「UI 事件」是 UI 層中應由 UI 或 ViewModel 處理的動作。最常見的事件類型是「使用者事件」。使用者與應用程式互動時產生使用者事件 (例如:輕觸螢幕或產生手勢),然後 UI 會使用回呼 (例如:onClick() 事件監聽器) 使用這些事件。
ViewModel 通常負責處理特定使用者事件的商業邏輯,例如:使用者點選按鈕重新整理部分資料。一般來說,ViewModel 會公開 UI 可呼叫的函式來進行處理。使用者事件也可能有 UI 可直接處理的 UI 行為邏輯,例如:前往不同畫面或顯示 Snackbar。
雖然相同應用程式中的「商業邏輯」在不同行動平台或板型規格仍會保持不變,但「UI 行為邏輯」是可能區分這些情況的實作詳細資料。UI 層頁面定義了以下類型的邏輯:
- 「商業邏輯」是指狀態變更的「處理方式」,例如:付款或儲存使用者偏好設定。網域和資料層通常會處理這個邏輯。在本指南中,「架構元件 ViewModel」類別的使用情境為處理商業邏輯的類別相關解決方案。
- UI 行為邏輯或 UI 邏輯是指狀態變更的「顯示方式」,例如:導覽邏輯或向使用者顯示訊息的方式。UI 會處理這個邏輯。
UI 事件決策樹
以下圖表顯示尋找處理特定事件用途最佳方式時的決策樹。本指南的其餘部分會詳細說明這些方法。
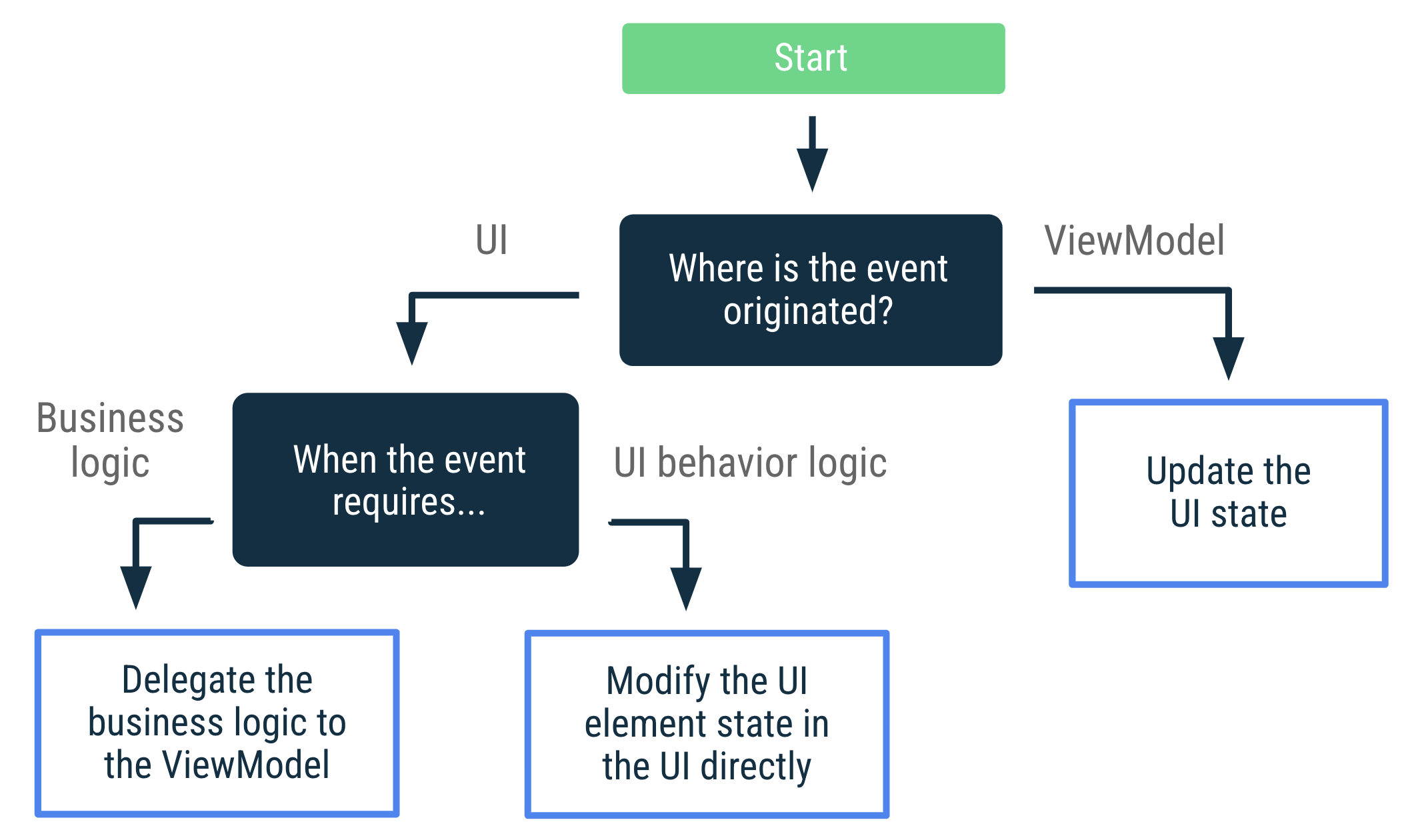
處理使用者事件
如果事件涉及修改 UI 元素的狀態 (例如:可展開項目的狀態),UI 即可直接處理使用者事件。如果事件需要執行商業邏輯,例如:重新整理畫面中的資料,則 ViewModel 應會處理此事件。
以下範例說明如何使用不同的按鈕展開 UI 元素 (UI 邏輯),並重新整理畫面資料 (商業邏輯):
View
class LatestNewsActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var binding: ActivityLatestNewsBinding
private val viewModel: LatestNewsViewModel by viewModels()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
/* ... */
// The expand details event is processed by the UI that
// modifies a View's internal state.
binding.expandButton.setOnClickListener {
binding.expandedSection.visibility = View.VISIBLE
}
// The refresh event is processed by the ViewModel that is in charge
// of the business logic.
binding.refreshButton.setOnClickListener {
viewModel.refreshNews()
}
}
}
Compose
@Composable
fun LatestNewsScreen(viewModel: LatestNewsViewModel = viewModel()) {
// State of whether more details should be shown
var expanded by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
Column {
Text("Some text")
if (expanded) {
Text("More details")
}
Button(
// The expand details event is processed by the UI that
// modifies this composable's internal state.
onClick = { expanded = !expanded }
) {
val expandText = if (expanded) "Collapse" else "Expand"
Text("$expandText details")
}
// The refresh event is processed by the ViewModel that is in charge
// of the UI's business logic.
Button(onClick = { viewModel.refreshNews() }) {
Text("Refresh data")
}
}
}
RecyclerViews 中的使用者事件
如果動作是在 UI 樹狀圖相對下方的位置產生 (例如:RecyclerView 項目或自訂 View 中),則 ViewModel 應仍會處理使用者事件。
舉例來說,假設來自 NewsActivity 的所有新聞項目都含有書籤按鈕。ViewModel 必須知道加入書籤的新聞項目 ID。當使用者將新聞項目加入書籤時,RecyclerView 轉接程式不會從 ViewModel 呼叫公開的 addBookmark(newsId) 函式,因為這需要 ViewModel 中的依附元件。ViewModel 會改為公開狀態物件呼叫的 NewsItemUiState,這包含處理事件的實作:
data class NewsItemUiState(
val title: String,
val body: String,
val bookmarked: Boolean = false,
val publicationDate: String,
val onBookmark: () -> Unit
)
class LatestNewsViewModel(
private val formatDateUseCase: FormatDateUseCase,
private val repository: NewsRepository
)
val newsListUiItems = repository.latestNews.map { news ->
NewsItemUiState(
title = news.title,
body = news.body,
bookmarked = news.bookmarked,
publicationDate = formatDateUseCase(news.publicationDate),
// Business logic is passed as a lambda function that the
// UI calls on click events.
onBookmark = {
repository.addBookmark(news.id)
}
)
}
}
這樣一來,RecyclerView 轉換程式就僅會處理需要 NewsItemUiState 物件清單的資料。轉接程式無法存取整個 ViewModel,因此比較不會濫用 ViewModel 公開的功能。如果您只允許使用 ViewModel 的活動類別,就是分隔所需處理的內容。這可確保 UI 專屬的物件 (例如:檢視區塊或 RecyclerView 轉接程式) 不會與 ViewModel 直接互動。
使用者事件函式的命名慣例
在本指南中,用於處理使用者事件的 ViewModel 函式會根據其處理的動作來命名,例如:addBookmark(id) 或 logIn(username, password)。
處理 ViewModel 事件
源自 ViewModel (ViewModel 事件) 的 UI 動作應一律導致 UI 狀態更新。這符合雙向資料流的原則。這項設定會使事件在設定變更後得以重現,並確保 UI 動作不會遺失。或者,如果您使用已儲存的狀態模組,也能在程序終止後重現事件。
對應 UI 動作至 UI 狀態並非簡單的程序,但會讓邏輯變得更簡單。舉例來說,您要決定的不是只有決定如何使 UI 導覽至特定畫面。您還必須進一步思考,決定如何在自己的 UI 狀態中呈現該使用者流程。換句話說,不要思考 UI 必須採取的動作,而是這些動作要如何影響 UI 狀態。
舉例來說,試想使用者於登入畫面中登入時前往主畫面的情況。您可利用下方的 UI 狀態建構此動作:
data class LoginUiState(
val isLoading: Boolean = false,
val errorMessage: String? = null,
val isUserLoggedIn: Boolean = false
)
此 UI 回應 isUserLoggedIn 狀態的變更,然後視需要前往正確的目的地:
View
class LoginViewModel : ViewModel() {
private val _uiState = MutableStateFlow(LoginUiState())
val uiState: StateFlow<LoginUiState> = _uiState.asStateFlow()
/* ... */
}
class LoginActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val viewModel: LoginViewModel by viewModels()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
/* ... */
lifecycleScope.launch {
repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
viewModel.uiState.collect { uiState ->
if (uiState.isUserLoggedIn) {
// Navigate to the Home screen.
}
...
}
}
}
}
}
Compose
class LoginViewModel : ViewModel() {
var uiState by mutableStateOf(LoginUiState())
private set
/* ... */
}
@Composable
fun LoginScreen(
viewModel: LoginViewModel = viewModel(),
onUserLogIn: () -> Unit
) {
val currentOnUserLogIn by rememberUpdatedState(onUserLogIn)
// Whenever the uiState changes, check if the user is logged in.
LaunchedEffect(viewModel.uiState) {
if (viewModel.uiState.isUserLoggedIn) {
currentOnUserLogIn()
}
}
// Rest of the UI for the login screen.
}
消耗事件會觸發狀態更新
在 UI 中消耗特定 ViewModel 事件,可能會導致其他 UI 狀態更新。舉例來說,當畫面上顯示暫時性訊息以告知使用者發生的情況時,UI 必須通知 ViewModel 於畫面顯示訊息時立即觸發另一個狀態更新。使用者消耗訊息 (關閉訊息或逾時後) 後發生的事件可以當做「使用者輸入內容」,因此 ViewModel 應該能夠得知此情況。在這種情況下,UI 狀態可透過下列方式建構:
// Models the UI state for the Latest news screen.
data class LatestNewsUiState(
val news: List<News> = emptyList(),
val isLoading: Boolean = false,
val userMessage: String? = null
)
當商業邏輯需要向使用者顯示新的暫時性訊息時,ViewModel 會以下列方式更新 UI 狀態:
View
class LatestNewsViewModel(/* ... */) : ViewModel() {
private val _uiState = MutableStateFlow(LatestNewsUiState(isLoading = true))
val uiState: StateFlow<LatestNewsUiState> = _uiState
fun refreshNews() {
viewModelScope.launch {
// If there isn't internet connection, show a new message on the screen.
if (!internetConnection()) {
_uiState.update { currentUiState ->
currentUiState.copy(userMessage = "No Internet connection")
}
return@launch
}
// Do something else.
}
}
fun userMessageShown() {
_uiState.update { currentUiState ->
currentUiState.copy(userMessage = null)
}
}
}
Compose
class LatestNewsViewModel(/* ... */) : ViewModel() {
var uiState by mutableStateOf(LatestNewsUiState())
private set
fun refreshNews() {
viewModelScope.launch {
// If there isn't internet connection, show a new message on the screen.
if (!internetConnection()) {
uiState = uiState.copy(userMessage = "No Internet connection")
return@launch
}
// Do something else.
}
}
fun userMessageShown() {
uiState = uiState.copy(userMessage = null)
}
}
ViewModel 無需瞭解 UI 如何在畫面上顯示訊息,而是只知道是否有需要顯示的使用者訊息。顯示暫時訊息後,UI 就必須通知 ViewModel,進而更新其他 UI 狀態,以便清除 userMessage 屬性:
View
class LatestNewsActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val viewModel: LatestNewsViewModel by viewModels()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
/* ... */
lifecycleScope.launch {
repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
viewModel.uiState.collect { uiState ->
uiState.userMessage?.let {
// TODO: Show Snackbar with userMessage.
// Once the message is displayed and
// dismissed, notify the ViewModel.
viewModel.userMessageShown()
}
...
}
}
}
}
}
Compose
@Composable
fun LatestNewsScreen(
snackbarHostState: SnackbarHostState,
viewModel: LatestNewsViewModel = viewModel(),
) {
// Rest of the UI content.
// If there are user messages to show on the screen,
// show it and notify the ViewModel.
viewModel.uiState.userMessage?.let { userMessage ->
LaunchedEffect(userMessage) {
snackbarHostState.showSnackbar(userMessage)
// Once the message is displayed and dismissed, notify the ViewModel.
viewModel.userMessageShown()
}
}
}
雖然訊息是暫時性的,但 UI 狀態能夠忠實反映每個時間點畫面上顯示的內容。使用者訊息只會有「顯示」和「不顯示」兩種狀況。
導覽事件
「消耗事件會觸發狀態更新」一節詳細說明了使用 UI 狀態在畫面上顯示使用者訊息的方式,導覽事件也是 Android 應用程式中常見的事件類型。
如果因使用者輕觸按鈕而在 UI 中觸發事件,UI 的回應方式是呼叫導覽控制器,或視情況向呼叫端可組合項公開事件。
View
class LoginActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var binding: ActivityLoginBinding
private val viewModel: LoginViewModel by viewModels()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
/* ... */
binding.helpButton.setOnClickListener {
navController.navigate(...) // Open help screen
}
}
}
Compose
@Composable
fun LoginScreen(
onHelp: () -> Unit, // Caller navigates to the right screen
viewModel: LoginViewModel = viewModel()
) {
// Rest of the UI
Button(onClick = onHelp) {
Text("Get help")
}
}
如果資料輸入在導覽前需要特定商業邏輯驗證,ViewModel 必須向 UI 公開該狀態。UI 也會回應狀態變更,並視情況進行導覽。處理 ViewModel 事件一節會說明這個用途。程式碼如下所示:
View
class LoginActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val viewModel: LoginViewModel by viewModels()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
/* ... */
lifecycleScope.launch {
repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
viewModel.uiState.collect { uiState ->
if (uiState.isUserLoggedIn) {
// Navigate to the Home screen.
}
...
}
}
}
}
}
Compose
@Composable
fun LoginScreen(
onUserLogIn: () -> Unit, // Caller navigates to the right screen
viewModel: LoginViewModel = viewModel()
) {
Button(
onClick = {
// ViewModel validation is triggered
viewModel.login()
}
) {
Text("Log in")
}
// Rest of the UI
val lifecycle = LocalLifecycleOwner.current.lifecycle
val currentOnUserLogIn by rememberUpdatedState(onUserLogIn)
LaunchedEffect(viewModel, lifecycle) {
// Whenever the uiState changes, check if the user is logged in and
// call the `onUserLogin` event when `lifecycle` is at least STARTED
snapshotFlow { viewModel.uiState }
.filter { it.isUserLoggedIn }
.flowWithLifecycle(lifecycle)
.collect {
currentOnUserLogIn()
}
}
}
在上述範例中,由於目前的「登入」到達網頁不會保持在返回堆疊中,因此應用程式可正常運作。使用者按下「返回」後無法返回。不過,若可能發生這種情況,解決方案需要額外的邏輯。
到達網頁保持在返回堆疊時的導覽事件
若 ViewModel 設定某種狀態,而產生畫面 A 到畫面 B 的導覽事件,但畫面 A 保持在導覽返回堆疊中,您可能需要其他邏輯,以免自動進入畫面 B。如要實作這項設定,必須具備額外狀態,指示 UI 是否應考慮前往其他畫面。狀態通常會顯示在 UI 中,因為導覽邏輯與 UI 有關,而不是 ViewModel。我們透過以下用途來說明。
假設您正在應用程式的註冊流程中,在「出生日期」驗證畫面中,若使用者輕觸一個日期,ViewModel 會在使用者輕觸「繼續」按鈕時驗證日期。ViewModel 會將驗證邏輯委派給資料層。如果日期有效,使用者會進入下一個畫面。此外,使用者還可以在不同的註冊畫面之間來回切換,以免需要變更某些資料。因此,註冊流程中的所有到達網頁會保留在相同的返回堆疊中。根據這些需求,您可以依照下列方式實作這個畫面:
View
// Key that identifies the `validationInProgress` state in the Bundle
private const val DOB_VALIDATION_KEY = "dobValidationKey"
class DobValidationFragment : Fragment() {
private var validationInProgress: Boolean = false
private val viewModel: DobValidationViewModel by viewModels()
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState)
val binding = // ...
validationInProgress = savedInstanceState?.getBoolean(DOB_VALIDATION_KEY) ?: false
binding.continueButton.setOnClickListener {
viewModel.validateDob()
validationInProgress = true
}
viewLifecycleOwner.lifecycleScope.launch {
viewModel.uiState
.flowWithLifecycle(viewLifecycleOwner.lifecycle)
.collect { uiState ->
// Update other parts of the UI ...
// If the input is valid and the user wants
// to navigate, navigate to the next screen
// and reset `validationInProgress` flag
if (uiState.isDobValid && validationInProgress) {
validationInProgress = false
navController.navigate(...) // Navigate to next screen
}
}
}
return binding
}
override fun onSaveInstanceState(outState: Bundle) {
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState)
outState.putBoolean(DOB_VALIDATION_KEY, validationInProgress)
}
}
Compose
class DobValidationViewModel(/* ... */) : ViewModel() {
var uiState by mutableStateOf(DobValidationUiState())
private set
}
@Composable
fun DobValidationScreen(
onNavigateToNextScreen: () -> Unit, // Caller navigates to the right screen
viewModel: DobValidationViewModel = viewModel()
) {
// TextField that updates the ViewModel when a date of birth is selected
var validationInProgress by rememberSaveable { mutableStateOf(false) }
Button(
onClick = {
viewModel.validateInput()
validationInProgress = true
}
) {
Text("Continue")
}
// Rest of the UI
/*
* The following code implements the requirement of advancing automatically
* to the next screen when a valid date of birth has been introduced
* and the user wanted to continue with the registration process.
*/
if (validationInProgress) {
val lifecycle = LocalLifecycleOwner.current.lifecycle
val currentNavigateToNextScreen by rememberUpdatedState(onNavigateToNextScreen)
LaunchedEffect(viewModel, lifecycle) {
// If the date of birth is valid and the validation is in progress,
// navigate to the next screen when `lifecycle` is at least STARTED,
// which is the default Lifecycle.State for the `flowWithLifecycle` operator.
snapshotFlow { viewModel.uiState }
.filter { it.isDobValid }
.flowWithLifecycle(lifecycle)
.collect {
validationInProgress = false
currentNavigateToNextScreen()
}
}
}
}
出生日期驗證的日期是 ViewModel 負責的商業邏輯。在多數情況下,ViewModel 會將該邏輯委派給資料層。將使用者導覽至下一個畫面的邏輯為「UI 邏輯」,因為這些要求可能會依據 UI 設定而有所不同。舉例來說,若要同時顯示多個註冊步驟,您可能不會希望使用者在平板電腦上自動前往另一個畫面。上述程式碼中的 validationInProgress 變數會實作這項功能,並處理 UI 是否應在出生日期有效,且使用者也想繼續註冊流程時,自動前往下一個畫面。
其他使用情況
如果您認為 UI 事件用途無法透過 UI 狀態更新解決,您可能需要重新思考應用程式中資料流動的方式。請思考以下原則:
- 每個類別只需完成各自必須負責的工作。 UI 負責的是畫面特定的行為邏輯,例如:導覽呼叫、點擊事件和取得權限要求。ViewModel 提供商業邏輯,並將層級中較低層級的結果轉換為 UI 狀態。
- 您要思考的是事件來源。 依照本指南開頭提供的決策樹,然後使各類別處理各自負責的工作。舉例來說,如果事件源自 UI,且會產生導覽事件,則該事件必須在 UI 中進行處理。某些邏輯可能會委派給 ViewModel,但處理事件無法完全委派給 ViewModel。
- 如果您有多個取用者,且擔心該事件會多次消耗,您可能需要重新思考應用程式架構。有多個並行取用者會導致合約的「一次性提交」變得極難保證,因此複雜性和輕微行為的數量會急遽增加。如果遇到此問題,請考慮在 UI 樹狀結構中將這些問題的層級往上提升。您可能需要在階層的較高層級定義不同實體的範圍。
- 思考需要消耗狀態的時機。 在某些情況下,您可能不希望應用程式在背景執行時保持使用狀態,例如:顯示
Toast時。在這種情況下,請考慮當 UI 在前景中時消耗狀態。
範例
以下 Google 範例為 UI 層中的 UI 事件。歡迎查看這些範例,瞭解實務做法:
為您推薦
- 注意:系統會在 JavaScript 關閉時顯示連結文字
- UI 層
- 狀態容器和 UI 狀態 {:#mad-arch}
- 應用程式架構指南
