Android Studio is the official IDE for Android development, and includes everything you need to build Android apps.
This page lists new features and improvements in the latest version in the stable channel, Android Studio Panda 1. You can download it here or update to it inside Android Studio by clicking Help > Check for updates (Android Studio > Check for updates on macOS)
This is a stable release of Android Studio. Note that patches might contain new minor features and bug fixes. See Android Studio release names to understand Android Studio version naming.
To see what's been fixed in this version of Android Studio, see the closed issues.
To view the release notes for older versions of Android Studio, see Past releases.
For early access to upcoming features and improvements, see the Preview builds of Android Studio.
If you encounter problems in Android Studio, check the Known issues or Troubleshoot page.
Android Gradle plugin and Android Studio compatibility
The Android Studio build system is based on Gradle, and the Android Gradle plugin (AGP) adds several features that are specific to building Android apps. The following table lists which version of AGP is required for each version of Android Studio.
| Android Studio version | Required AGP version |
|---|---|
| Panda 1 | 2025.3.1 | 4.0-9.0 |
| Otter 3 Feature Drop | 2025.2.3 | 4.0-9.0 |
| Otter 2 Feature Drop | 2025.2.2 | 4.0-8.13 |
| Otter | 2025.2.1 | 4.0-8.13 |
| Narwhal 4 Feature Drop | 2025.1.4 | 4.0-8.13 |
| Narwhal 3 Feature Drop | 2025.1.3 | 4.0-8.13 |
| Narwhal Feature Drop | 2025.1.2 | 4.0-8.12 |
| Narwhal | 2025.1.1 | 3.2-8.11 |
| Meerkat Feature Drop | 2024.3.2 | 3.2-8.10 |
| Meerkat | 2024.3.1 | 3.2-8.9 |
Older versions
| Android Studio version | Required AGP version |
|---|---|
| Ladybug Feature Drop | 2024.2.2 | 3.2-8.8 |
| Ladybug | 2024.2.1 | 3.2-8.7 |
| Koala Feature Drop | 2024.1.2 | 3.2-8.6 |
| Koala | 2024.1.1 | 3.2-8.5 |
| Jellyfish | 2023.3.1 | 3.2-8.4 |
| Iguana | 2023.2.1 | 3.2-8.3 |
| Hedgehog | 2023.1.1 | 3.2-8.2 |
| Giraffe | 2022.3.1 | 3.2-8.1 |
| Flamingo | 2022.2.1 | 3.2-8.0 |
| Electric Eel | 2022.1.1 | 3.2-7.4 |
| Dolphin | 2021.3.1 | 3.2-7.3 |
| Chipmunk | 2021.2.1 | 3.2-7.2 |
| Bumblebee | 2021.1.1 | 3.2-7.1 |
| Arctic Fox | 2020.3.1 | 3.1-7.0 |
For information on what’s new in the Android Gradle plugin, see the Android Gradle plugin release notes.
Minimum versions of tools for Android API level
There are minimum versions of Android Studio and AGP that support a specific API
level. Using lower versions of Android Studio or AGP than required by your
project's targetSdk or compileSdk could lead to unexpected issues. We
recommend using the latest preview version of Android Studio and AGP to work on
projects that target preview versions of the Android OS. You can
install
preview versions of Android Studio alongside a stable version.
The minimum versions of Android Studio and AGP are as follows:
| API level | Minimum Android Studio version | Minimum AGP version |
|---|---|---|
| 36.1 | Narwhal 3 Feature Drop | 2025.1.3 | 8.13.0 |
| 36.0 | Meerkat | 2024.3.1 Patch 1 | 8.9.1 |
| 35 | Koala Feature Drop | 2024.2.1 | 8.6.0 |
| 34 | Hedgehog | 2023.1.1 | 8.1.1 |
| 33 | Flamingo | 2022.2.1 | 7.2 |
Android Studio and Cloud services compatibility
Android Studio includes service integrations that help you and your team make faster progress as you develop, release, and maintain Android apps. This includes Cloud services such as Gemini in Android Studio, Play Vitals, and Firebase Crashlytics. Cloud services are only available on the latest stable channel version of Android Studio and major versions (including their patches) released in the previous 10 months. When a version falls outside of that compatibility window, service integrations become disabled and you are required to update Android Studio.
Android Studio versions that are currently compatible with Cloud services
As of the stable channel release of Android Studio Meerkat Feature Drop, all versions of Studio are compatible with Cloud services. Enforcement will begin with Android Studio Narwhal Feature Drop.
Studio Labs
Studio Labs lets you try out the latest AI experimental features in a stable version of Android Studio, so you can more quickly integrate our AI assistance offerings in your development workflow. For more information, see Studio Labs.
The following are features currently available in Studio Labs.
| Feature | Description | Docs |
|---|---|---|
| Compose preview generation | Gemini can automatically generate Compose previews, including mock data for preview parameters, for a specific composable or all composables in a file. | Generate Compose previews |
| Transform UI | Use natural language to update your app UI directly from the Compose preview panel. | Transform UI |
| Journeys for Android Studio | Use natural language to describe steps and assertions for end-to-end tests. | Journeys for Android Studio |
The following are new features in Android Studio Panda 1.
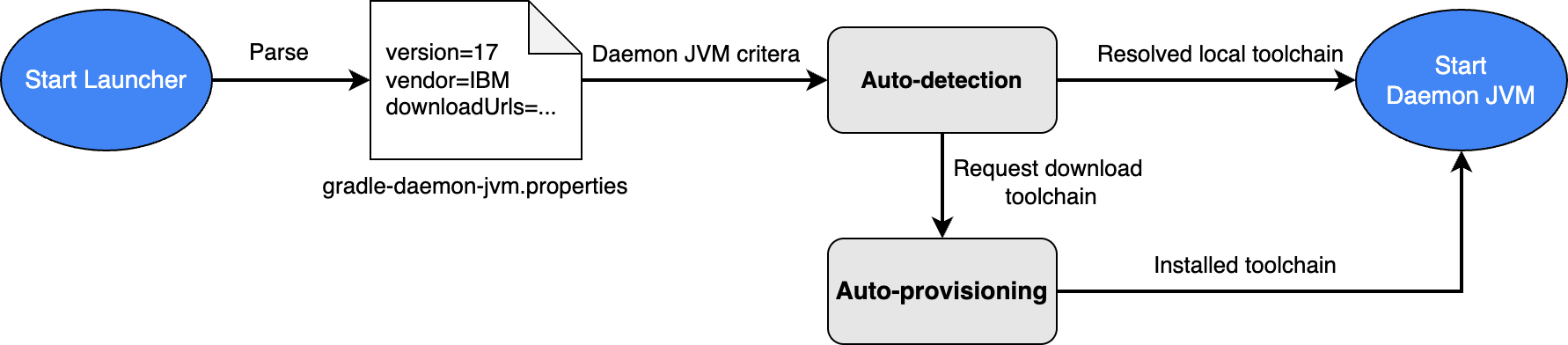
Simplified JDK management with Gradle Daemon JVM Criteria
To simplify JDK management for Gradle builds, Android Studio now uses Gradle Daemon JVM criteria by default for new projects. This feature lets Gradle auto-detect compatible JDK for your project installed in your machine to execute Gradle builds or auto-provision the required JDK by downloading it if it cannot be found locally. This feature was stabilized in Gradle 9.2.0.
This simplifies project setup and improves JDK management in several ways:
- Fewer setup errors: You no longer need to have a specific JDK installed to import and build a project, which reduces setup-related errors given invalid JDK selection.
- Consistent builds: JDK selection for Gradle builds is not only consistent across different machines but also between the IDE and command-line, which prevents spawning multiple Gradle Daemons that adversely affect performance.
For existing projects that use a compatible Gradle version, Android Studio shows a notification offering an option to automatically migrate your project's defined Gradle JDK configuration to Daemon JVM criteria, while maintaining the same specifications.