滑動檢視畫面可讓您透過橫向移動的手勢 (也就是左右「滑動」),在同層級畫面 (如分頁) 之間導覽。這種導覽模式又稱為「橫向分頁」。本主題將說明如何建立方便切換分頁且包含滑動檢視畫面的版面,也將說明如何顯示不歸為分頁的標題列。
實作滑動檢視畫面
您可以使用 AndroidX 的 ViewPager2 小工具建立滑動檢視畫面。如要使用 ViewPager2 和分頁,需要在專案中的 ViewPager2 和 Material Design 元件新增依附元件。
如要透過 ViewPager2 設定版面配置,請將 <ViewPager2> 元素新增到您的 XML 版面配置中。例如,如果滑動檢視畫面中的每個頁面都要耗用整個版面配置,則版面配置應如下所示:
<androidx.viewpager2.widget.ViewPager2
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/pager"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
如要插入代表各個頁面的子檢視畫面,請將這個版面配置掛接到 FragmentStateAdapter。以下說明如何使用它來滑動 Fragment 物件集合:
Kotlin
class CollectionDemoFragment : Fragment() { // When requested, this adapter returns a DemoObjectFragment, // representing an object in the collection. private lateinit var demoCollectionAdapter: DemoCollectionAdapter private lateinit var viewPager: ViewPager2 override fun onCreateView( inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle? ): View? { return inflater.inflate(R.layout.collection_demo, container, false) } override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { demoCollectionAdapter = DemoCollectionAdapter(this) viewPager = view.findViewById(R.id.pager) viewPager.adapter = demoCollectionAdapter } } class DemoCollectionAdapter(fragment: Fragment) : FragmentStateAdapter(fragment) { override fun getItemCount(): Int = 100 override fun createFragment(position: Int): Fragment { // Return a NEW fragment instance in createFragment(int) val fragment = DemoObjectFragment() fragment.arguments = Bundle().apply { // Our object is just an integer :-P putInt(ARG_OBJECT, position + 1) } return fragment } } private const val ARG_OBJECT = "object" // Instances of this class are fragments representing a single // object in our collection. class DemoObjectFragment : Fragment() { override fun onCreateView( inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle? ): View { return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_collection_object, container, false) } override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { arguments?.takeIf { it.containsKey(ARG_OBJECT) }?.apply { val textView: TextView = view.findViewById(android.R.id.text1) textView.text = getInt(ARG_OBJECT).toString() } } }
Java
public class CollectionDemoFragment extends Fragment { // When requested, this adapter returns a DemoObjectFragment, // representing an object in the collection. DemoCollectionAdapter demoCollectionAdapter; ViewPager2 viewPager; @Nullable @Override public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { return inflater.inflate(R.layout.collection_demo, container, false); } @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { demoCollectionAdapter = new DemoCollectionAdapter(this); viewPager = view.findViewById(R.id.pager); viewPager.setAdapter(demoCollectionAdapter); } } public class DemoCollectionAdapter extends FragmentStateAdapter { public DemoCollectionAdapter(Fragment fragment) { super(fragment); } @NonNull @Override public Fragment createFragment(int position) { // Return a NEW fragment instance in createFragment(int) Fragment fragment = new DemoObjectFragment(); Bundle args = new Bundle(); // Our object is just an integer :-P args.putInt(DemoObjectFragment.ARG_OBJECT, position + 1); fragment.setArguments(args); return fragment; } @Override public int getItemCount() { return 100; } } // Instances of this class are fragments representing a single // object in our collection. public class DemoObjectFragment extends Fragment { public static final String ARG_OBJECT = "object"; @Nullable @Override public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_collection_object, container, false); } @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { Bundle args = getArguments(); ((TextView) view.findViewById(android.R.id.text1)) .setText(Integer.toString(args.getInt(ARG_OBJECT))); } }
下列各節說明如何新增分頁,以便瀏覽頁面。
使用 TabLayout 新增分頁
TabLayout 可讓您以橫向排列的方式顯示分頁。與 ViewPager2 搭配使用時,TabLayout 可提供熟悉的介面,以便在滑動檢視畫面中瀏覽頁面。
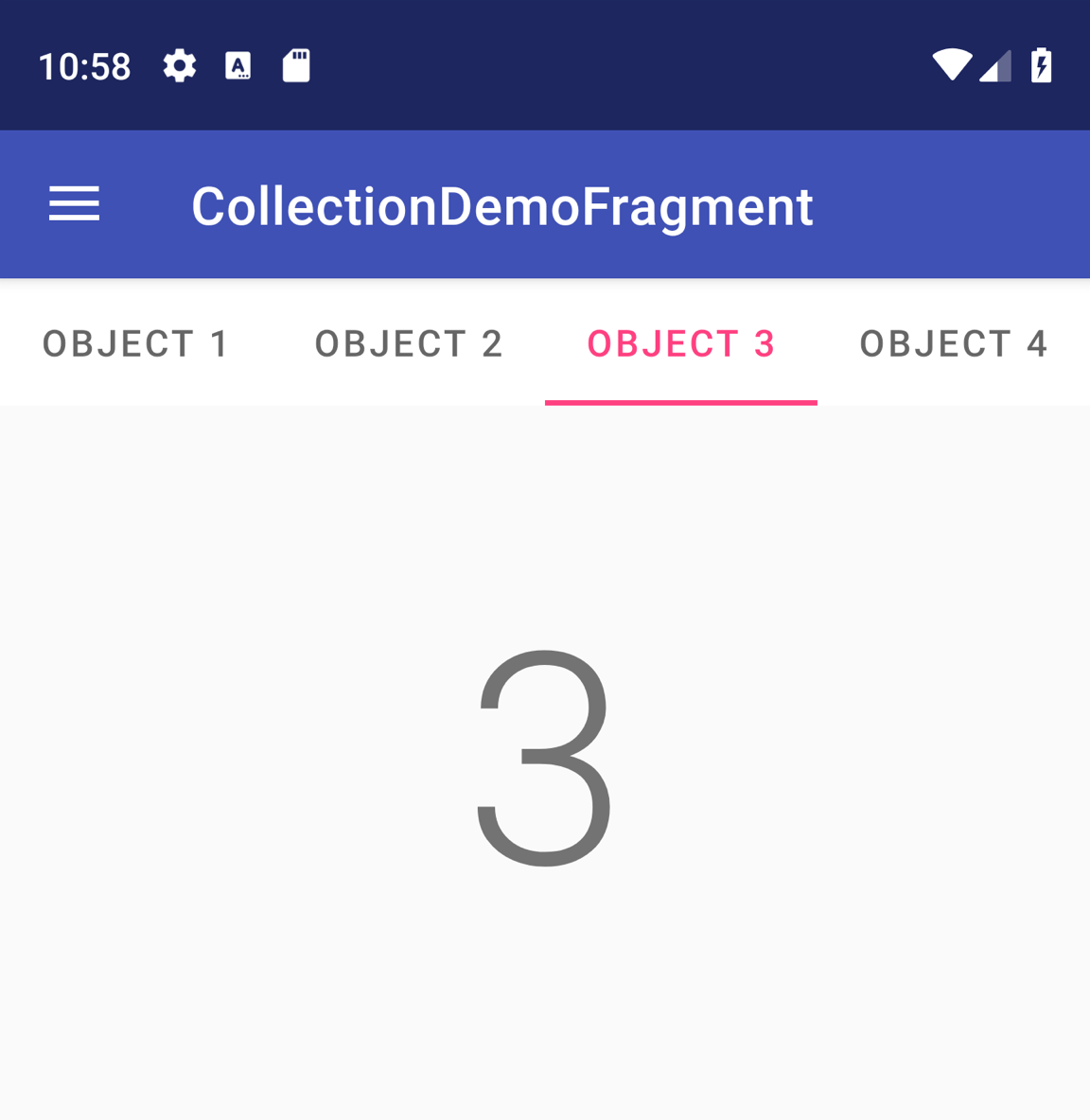
圖 1:含有四個分頁的 TabLayout。
如要在 ViewPager2 中加入 TabLayout,請在 <ViewPager2> 元素上方加入 <TabLayout> 元素,如下所示:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<com.google.android.material.tabs.TabLayout
android:id="@+id/tab_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<androidx.viewpager2.widget.ViewPager2
android:id="@+id/pager"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
接下來,請建立 TabLayoutMediator,將 TabLayout 連結至 ViewPager2,並依下列方式附加:
Kotlin
class CollectionDemoFragment : Fragment() { ... override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { val tabLayout = view.findViewById(R.id.tab_layout) TabLayoutMediator(tabLayout, viewPager) { tab, position -> tab.text = "OBJECT ${(position + 1)}" }.attach() } ... }
Java
public class CollectionDemoFragment extends Fragment { ... @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { TabLayout tabLayout = view.findViewById(R.id.tab_layout); new TabLayoutMediator(tabLayout, viewPager, (tab, position) -> tab.setText("OBJECT " + (position + 1)) ).attach(); } ... }
如需分頁版面配置的其他設計指南,請參閱「分頁質感設計說明文件」。
其他資源
如要進一步瞭解 ViewPager2,請參閱下列其他資源:
範例
- GitHub 上的 ViewPager2 範例
影片
- 翻頁:遷移至 MigratePager2 (2019 年 Android 開發人員高峰會)
