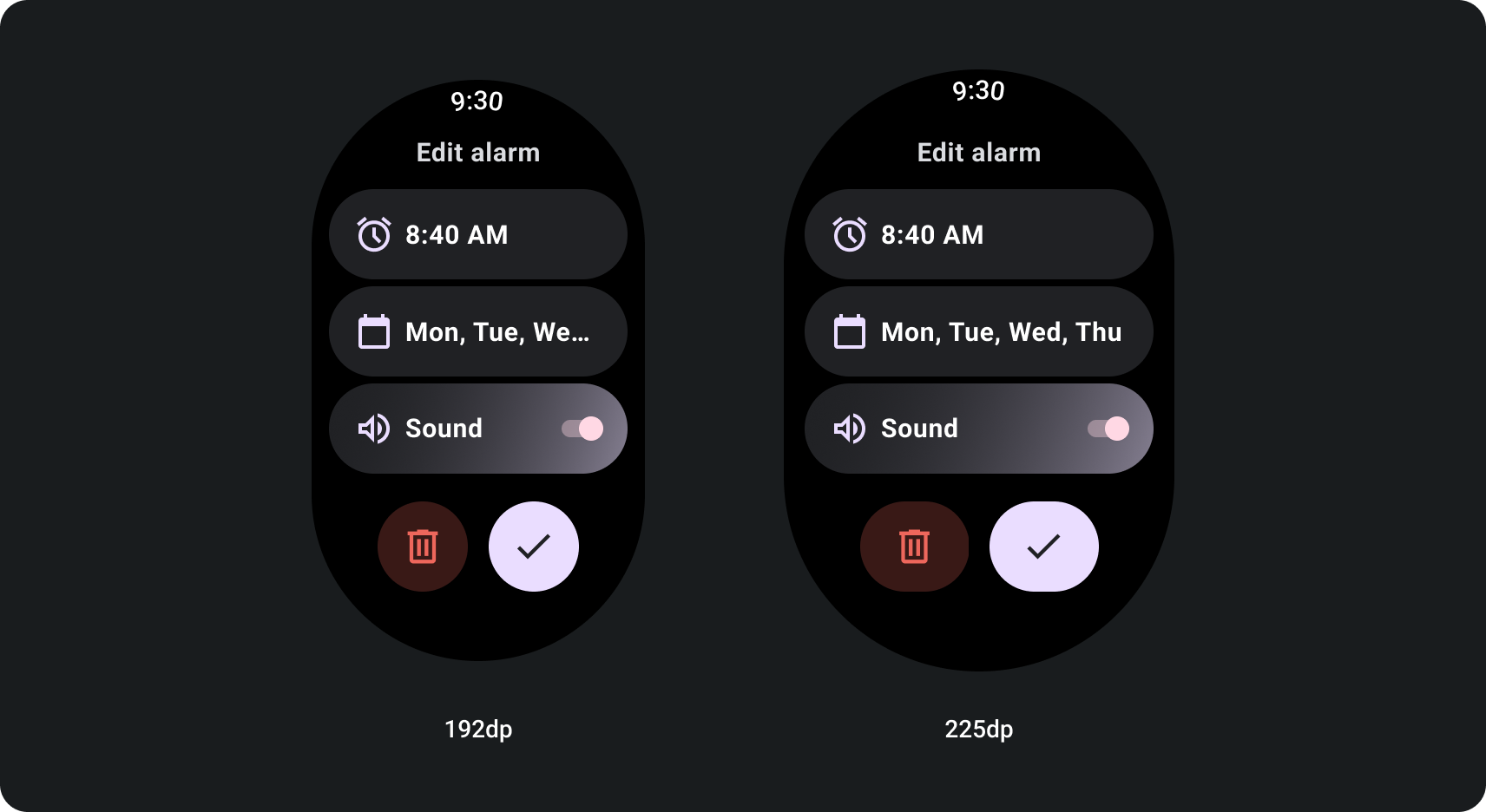
画面サイズのブレークポイントを使用してアダプティブ スクロール ビューを作成する方法
レスポンシブ デザインの手法を採用したスクロールビューは通常、 サポートしています。ただし、特殊なケースでは、ブレークポイントを使用して、 ディメンションのオーバーライド、追加オプションを表示するレイアウトの拡張、 コンテンツを画面に合わせて見やすくしたり、次の例をご覧ください。 は、大画面で下の 2 つのボタンを大きくする方法を示しています。
Figma デザインキット
デザインキットのダウンロード ページにアクセスして、組み込みの Duet AI による コンポーネント、オプション、推奨事項から、さまざまなアプリやタイルを作成できます。 ベスト プラクティスに従う設計になっています。

