The Google Maps app for Android exposes several intents that you can use to launch Google Maps in display, search, navigation, or Street View modes. To embed a map in your app, refer to the Maps SDK for Android Quickstart.
For Android Automotive OS (AAOS) platforms, there are specific considerations and additional intents available. See the Google Maps for Android Automotive Intents documentation for more details.
Overview
Intents let you start an activity in another app by describing an action
you would like to perform (such as "display a map" or "show directions to the
airport") in an Intent object. The Google Maps app for Android
supports several different intents,allowing you to launch the Google Maps app
and perform one of four actions:
- Display a map at a specified location and zoom level.
- Search for locations or places, and display them on a map.
- Request directions from one location to another. Directions can be returned for three modes of transportation: driving, walking, bicycling.
- Display panorama imagery in Google Street View.
This page describes the intents that you can use with Google Maps app for Android. For more information about intents, see Intents and intent filters and Common intents.
Intent requests
To launch Google Maps with an intent, you must first create an Intent
object, specifying its action, URI, and package.
- Action: All Google Maps intents are called as a View action —
ACTION_VIEW. - URI: Google Maps intents use URL-encoded URIs that specify a selected action, along with some data with which to perform the action.
Package: Calling
setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")ensures that the Google Maps app for Android handles the Intent. If the package isn't set, the system determines which apps can handle theIntent. If multiple apps are available, the user might be asked which app they would like to use.
After creating the Intent, you can request that the system launch the related
app in a number of ways. A common method is to pass the Intent to the
startActivity() method. The system launches the necessary app —
in this case Google Maps — and start the corresponding Activity.
Java
// Create a Uri from an intent string. Use the result to create an Intent.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.streetview:cbll=46.414382,10.013988");
// Create an Intent from gmmIntentUri. Set the action to ACTION_VIEW
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
// Make the Intent explicit by setting the Google Maps package
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
// Attempt to start an activity that can handle the Intent
startActivity(mapIntent);
Kotlin
// Create a Uri from an intent string. Use the result to create an Intent.
val gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.streetview:cbll=46.414382,10.013988")
// Create an Intent from gmmIntentUri. Set the action to ACTION_VIEW
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
// Make the Intent explicit by setting the Google Maps package
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
// Attempt to start an activity that can handle the Intent
startActivity(mapIntent)
If the system can't identify an app that can respond to the intent, your app might crash. For this reason, first verify that a receiving application is installed before you present one of these intents to a user.
To verify that an app is available to receive the intent, call
resolveActivity() on your Intent object. If the result is
non-null, there is at least one app that can handle the intent and it's safe to
call startActivity(). If the result is null, don't use the intent and,
if possible, disable the feature that invokes the intent.
Java
if (mapIntent.resolveActivity(getPackageManager()) != null) {
...
}
Kotlin
mapIntent.resolveActivity(packageManager)?.let {
...
}
For example, to display a map of San Francisco, you can use the following code:
Java
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
if (mapIntent.resolveActivity(getPackageManager()) != null) {
startActivity(mapIntent);
}
Kotlin
val gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
mapIntent.resolveActivity(packageManager)?.let {
startActivity(mapIntent)
}
URL encoded query strings
All strings passed to the Google Maps Intents must be URI encoded. For example,
the string 1st & Pike, Seattle should become 1st%20%26%20Pike%2C%20Seattle.
Spaces in the string can be encoded with %20 or replaced with the plus sign
(+).
You can use the android.net.Uri encode() method to encode your strings.
For example:
Java
Uri gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4192?q=" + Uri.encode("1st & Pike, Seattle"));
Kotlin
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4192?q=" + Uri.encode("1st & Pike, Seattle"))
Display a map
Use the geo: intent to display a map at a specified location and zoom level.
geo:latitude,longitude?z=zoom
Parameters
latitudeandlongitudeset the center point of the map.zoptionally sets the initial zoom level of the map. Accepted values range from 0 (the whole world) to 21 (individual buildings). The upper limit can vary depending on the map data available at the selected location.
Examples
Java
// Creates an Intent that loads a map of San Francisco
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Kotlin
// Creates an Intent that loads a map of San Francisco
val gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
Search for a location
Use this intent to display search queries within a specified viewport. When the query has a single result, you can use this intent to display a pin at a particular place or address, such as a landmark, business, geographic feature, or town.
geo:latitude,longitude?q=query
geo:0,0?q=my+street+address
geo:0,0?q=latitude,longitude(label)
Parameters
In addition to the parameters used to display a map, Search supports the following parameters:
qdefines the place(s) to highlight on the map. Theqparameter is required for all Search requests. It accepts a location as either a place name or address. The string should be URL-encoded, so an address such asCity Hall, New York, NYshould be converted toCity+Hall,New+York,NY.labellets you set a custom label at a place identified on the map. Thelabelmust be specified as a String.
Categorical search
If you pass a general search term, Google Maps attempts to find a location near the latitude and longitude you specified that matches your criteria. If no location is specified, Google Maps tries to find nearby listings. For example:
Java
// Search for restaurants nearby
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:0,0?q=restaurants");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
// Search for restaurants in San Francisco.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194?q=restaurants");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Kotlin
// Search for restaurants nearby.
val gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:0,0?q=restaurants")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
// Search for restaurants in San Francisco.
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194?q=restaurants")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
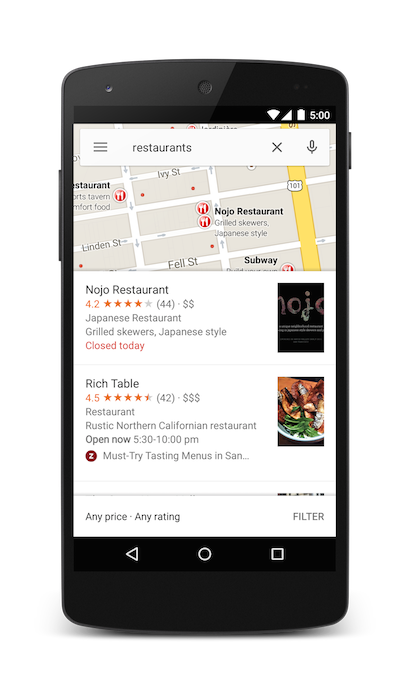
You can further bias the search results by specifying a zoom parameter along with the query string. In the following example, adding a zoom of 10 attempts to find restaurants at a city level instead of nearby.
Java
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194?z=10&q=restaurants");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Kotlin
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194?z=10&q=restaurants")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
Location search
Searching for a specific address displays a pin at that location.
Java
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:0,0?q=1600 Amphitheatre Parkway, Mountain+View, California");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Kotlin
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("geo:0,0?q=1600 Amphitheatre Parkway, Mountain+View, California")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
The preceding example sets a latitude and longitude of 0,0 but passes an
address as a query string. When searching for a specific location, the latitude
and longitude aren't required. However, if you don't know the exact address, you
can attempt to bias the results of the search by specifying a coordinate. For
example, performing an address search for 'Main Street' might return too many
results.
Java
// Searching for 'Main Street' returns too many results.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:0,0?q=101+main+street");
Kotlin
// Searching for 'Main Street' returns too many results.
val gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:0,0?q=101+main+street")
Adding a latitude and longitude to the intent URI biases the results towards a particular area:
Java
// Searches for 'Main Street' near San Francisco.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194?q=101+main+street");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Kotlin
// Searches for 'Main Street' near San Francisco.
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("geo:37.7749,-122.4194?q=101+main+street")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
When you know your search returns a single value, you might want to pass an
optional label. Labels must be specified as a String and appear under the
map marker. Note that labels are only available when q is specified as a
latitude and longitude coordinate.
Java
// Display a label at the location of Google's Sydney office.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("geo:0,0?q=-33.8666,151.1957(Google+Sydney)");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Kotlin
// Display a label at the location of Google's Sydney office.
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("geo:0,0?q=-33.8666,151.1957(Google+Sydney)")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
As an alternative to a street address or a latitude and longitude, you can display a pin at a known location using a plus code.
Java
// Display the location of Google, San Francisco using a global plus code.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("http://plus.codes/849VQJQ5+XX");
// Equivalently, define the same location using a local plus code.
gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("https://plus.codes/QJQ5+XX,San%20Francisco");
// Construct and use the Intent as in the preceding examples.
Kotlin
// Display the location of Google, San Francisco using a global plus code.
var gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("http://plus.codes/849VQJQ5+XX")
// Equivalently, define the same location using a local plus code.
gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("https://plus.codes/QJQ5+XX,San%20Francisco")
// Construct and use the Intent as in the preceding examples.
Launch turn-by-turn navigation
Use this intent URI to launch Google Maps navigation with turn-by-turn directions to the address or coordinate specified. Directions are always given from the user's current location.
google.navigation:q=a+street+address
google.navigation:q=latitude,longitude
Parameters
q: Sets the endpoint for navigation searches. This value can be latitude and longitude coordinates or a query-formatted address. If it's a query string that returns more than one result, the first result is selected.modesets the method of transportation.modeis optional and can be set to one of the following:dfor driving (default)bfor bicyclinglfor two-wheelerwfor walking
avoidsets features the route should try to avoid.avoidis optional and can be set to one or more of the following:tfor tollshfor highwaysffor ferries
Examples
The following Intent requests turn-by-turn navigation to Taronga Zoo, in
Sydney Australia:
Java
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.navigation:q=Taronga+Zoo,+Sydney+Australia");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Kotlin
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("google.navigation:q=Taronga+Zoo,+Sydney+Australia")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
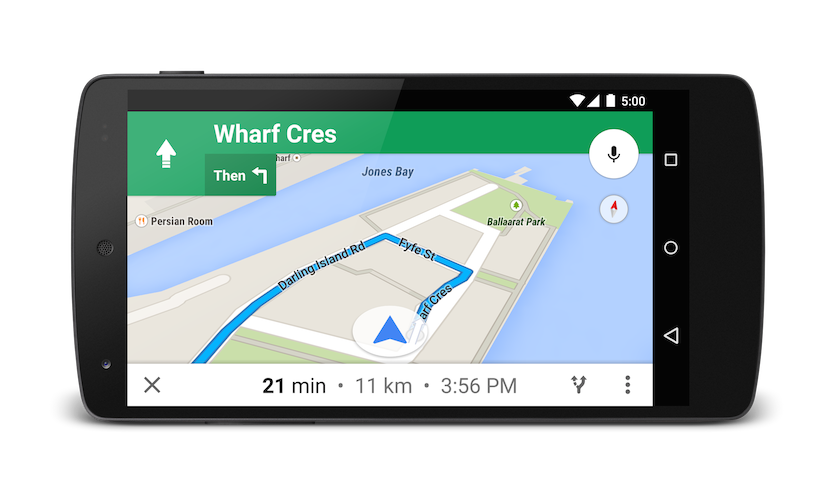
If you prefer not to pay tolls or ride a ferry, you can request routing that tries to avoid those features.
Java
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.navigation:q=Taronga+Zoo,+Sydney+Australia&avoid=tf");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Kotlin
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("google.navigation:q=Taronga+Zoo,+Sydney+Australia&avoid=tf")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
If you prefer a bit of exercise, you can request bicycling directions instead.
Java
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.navigation:q=Taronga+Zoo,+Sydney+Australia&mode=b");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Kotlin
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("google.navigation:q=Taronga+Zoo,+Sydney+Australia&mode=b")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
If you prefer to take a motorized two-wheeler, you can request that the
directions include narrow roads and trails unavailable to cars. The following
intent returns a route in India.
Java
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.navigation:q=Connaught+Place,+New+Delhi,Delhi&mode=l");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Kotlin
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("google.navigation:q=Connaught+Place,+New+Delhi,Delhi&mode=l")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
Display a Street View panorama
Use the google.streetview intent to launch Google Street View. Google Street
View provides panoramic views from designated locations throughout its coverage
area. User contributed Photospheres, and Street View special
collections are also available.
google.streetview:cbll=latitude,longitude&cbp=0,bearing,0,zoom,tilt
google.streetview:panoid=id&cbp=0,bearing,0,zoom,tilt
Parameters
All google.streetview URIs must include either a cbll or a panoid
parameter:
cbllaccepts a latitude and a longitude as comma-separated values (46.414382,10.013988). The app shows the panorama photographed closest to this location. Because Street View imagery is periodically refreshed, and photographs might be taken from slightly different positions each time, it's possible that your location might snap to a different panorama when imagery is updated.panoidis a specific panorama ID. Google Maps uses the panorama ID if both apanoidand acbllare specified. Panorama IDs are available to an Android app from theStreetViewPanoramaLocationobject.cbpis an optional parameter that adjusts the initial orientation of the camera. Thecbpparameter takes 5 comma-separated values, all of which are optional. The most significant values are the second, fourth, and fifth which set the bearing, zoom, and tilt respectively. The first and third values aren't supported, and should be set to0.bearing: indicates the compass heading of the camera in degrees clockwise from North. True north is 0, east is 90, south is 180, west is- Values passed to bearing wraps; that is, 0°, 360° and 720° all point in the same direction. Bearing is defined as the second of five comma-separated values.
zoom: Sets the zoom level of the camera. The default zoom level is set at 0. A zoom of 1 would double the magnification. The zoom is clamped between 0 and the maximum zoom level for the current panorama. This means that any value falling outside this range is set to the closest extreme that falls within the range. For example, a value of -1 is set to 0. Zoom is the fourth of five comma-separated values.tilt: specifies the angle, up or down, of the camera. The range is -90 through 0 to 90, with 90 looking straight down, 0 centered on the horizon, and -90 looking straight up.
Examples
The following are some examples of using the Street View intent.
Java
// Displays an image of the Swiss Alps.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.streetview:cbll=46.414382,10.013988");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
// Uses a PanoID to show an image from Maroubra beach in Sydney, Australia.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.streetview:panoid=Iaa2JyfIggYAAAQfCZU9KQ");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
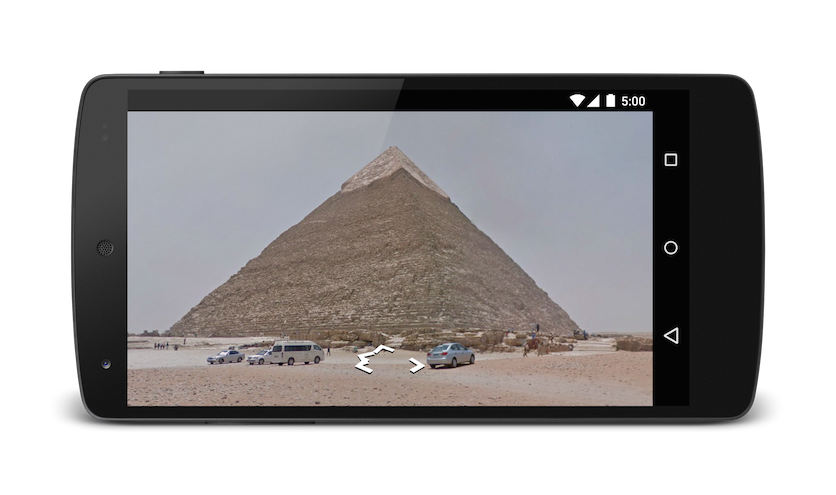
// Opens Street View between two Pyramids in Giza. The values passed to the
// cbp parameter angles the camera slightly up, and towards the east.
Uri gmmIntentUri = Uri.parse("google.streetview:cbll=29.9774614,31.1329645&cbp=0,30,0,0,-15");
Intent mapIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri);
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps");
startActivity(mapIntent);
Kotlin
// Displays an image of the Swiss Alps.
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("google.streetview:cbll=46.414382,10.013988")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
// Uses a PanoID to show an image from Maroubra beach in Sydney, Australia.
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("google.streetview:panoid=Iaa2JyfIggYAAAQfCZU9KQ")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)
// Opens Street View between two Pyramids in Giza. The values passed to the
// cbp parameter angles the camera slightly up, and towards the east.
val gmmIntentUri =
Uri.parse("google.streetview:cbll=29.9774614,31.1329645&cbp=0,30,0,0,-15")
val mapIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, gmmIntentUri)
mapIntent.setPackage("com.google.android.apps.maps")
startActivity(mapIntent)