Paging 2 library overview Part of Android Jetpack.
The Paging Library helps you load and display small chunks of data at a time. Loading partial data on demand reduces usage of network bandwidth and system resources.
This guide provides several conceptual examples of the library, along with an overview of how it works. To view complete examples of how this library functions, try out the codelab and samples from the additional resources section.
Setup
To import Paging components into your Android app, add the following
dependencies to your app's build.gradle file:
Groovy
dependencies { def paging_version = "2.1.2" implementation "androidx.paging:paging-runtime:$paging_version" // For Kotlin use paging-runtime-ktx // alternatively - without Android dependencies for testing testImplementation "androidx.paging:paging-common:$paging_version" // For Kotlin use paging-common-ktx // optional - RxJava support implementation "androidx.paging:paging-rxjava2:$paging_version" // For Kotlin use paging-rxjava2-ktx }
Kotlin
dependencies { val paging_version = "2.1.2" implementation("androidx.paging:paging-runtime:$paging_version") // For Kotlin use paging-runtime-ktx // alternatively - without Android dependencies for testing testImplementation("androidx.paging:paging-common:$paging_version") // For Kotlin use paging-common-ktx // optional - RxJava support implementation("androidx.paging:paging-rxjava2:$paging_version") // For Kotlin use paging-rxjava2-ktx }
Library architecture
This section describes and shows the main components of the paging library.
PagedList
The Paging Library's key component is the
PagedList class, which loads
chunks of your app's data, or pages. As more data is needed, it's
paged into the existing PagedList object. If any loaded data changes, a new
instance of PagedList is emitted to the observable data holder from a
LiveData or RxJava2-based object. As
PagedList objects are generated,
your app's UI presents their contents, all while respecting your UI controllers'
lifecycles.
The following code snippet shows how you can configure your app's view model to
load and present data using a LiveData holder of PagedList objects:
Kotlin
class ConcertViewModel(concertDao: ConcertDao) : ViewModel() { val concertList: LiveData<PagedList<Concert>> = concertDao.concertsByDate().toLiveData(pageSize = 50) }
Java
public class ConcertViewModel extends ViewModel { private ConcertDao concertDao; public final LiveData<PagedList<Concert>> concertList; // Creates a PagedList object with 50 items per page. public ConcertViewModel(ConcertDao concertDao) { this.concertDao = concertDao; concertList = new LivePagedListBuilder<>( concertDao.concertsByDate(), 50).build(); } }
Data
Each instance of PagedList loads
an up-to-date snapshot of your app's data from its corresponding
DataSource object. Data flows
from your app's backend or database into the PagedList object.
The following example uses the Room persistence library to organize your app's data, but if you want to store your data using another means, you can also provide your own data source factory.
Kotlin
@Dao interface ConcertDao { // The Int type parameter tells Room to use a PositionalDataSource object. @Query("SELECT * FROM concerts ORDER BY date DESC") fun concertsByDate(): DataSource.Factory<Int, Concert> }
Java
@Dao public interface ConcertDao { // The Integer type parameter tells Room to use a // PositionalDataSource object. @Query("SELECT * FROM concerts ORDER BY date DESC") DataSource.Factory<Integer, Concert> concertsByDate(); }
To learn more about how you can load data into PagedList objects, see the
guide on how to Load paged data.
UI
The PagedList class works with a
PagedListAdapter to load items into a
RecyclerView. These
classes work together to fetch and display content as it's loaded, prefetching
out-of-view content and animating content changes.
To learn more, see the guide on how to Display paged lists.
Support different data architectures
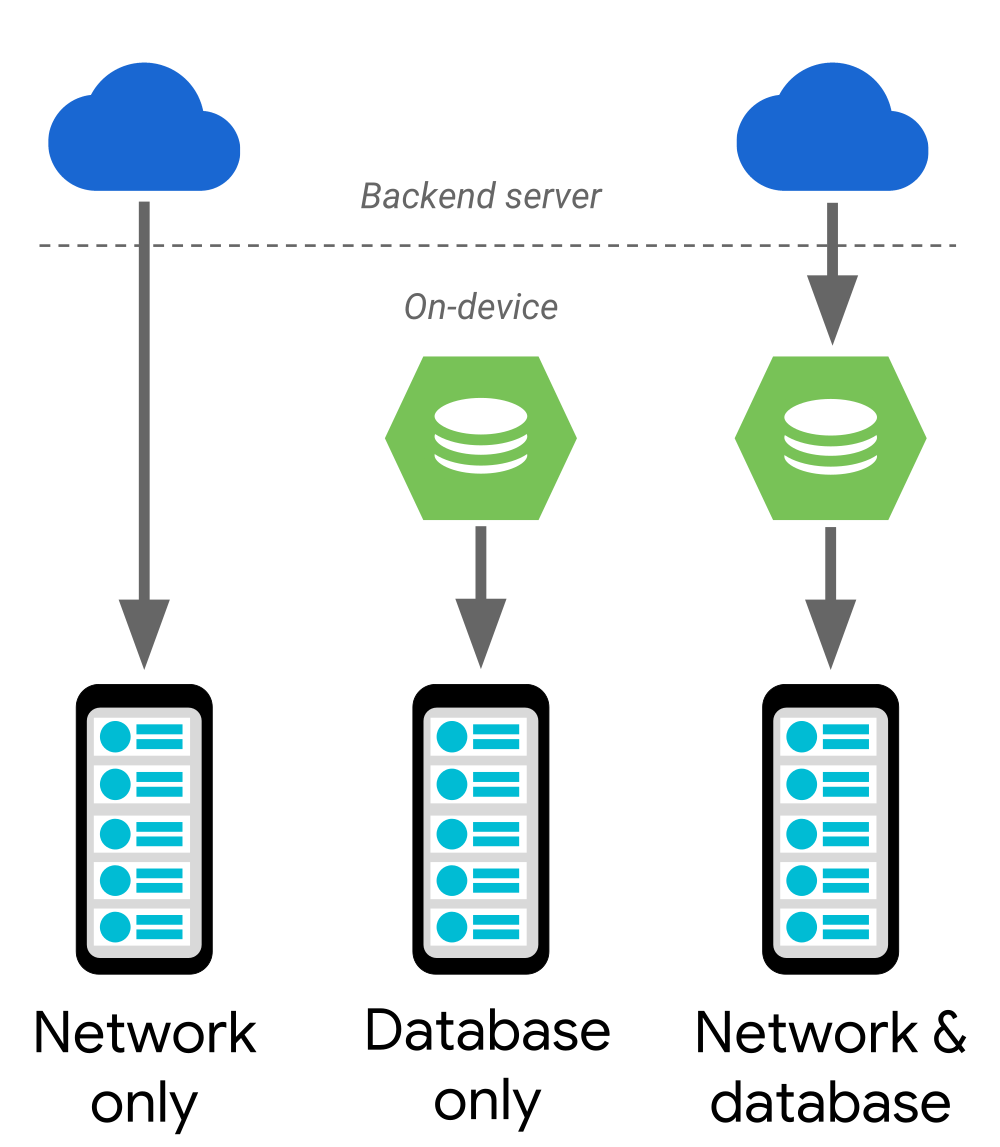
The Paging Library supports the following data architectures:
- Served only from a backend server.
- Stored only in an on-device database.
- A combination of the other sources, using the on-device database as a cache.
Figure 1 shows how data flows in each of these architecture scenarios. In the case of a network-only or database-only solution, the data flows directly to your app's UI model. If you're using a combined approach, data flows from your backend server, into an on-device database, and then to your app's UI model. Every once in a while, the endpoint of each data flow runs out of data to load, at which point it requests more data from the component that provided the data. For example, when an on-device database runs out of data, it requests more data from the server.
The remainder of this section provides recommendations for configuring each data flow use case.
Network only
To display data from a backend server, use the synchronous version of the
Retrofit API to load
information into your own custom DataSource
object.
Database only
Set up your RecyclerView
to observe local storage, preferably using the Room persistence
library. That way, whenever data is
inserted or modified in your app's database, these changes are automatically
reflected in the RecyclerView that's displaying this data.
Network and database
After you've started observing the database, you can listen for when the
database is out of data by using
PagedList.BoundaryCallback.
You can then fetch more items from your network and insert them into the
database. If your UI is observing the database, that's all you need to do.
Handle network errors
When using a network to fetch or page the data that you're displaying using the Paging Library, it's important to not treat the network as being either "available" or "unavailable" all the time, as many connections are intermittent or flaky:
- A particular server might fail to respond to a network request.
- The device might be connected to a network that's slow or weak.
Instead, your app should check each request for failures and recover as gracefully as possible in cases where the network isn't available. For example, you can provide a "retry" button for users to select if the data refresh step doesn't work. If an error occurs during the data paging step, it's best to retry the paging requests automatically.
Update your existing app
If your app already consumes data from a database or a backend source, it's possible to upgrade directly to functionality that the Paging Library provides. This section shows how to upgrade an app that has a common existing design.
Custom paging solutions
If you use custom functionality to load small subsets of data from your app's
data source, you can replace this logic with that from the
PagedList class. Instances of
PagedList offer built-in connections to common data sources. These instances
also provide adapters for
RecyclerView objects that
you might include in your app's UI.
Data loaded using lists instead of pages
If you use an in-memory list as the backing data structure for your UI's
adapter, consider observing data updates using a
PagedList class if the number
of items in the list can become large. Instances of PagedList can use either
LiveData<PagedList> or
Observable<List> to pass data updates to your app's UI, minimizing load times
and memory usage. Better still, replacing a List
object with a PagedList object in your app doesn't require any changes to your
app's UI structure or data updating logic.
Associate a data cursor with a list view using CursorAdapter
Your app might use a CursorAdapter
to associate data from a Cursor with a
ListView. In that case, you usually need
to migrate from a ListView to a
RecyclerView as your
app's list UI container, then replace the Cursor
component with either Room or
PositionalDataSource, depending on whether instances of Cursor access a
SQLite database.
In some situations, such as when working with instances of
Spinner, you provide only the adapter
itself. A library then takes the data that's loaded into that adapter and
displays the data for you. In these situations, change the type of your
adapter's data to
LiveData<PagedList>, then wrap
this list in an ArrayAdapter object
before attempting to have a library class inflate these items in a UI.
Load content asynchronously using AsyncListUtil
If you're using
AsyncListUtil objects to
load and display groups of information asynchronously, the Paging Library lets
you load data more easily:
- Your data doesn't need to be positional. The Paging Library lets you load data directly from your backend using keys that the network provides.
- Your data can be uncountably large. Using the Paging Library, you can load data into pages until there isn't any data remaining.
- You can observe your data more easily. The Paging library can present your data that your app's ViewModel holds in an observable data structure.
Database examples
The following code snippets show several possible ways of having all the pieces work together.
Observing paged data using LiveData
The following code snippet shows all the pieces working together. As concert
events are added, removed, or changed in the database, the content in the
RecyclerView is
automatically and efficiently updated:
Kotlin
@Dao interface ConcertDao { // The Int type parameter tells Room to use a PositionalDataSource // object, with position-based loading under the hood. @Query("SELECT * FROM concerts ORDER BY date DESC") fun concertsByDate(): DataSource.Factory<Int, Concert> } class ConcertViewModel(concertDao: ConcertDao) : ViewModel() { val concertList: LiveData<PagedList<Concert>> = concertDao.concertsByDate().toLiveData(pageSize = 50) } class ConcertActivity : AppCompatActivity() { public override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Use the 'by viewModels()' Kotlin property delegate // from the activity-ktx artifact val viewModel: ConcertViewModel by viewModels() val recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.concert_list) val adapter = ConcertAdapter() viewModel.concertList.observe(this, PagedList(adapter::submitList)) recyclerView.setAdapter(adapter) } } class ConcertAdapter() : PagedListAdapter<Concert, ConcertViewHolder>(DIFF_CALLBACK) { fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ConcertViewHolder, position: Int) { val concert: Concert? = getItem(position) // Note that "concert" is a placeholder if it's null. holder.bindTo(concert) } companion object { private val DIFF_CALLBACK = object : DiffUtil.ItemCallback<Concert>() { // Concert details may have changed if reloaded from the database, // but ID is fixed. override fun areItemsTheSame(oldConcert: Concert, newConcert: Concert) = oldConcert.id == newConcert.id override fun areContentsTheSame(oldConcert: Concert, newConcert: Concert) = oldConcert == newConcert } } }
Java
@Dao public interface ConcertDao { // The Integer type parameter tells Room to use a PositionalDataSource // object, with position-based loading under the hood. @Query("SELECT * FROM concerts ORDER BY date DESC") DataSource.Factory<Integer, Concert> concertsByDate(); } public class ConcertViewModel extends ViewModel { private ConcertDao concertDao; public final LiveData<PagedList<Concert>> concertList; public ConcertViewModel(ConcertDao concertDao) { this.concertDao = concertDao; concertList = new LivePagedListBuilder<>( concertDao.concertsByDate(), /* page size */ 50).build(); } } public class ConcertActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); ConcertViewModel viewModel = new ViewModelProvider(this).get(ConcertViewModel.class); RecyclerView recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.concert_list); ConcertAdapter adapter = new ConcertAdapter(); viewModel.concertList.observe(this, adapter::submitList); recyclerView.setAdapter(adapter); } } public class ConcertAdapter extends PagedListAdapter<Concert, ConcertViewHolder> { protected ConcertAdapter() { super(DIFF_CALLBACK); } @Override public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull ConcertViewHolder holder, int position) { Concert concert = getItem(position); if (concert != null) { holder.bindTo(concert); } else { // Null defines a placeholder item - PagedListAdapter automatically // invalidates this row when the actual object is loaded from the // database. holder.clear(); } } private static DiffUtil.ItemCallback<Concert> DIFF_CALLBACK = new DiffUtil.ItemCallback<Concert>() { // Concert details may have changed if reloaded from the database, // but ID is fixed. @Override public boolean areItemsTheSame(Concert oldConcert, Concert newConcert) { return oldConcert.getId() == newConcert.getId(); } @Override public boolean areContentsTheSame(Concert oldConcert, Concert newConcert) { return oldConcert.equals(newConcert); } }; }
Observing paged data using RxJava2
If you prefer using
RxJava2 instead of
LiveData, you can instead
create an Observable or Flowable object:
Kotlin
class ConcertViewModel(concertDao: ConcertDao) : ViewModel() { val concertList: Observable<PagedList<Concert>> = concertDao.concertsByDate().toObservable(pageSize = 50) }
Java
public class ConcertViewModel extends ViewModel { private ConcertDao concertDao; public final Observable<PagedList<Concert>> concertList; public ConcertViewModel(ConcertDao concertDao) { this.concertDao = concertDao; concertList = new RxPagedListBuilder<>( concertDao.concertsByDate(), /* page size */ 50) .buildObservable(); } }
You can then start and stop observing the data using the code in the following snippet:
Kotlin
class ConcertActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val adapter = ConcertAdapter() // Use the 'by viewModels()' Kotlin property delegate // from the activity-ktx artifact private val viewModel: ConcertViewModel by viewModels() private val disposable = CompositeDisposable() public override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) val recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.concert_list) recyclerView.setAdapter(adapter) } override fun onStart() { super.onStart() disposable.add(viewModel.concertList .subscribe(adapter::submitList))) } override fun onStop() { super.onStop() disposable.clear() } }
Java
public class ConcertActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private ConcertAdapter adapter = new ConcertAdapter(); private ConcertViewModel viewModel; private CompositeDisposable disposable = new CompositeDisposable(); @Override public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); RecyclerView recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.concert_list); viewModel = new ViewModelProvider(this).get(ConcertViewModel.class); recyclerView.setAdapter(adapter); } @Override protected void onStart() { super.onStart(); disposable.add(viewModel.concertList .subscribe(adapter.submitList(flowableList) )); } @Override protected void onStop() { super.onStop(); disposable.clear(); } }
The code for the ConcertDao and ConcertAdapter are the same for an
RxJava2-based
solution as they are for a
LiveData-based solution.
Provide feedback
Share your feedback and ideas with us through these resources:
- Issue tracker

- Report issues so we can fix bugs.
Additional resources
To learn more about the Paging Library, consult the following resources.
Samples
Codelabs
Videos
- Android Jetpack: manage infinite lists with RecyclerView and Paging (Google I/O '18)
- Android Jetpack: Paging
Recommended for you
- Note: link text is displayed when JavaScript is off
- Migrate to Paging 3
- Display paged lists
- Gather paged data
