スクロールするアプリビューのレイアウトには、リスト(TransformingLazyColumn)とダイアログがあります。これらのレイアウトはアプリ画面の大部分を占め、大画面サイズに適応する必要があるコンポーネントのコレクションを表します。コンポーネントがレスポンシブであることを確認します。つまり、使用可能な幅いっぱいに広がり、画面の高さの大部分が使用可能になったときに TransformingLazyColumn の調整を採用します。これらのレイアウトはすでにレスポンシブに構築されていますが、広くなった広告枠をさらに活用するための推奨事項がいくつかあります。
レスポンシブで最適化されたデザインを作成する
デザイン レイアウトを大きな画面サイズに適応させるため、レイアウトとコンポーネントの動作を更新し、レスポンシブ動作(パーセンテージベースの余白やパディングなど)を組み込みました。この問題に対処するため、Android UI ライブラリのレイアウトとコンポーネントを更新し、レスポンシブな動作(パーセンテージベースの余白やパディングなど)を組み込みました。Compose コンポーネントを使用している場合は、この応答性を自動的に継承できます。
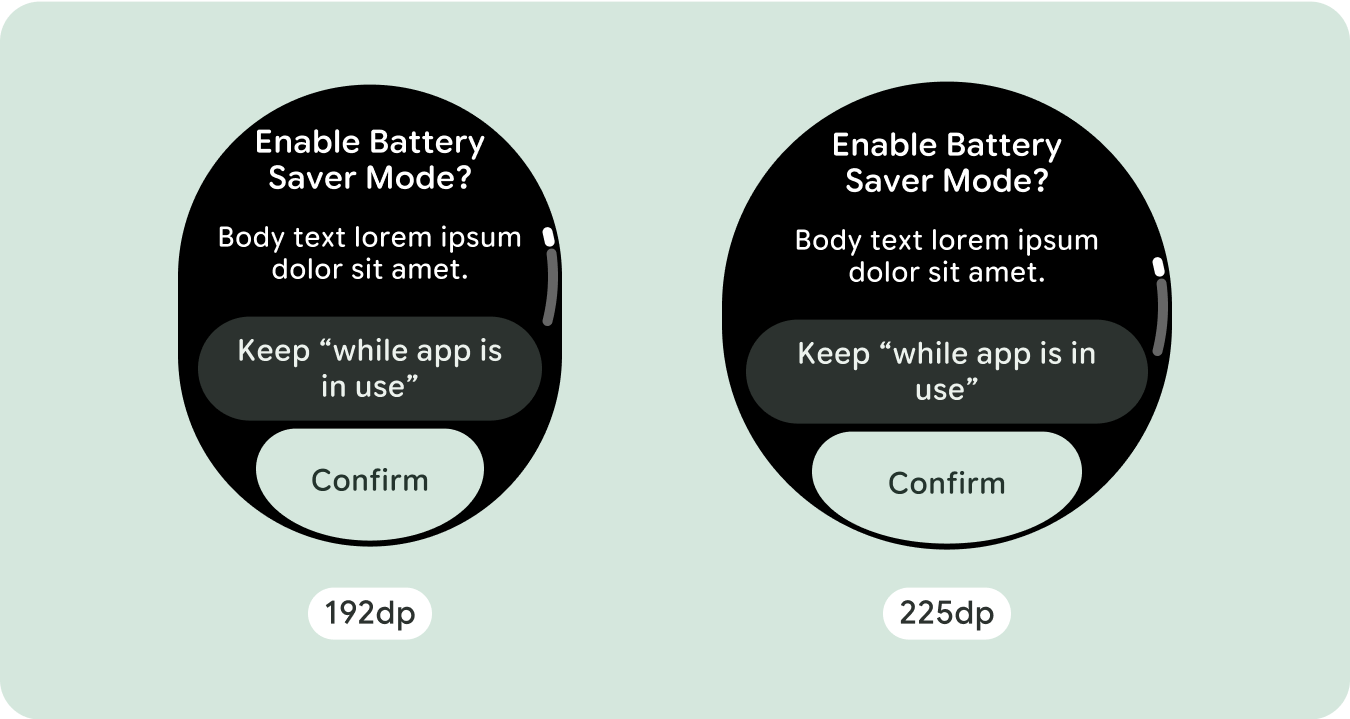
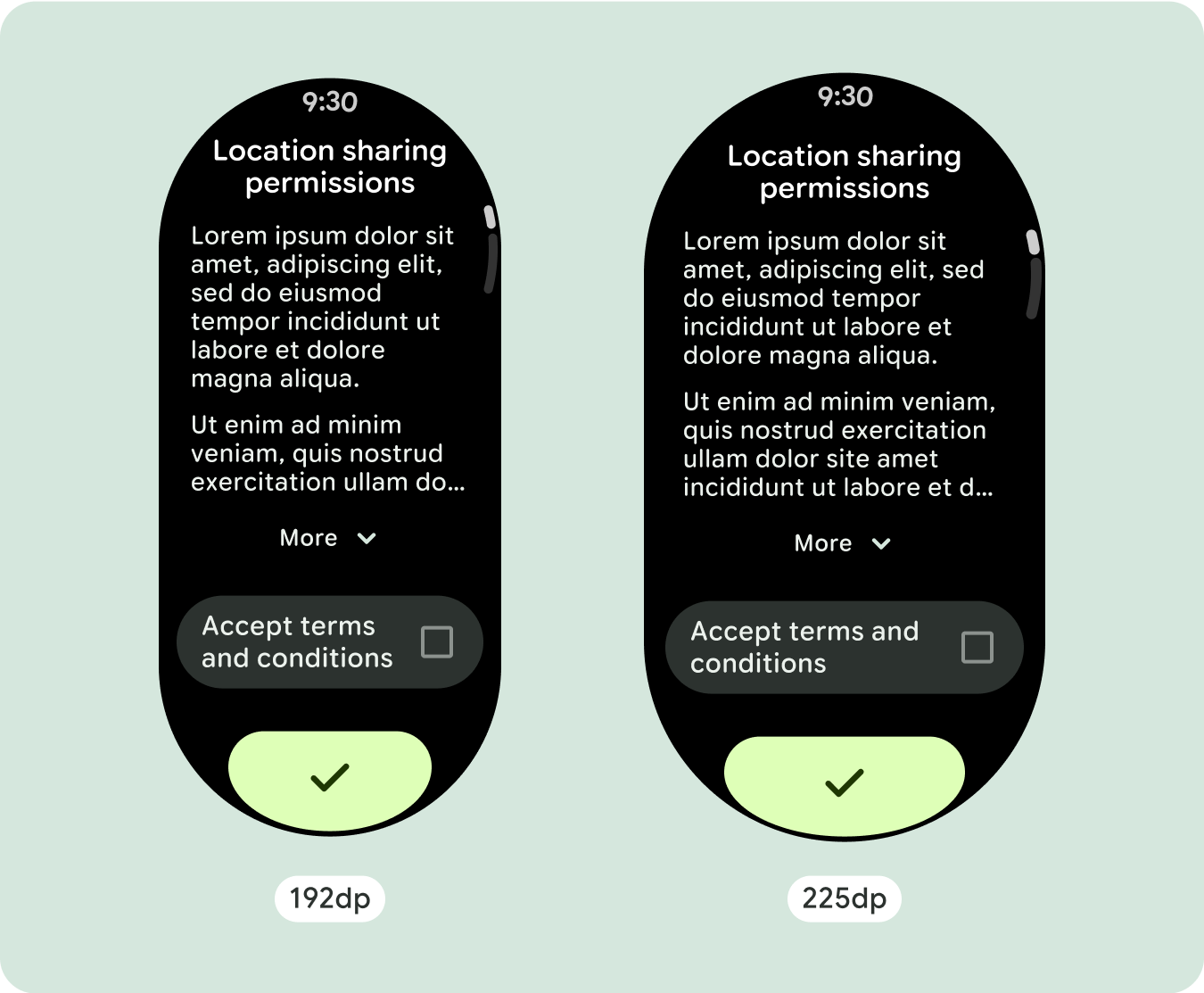
独自の画面デザインの場合は、さまざまな画面サイズで徹底的にテストし、コンポーネントと要素がスムーズに適応し、コンテンツが切り取られないようにします。パーセンテージの余白は、スペーサーを効果的にスケーリングするのに役立ちます。225dp のブレークポイントを使用して、大きなスマートウォッチの画面に追加情報や高度な機能を導入することをおすすめします。
コンポーネントが使用可能な幅を埋めていることを確認する
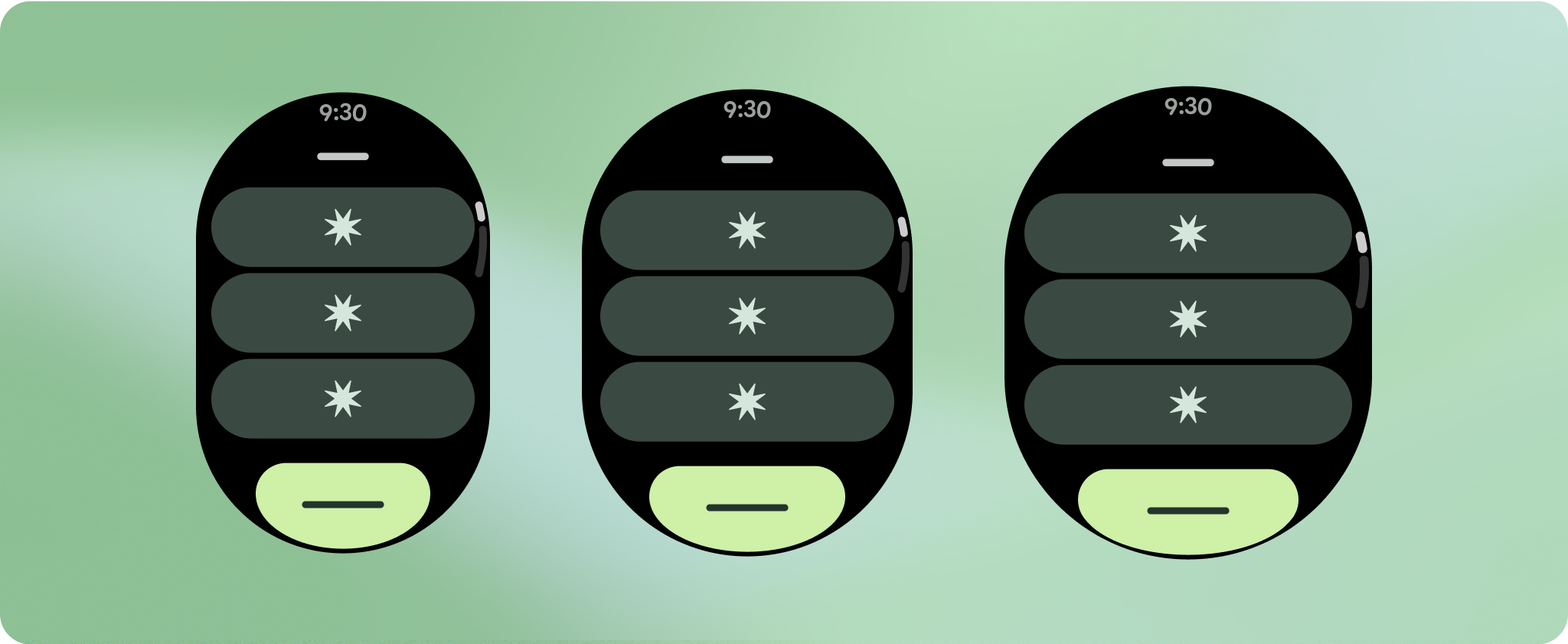
すべてのコンポーネントはレスポンシブに構築されているため、使用可能な幅と高さに収まります。画面の丸い角によってコンテンツが切り取られないように、必要な余白があることを確認してください。
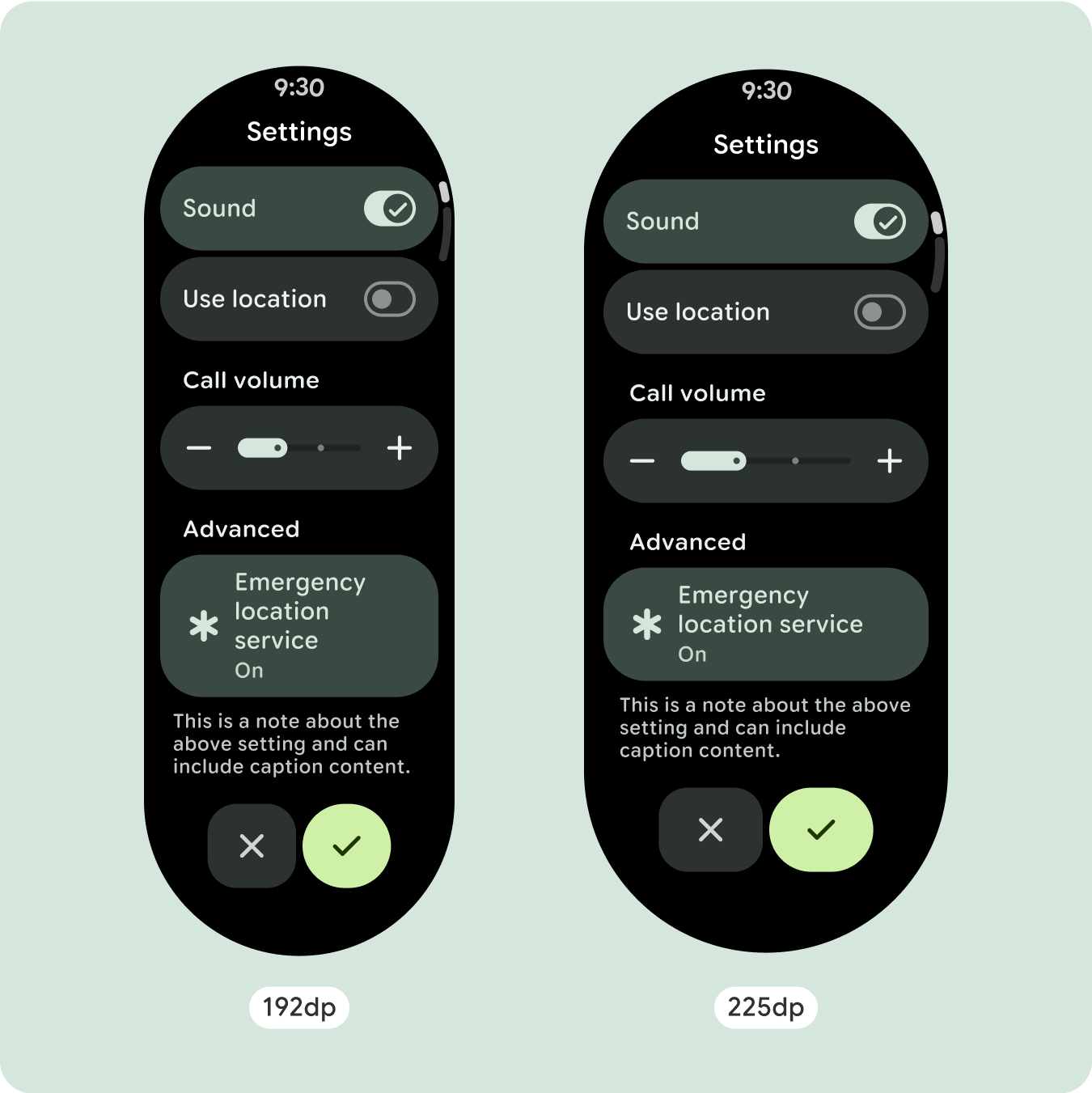
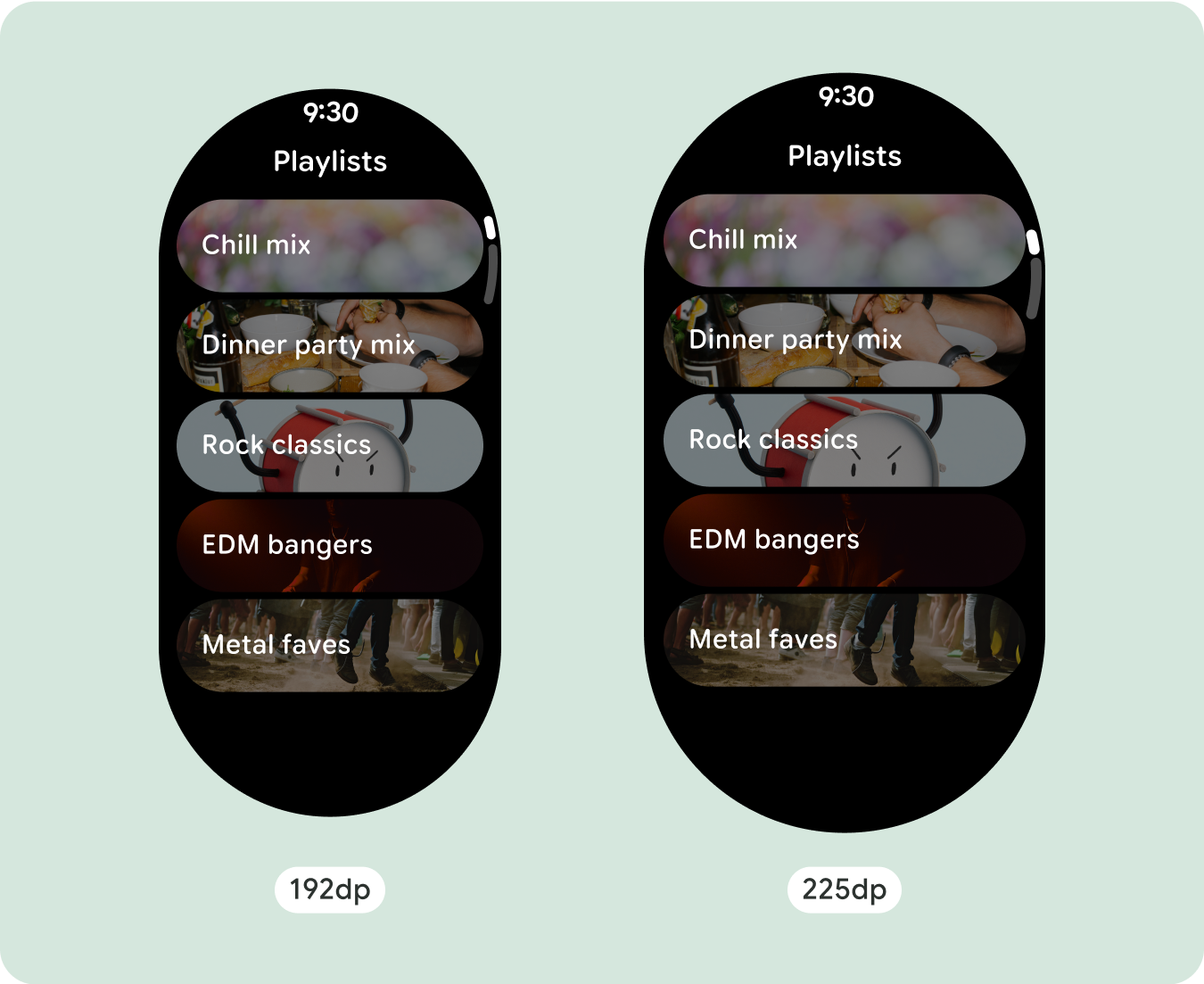
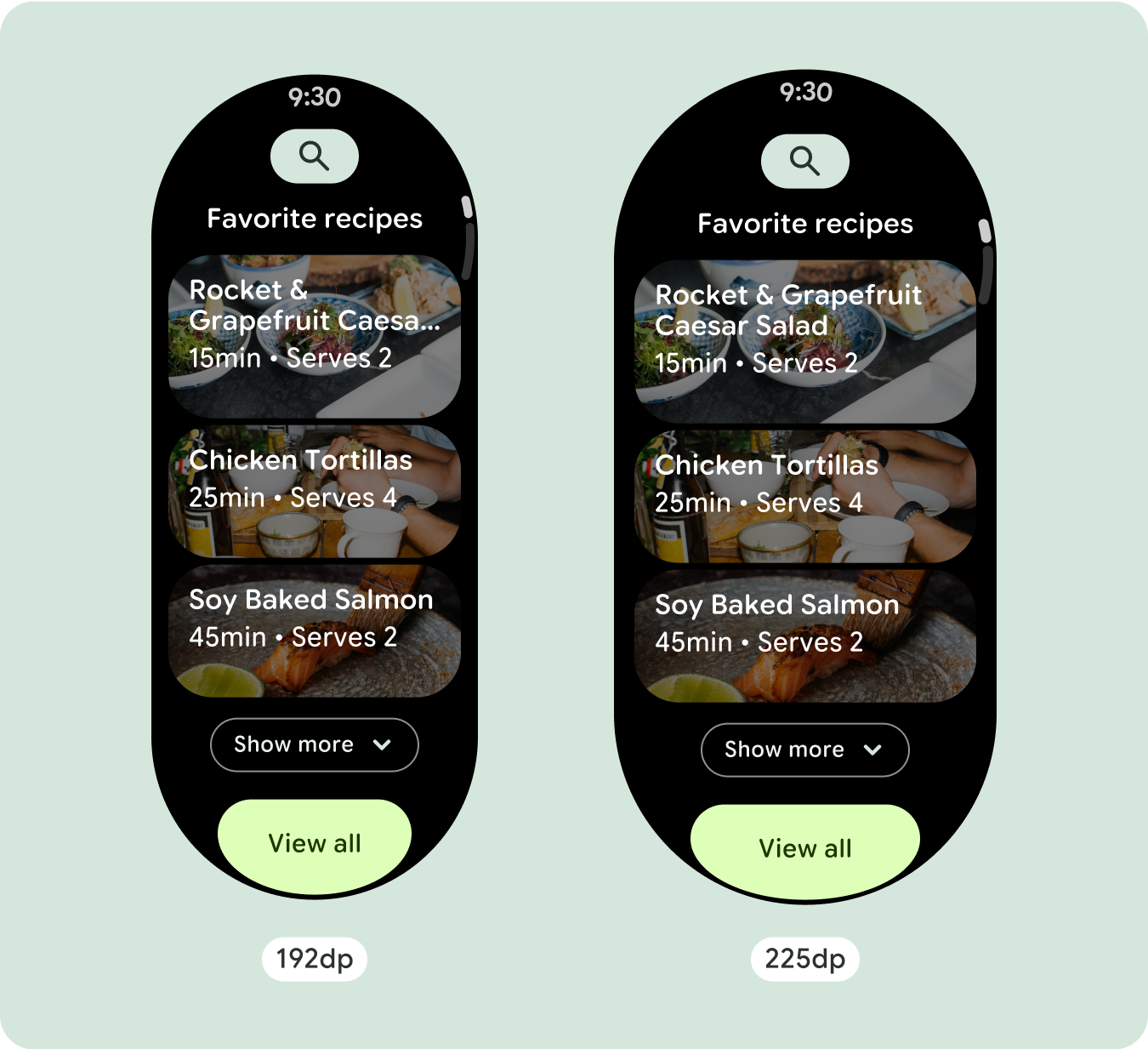
追加のテキスト文字を表示する
ほとんどのコンポーネントには、使用可能な幅いっぱいに広がるテキスト ボックスがあります。つまり、画面幅が広くなると、文字数も自動的に増えます。
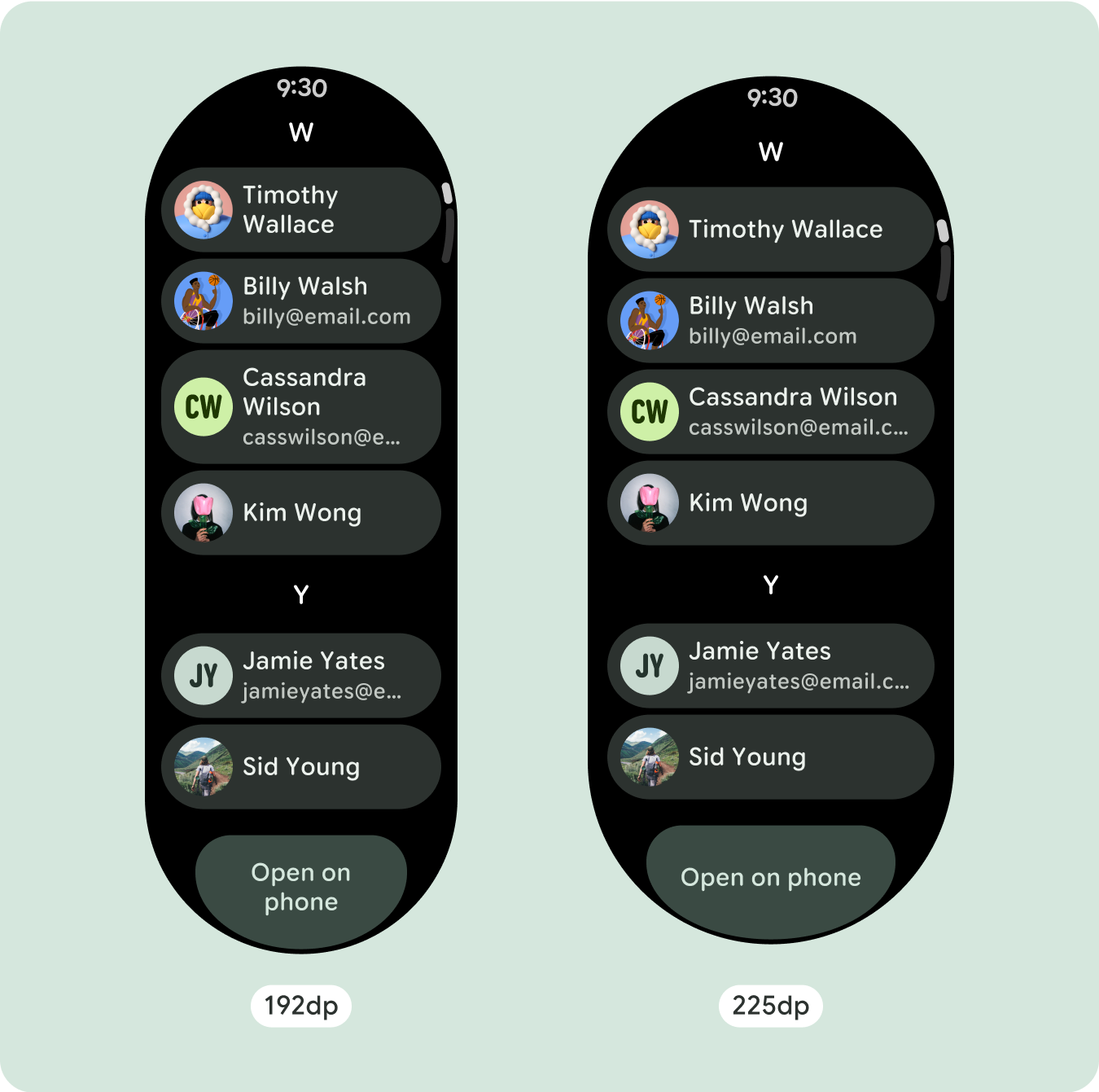

アダプティブで差別化されたデザインを作成する
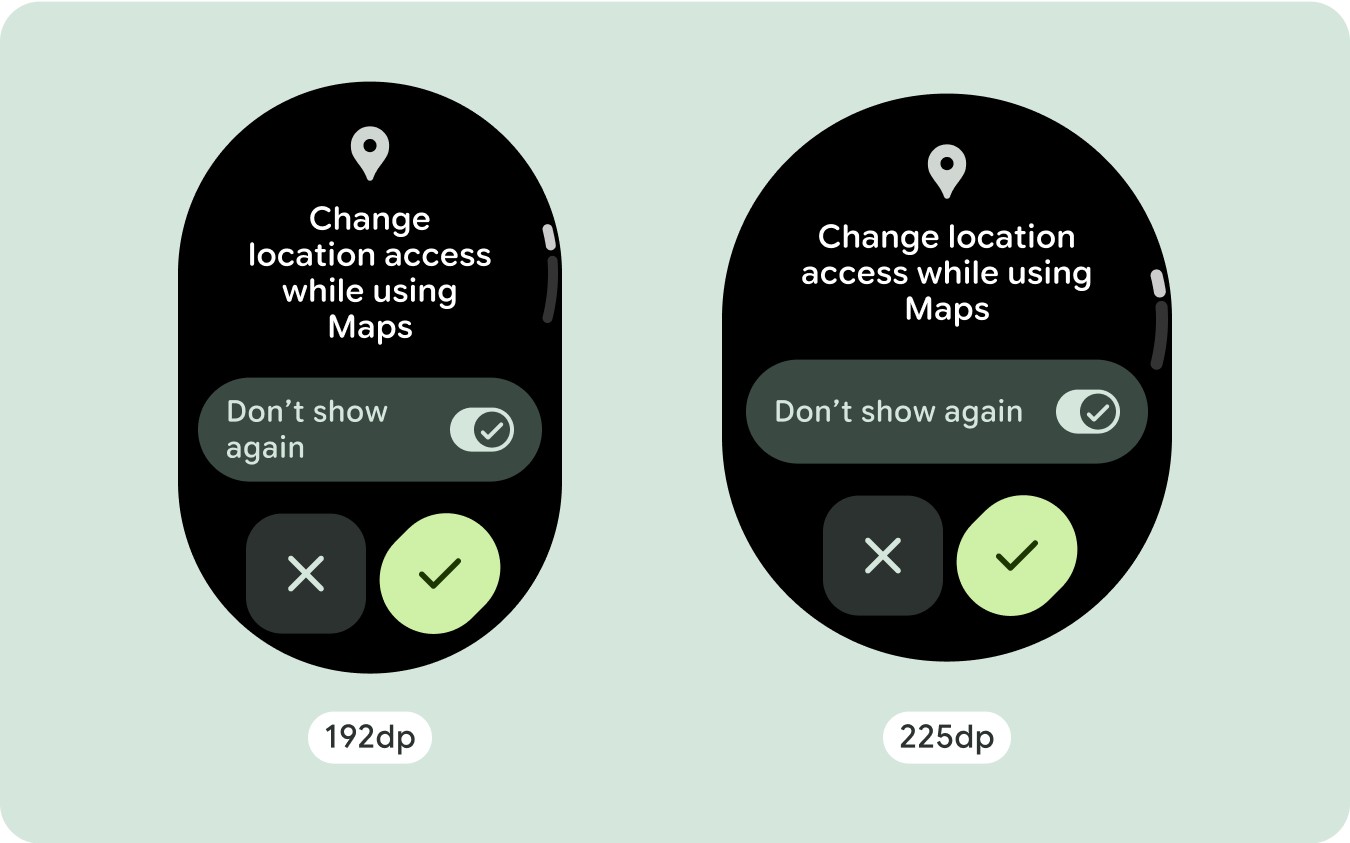
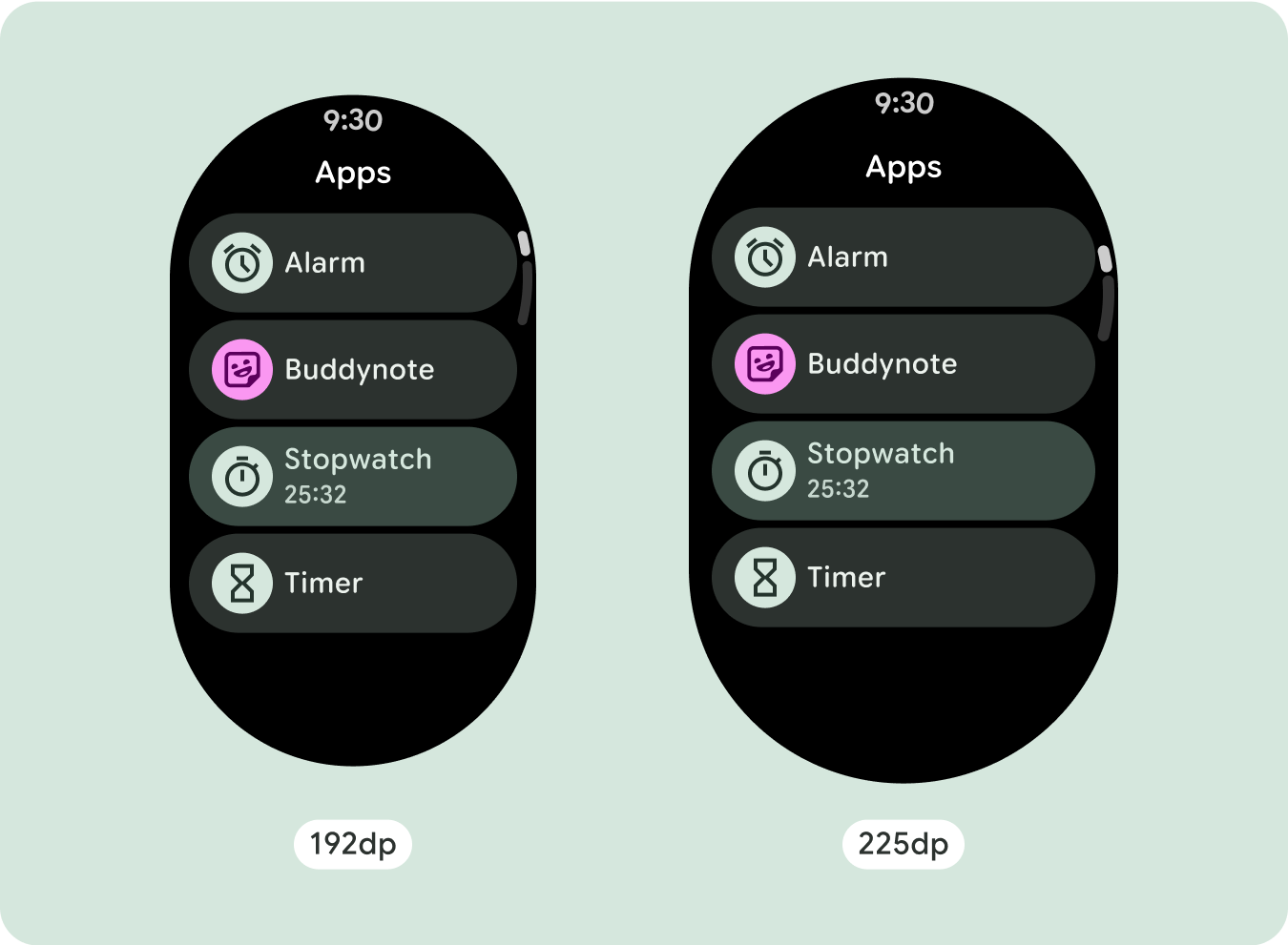
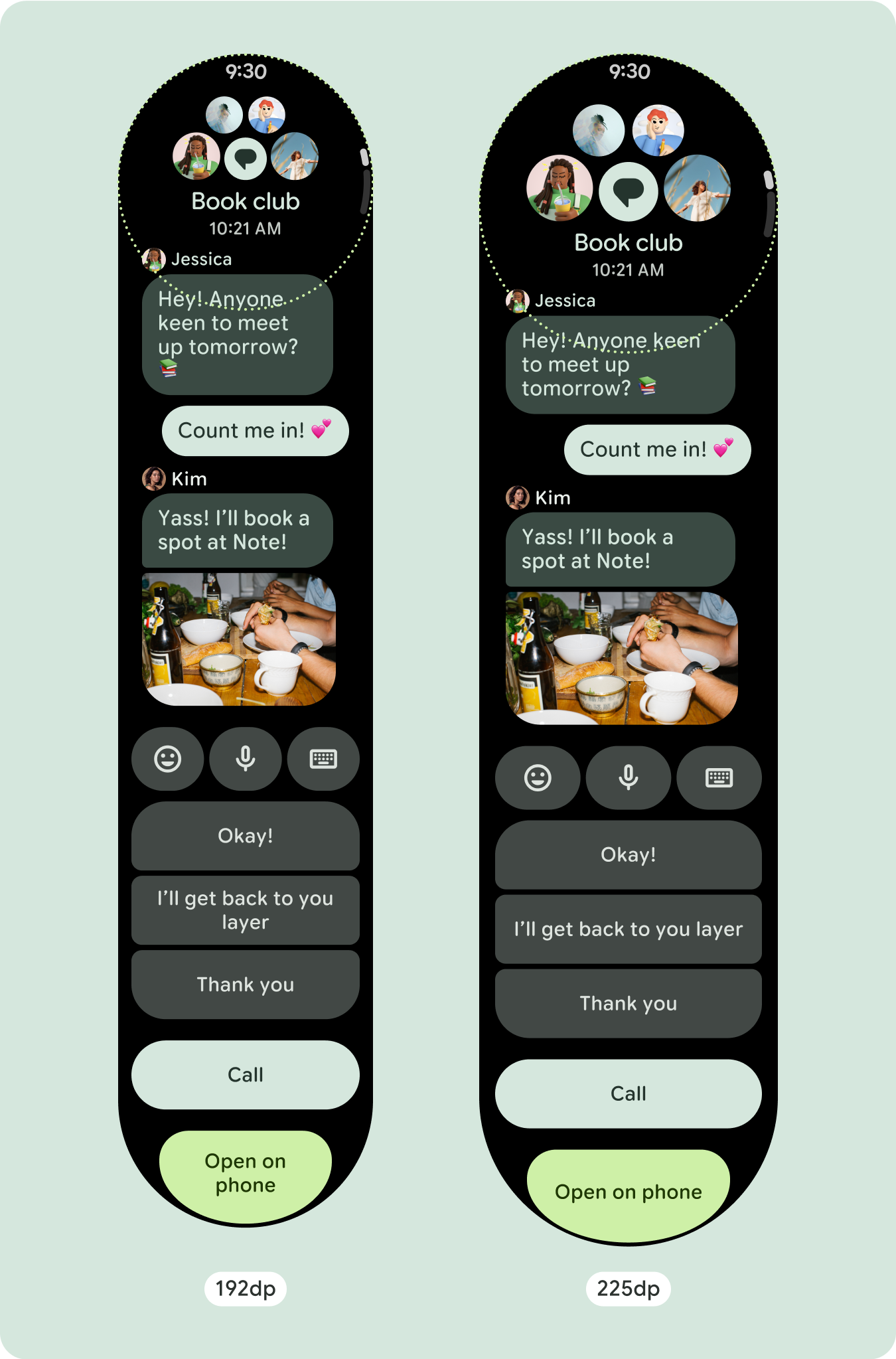
スクロール レイアウトでは、以前は画面の折りたたみ部分に隠れていたコンテンツが自動的に表示されるため、価値を高めるために必要な作業はほとんどありません。各コンポーネントは使用可能な幅を埋めます。場合によっては、コンポーネントにテキストの行が追加される(カードなど)場合や、コンポーネントが使用可能な幅いっぱいに伸びる(アイコンボタンなど)場合があります。
大画面サイズの追加スペースを最大限に活用するには、225 dp にサイズ ブレークポイントを追加します。このブレークポイントを使用すると、追加のコンテンツを表示したり、ボタンやデータを追加したり、大きな画面に合わせてレイアウトを変更したりできます。これには、ブレークポイントごとに異なる設計が必要です。大きな画面のデザイン(225 インチ以上)には、次の要素を追加できます。
既存のコンポーネントのサイズを増やす、または状態を変更する
これは、より詳細な情報を表示したり、コンテンツを簡単に確認できるようにしたりするために行われます。

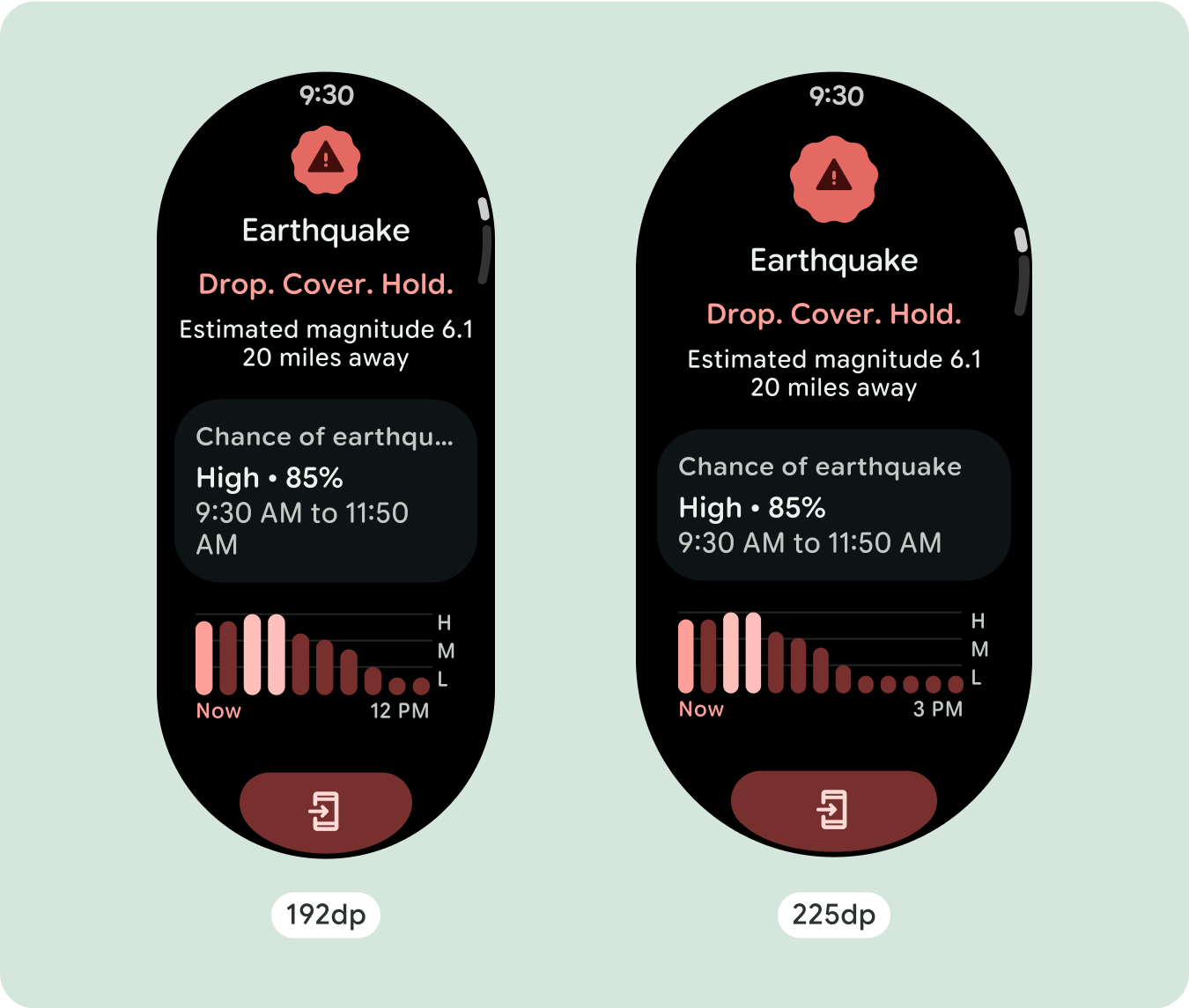
最適化された差別化されたレイアウト
225dp のブレークポイントを超えるとレイアウトが若干変更され、デフォルト ビューの折り返しの上のコンテンツが最適化されますが、折り返しの下の同じコンテンツは、画面サイズに関係なく引き続き利用できます。
レスポンシブな動作と適応性の高い動作
Compose ライブラリ内のすべてのコンポーネントは、幅と高さを広げて、より広い画面サイズに自動的に適応します。レスポンシブ デザインの手法を使用するスクロールビューは、通常、さまざまな画面サイズに適応します。ただし、特別なケースでは、ブレークポイントを使用してディメンションをオーバーライドし、レイアウトを拡張して機能を拡張したり、一目でわかるようにしたり、コンテンツを画面に適切に収めたりできます。
クリッピングを回避し、要素を比例してスケーリングするには、上、下、左右のすべての余白をパーセンテージで定義する必要があります。PositionIndicator はユーザーがスクロールしたときに表示され、画面のベゼルのサイズに関係なく自動的に画面のベゼルに沿って表示されます。
チェックリスト
- 上部、下部、両側に推奨される余白を適用します。
- 外側のマージンをパーセンテージ値で定義して、スクロール可能なコンテナの開始と終了でクリッピングが発生しないようにします。
- UI 要素間に固定の DP 値でマージンを適用します。
- 225dp でブレークポイントを適用して、追加のコンテンツを導入したり、大きな画面サイズで既存のコンテンツをより簡単に確認できるようにしたりすることを検討してください。
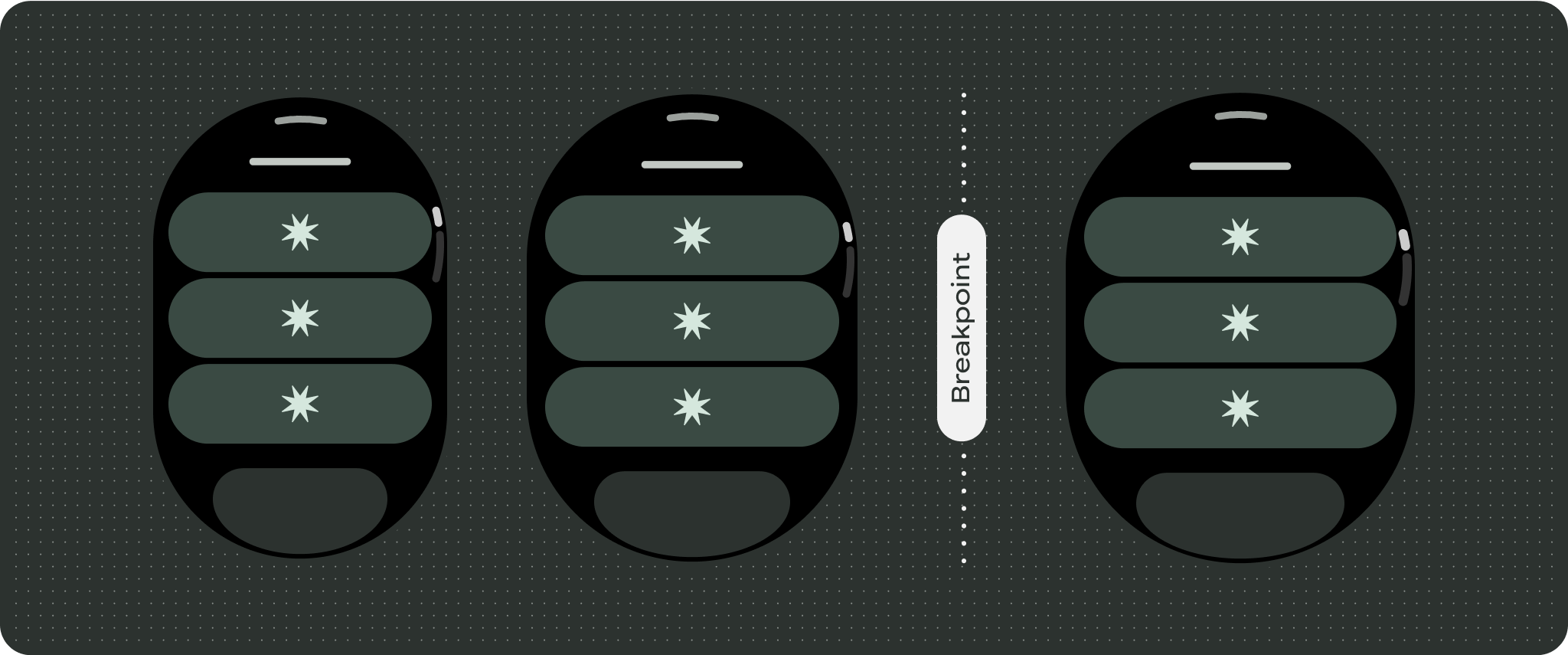
差別化されたエクスペリエンスを作成する
スクロール ビューは高度にカスタマイズ可能で、任意のコンポーネントを任意の順序で追加できます。上部と下部の余白は、上部と下部に配置するコンポーネントによって変更できます。これは、画面の湾曲が拡大してコンテンツが切り取られるのを防ぐためです。

