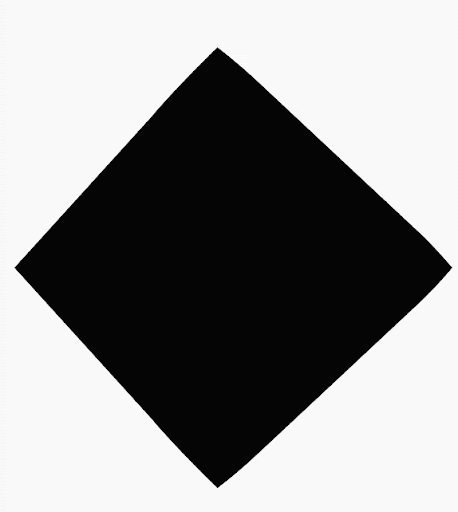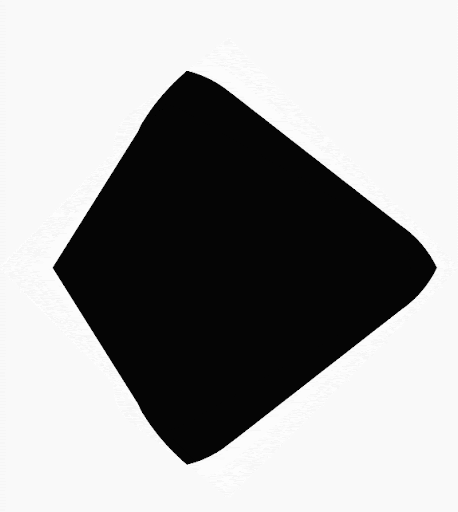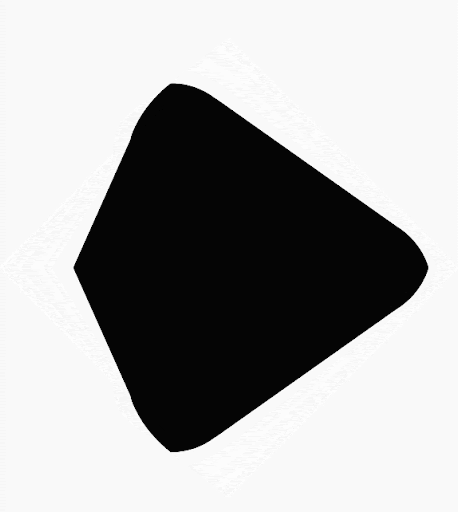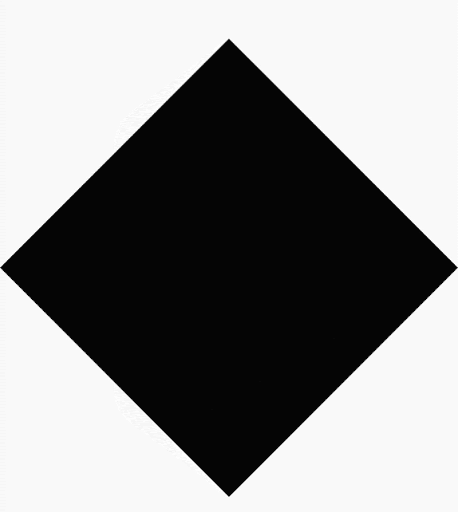
Compose ช่วยให้คุณสร้างรูปร่างจากรูปหลายเหลี่ยมได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น คุณสร้างรูปร่างต่อไปนี้ได้
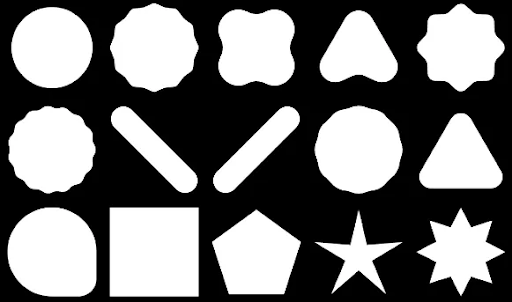
หากต้องการสร้างรูปหลายเหลี่ยมโค้งที่กำหนดเองใน Compose ให้เพิ่มการอ้างอิง
graphics-shapes ลงใน
app/build.gradle
implementation "androidx.graphics:graphics-shapes:1.0.1"
ไลบรารีนี้ช่วยให้คุณสร้างรูปร่างที่ทำจากรูปหลายเหลี่ยมได้ แม้ว่ารูปหลายเหลี่ยมจะมีเพียงขอบตรงและมุมแหลม แต่รูปทรงเหล่านี้ก็มีมุมโค้งมนให้เลือกใช้ได้ ซึ่งช่วยให้เปลี่ยนรูปร่างระหว่างรูปร่าง 2 แบบได้ง่ายๆ การมอร์ฟระหว่างรูปร่างที่กำหนดเองนั้นทำได้ยาก และมักจะเป็น ปัญหาในเวลาออกแบบ แต่ไลบรารีนี้ช่วยให้การเปลี่ยนรูปร่างระหว่างรูปทรงเหล่านี้เป็นเรื่องง่ายด้วยโครงสร้างรูปหลายเหลี่ยมที่คล้ายกัน
สร้างรูปหลายเหลี่ยม
ข้อมูลโค้ดต่อไปนี้จะสร้างรูปร่างรูปหลายเหลี่ยมพื้นฐานที่มี 6 จุดตรงกลาง ของพื้นที่วาดภาพ
Box( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val roundedPolygon = RoundedPolygon( numVertices = 6, radius = size.minDimension / 2, centerX = size.width / 2, centerY = size.height / 2 ) val roundedPolygonPath = roundedPolygon.toPath().asComposePath() onDrawBehind { drawPath(roundedPolygonPath, color = Color.Blue) } } .fillMaxSize() )
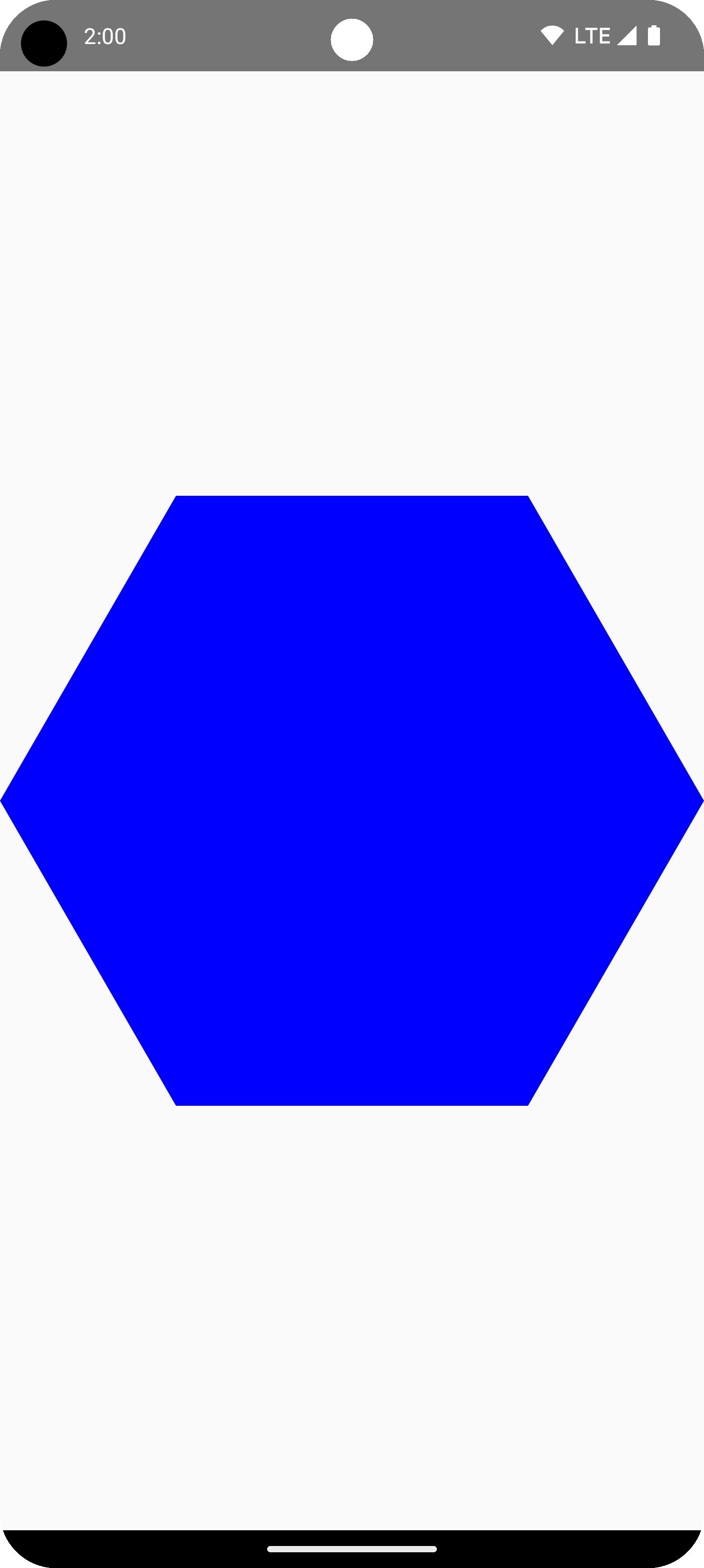
ในตัวอย่างนี้ ไลบรารีจะสร้าง RoundedPolygon ซึ่งเก็บเรขาคณิต
ที่แสดงรูปร่างที่ขอ หากต้องการวาดรูปร่างนั้นในแอป Compose
คุณต้องรับออบเจ็กต์ Path จากรูปร่างนั้นเพื่อเปลี่ยนรูปร่างให้อยู่ในรูปแบบที่ Compose
รู้วิธีวาด
ปัดมุมของรูปหลายเหลี่ยม
หากต้องการปัดมุมของรูปหลายเหลี่ยม ให้ใช้พารามิเตอร์ CornerRounding โดยมีพารามิเตอร์ 2 ตัว ได้แก่ radius และ smoothing มุมโค้งแต่ละมุมประกอบด้วย
เส้นโค้งลูกบาศก์ 1-3 เส้น โดยตรงกลางมีรูปร่างเป็นส่วนโค้งวงกลม ขณะที่เส้นโค้งด้านข้าง 2 เส้น ("ประกบ")
จะเปลี่ยนจากขอบของรูปร่างไปยังเส้นโค้งตรงกลาง
รัศมี
radius คือรัศมีของวงกลมที่ใช้ปัดเศษจุดยอด
ตัวอย่างเช่น สามเหลี่ยมมุมโค้งต่อไปนี้สร้างขึ้นดังนี้

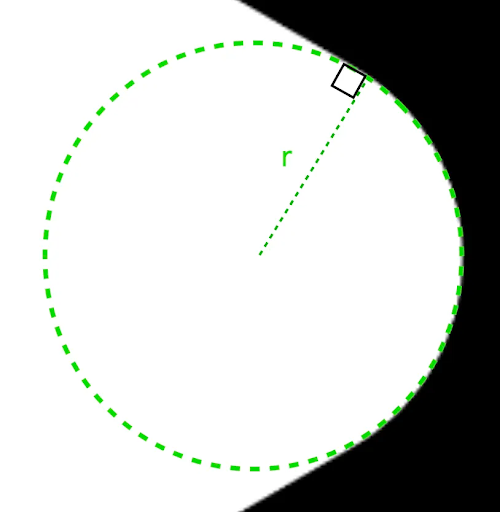
r จะกำหนดขนาดการปัดเศษแบบวงกลมของ
มุมที่ปัดเศษการเกลี่ย
การปรับให้เรียบเป็นปัจจัยที่กำหนดระยะเวลาที่ใช้ในการเปลี่ยนจากส่วนโค้งมนของมุมไปยังขอบ ค่าปัจจัยการปรับให้เรียบเป็น 0
(ไม่ปรับให้เรียบ ซึ่งเป็นค่าเริ่มต้นสำหรับ CornerRounding) จะทำให้เกิดการปัดมุมเป็นวงกลมโดยสมบูรณ์
ค่าปัจจัยการปรับให้เรียบที่ไม่ใช่ 0 (สูงสุด 1.0) จะทำให้
มุมโค้งมนด้วยเส้นโค้ง 3 เส้นแยกกัน
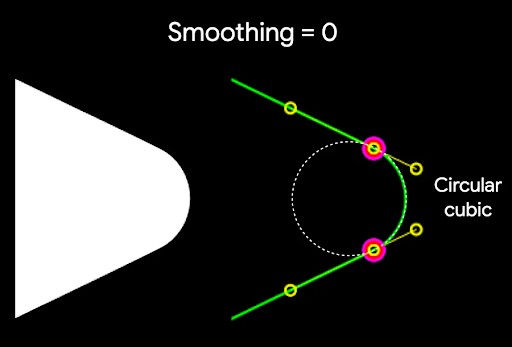
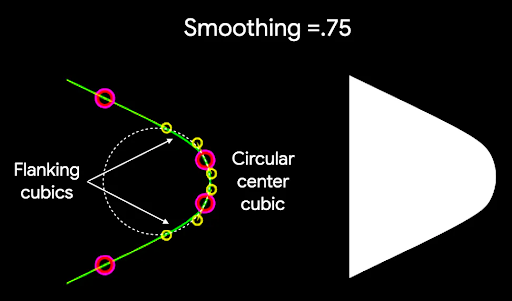
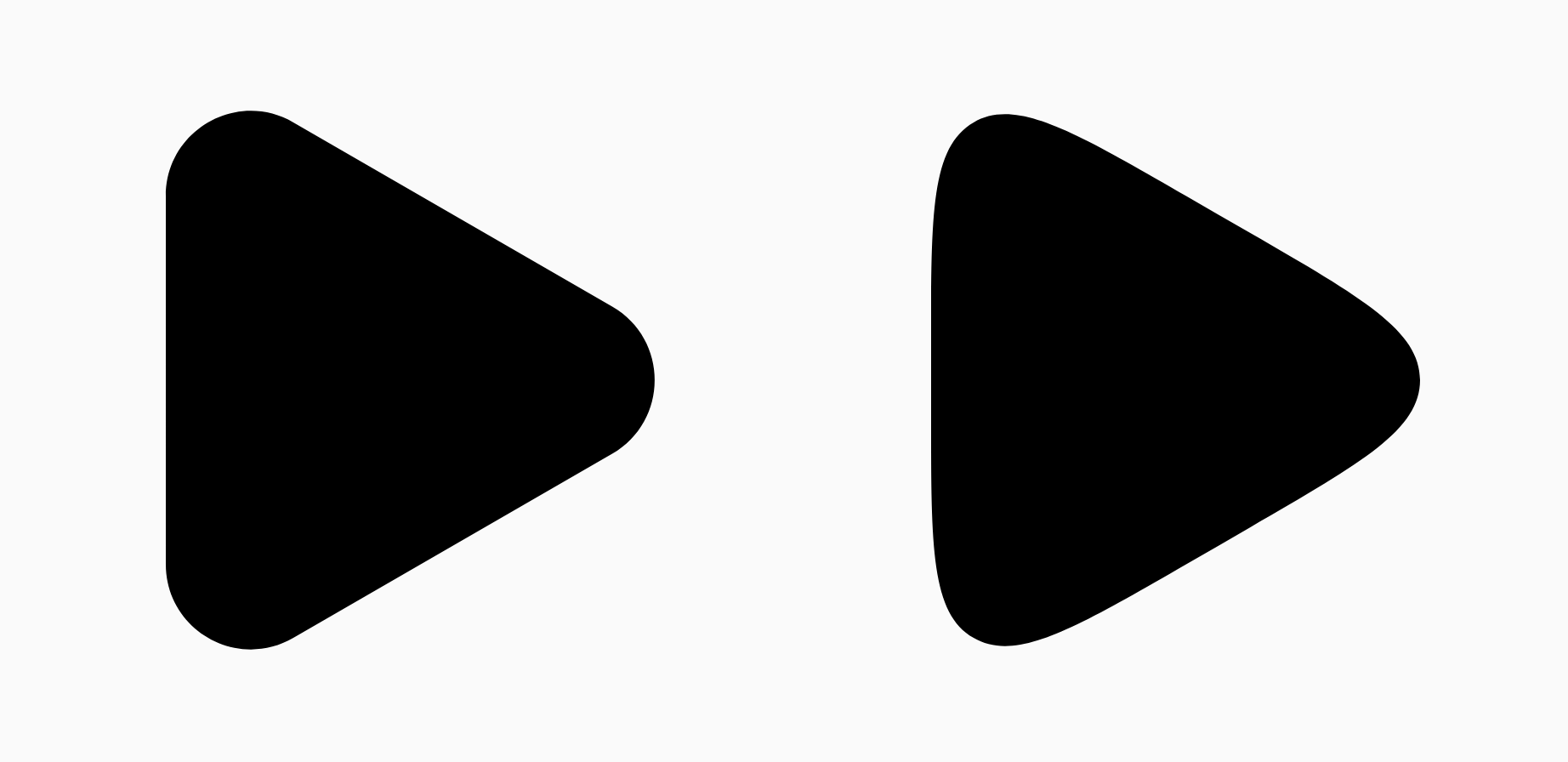
เช่น ข้อมูลโค้ดด้านล่างแสดงความแตกต่างเล็กน้อยในการตั้งค่า การปรับให้เรียบเป็น 0 เทียบกับ 1
Box( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val roundedPolygon = RoundedPolygon( numVertices = 3, radius = size.minDimension / 2, centerX = size.width / 2, centerY = size.height / 2, rounding = CornerRounding( size.minDimension / 10f, smoothing = 0.1f ) ) val roundedPolygonPath = roundedPolygon.toPath().asComposePath() onDrawBehind { drawPath(roundedPolygonPath, color = Color.Black) } } .size(100.dp) )
ขนาดและตำแหน่ง
โดยค่าเริ่มต้น ระบบจะสร้างรูปร่างที่มีรัศมี 1 รอบจุดศูนย์กลาง (0, 0)
รัศมีนี้แสดงถึงระยะทางระหว่างจุดศูนย์กลางกับจุดยอดภายนอก
ของรูปหลายเหลี่ยมที่ใช้เป็นฐานของรูปร่าง โปรดทราบว่าการปัดมุม
จะทำให้รูปร่างเล็กลงเนื่องจากมุมที่ปัดแล้วจะอยู่ใกล้กับ
จุดศูนย์กลางมากกว่าจุดยอดที่ปัด หากต้องการปรับขนาดรูปหลายเหลี่ยม ให้ปรับค่า radius
หากต้องการปรับตำแหน่ง ให้เปลี่ยน centerX หรือ centerY ของรูปหลายเหลี่ยม
หรือจะเปลี่ยนรูปแบบออบเจ็กต์เพื่อเปลี่ยนขนาด ตำแหน่ง และการหมุน
โดยใช้DrawScopeฟังก์ชันการเปลี่ยนรูปแบบมาตรฐาน เช่น
DrawScope#translate() ก็ได้
เปลี่ยนรูปร่าง
ออบเจ็กต์ Morph คือรูปร่างใหม่ที่แสดงภาพเคลื่อนไหวระหว่างรูปร่างหลายเหลี่ยม 2 รูปร่าง
หากต้องการเปลี่ยนรูปร่างระหว่าง 2 รูปร่าง ให้สร้าง 2 RoundedPolygons และออบเจ็กต์ Morph
ที่ใช้ 2 รูปร่างนี้ หากต้องการคำนวณรูปร่างระหว่างรูปร่างเริ่มต้นและรูปร่างสิ้นสุด
ให้ระบุค่า progress ระหว่าง 0 ถึง 1 เพื่อกำหนดรูปแบบ
ระหว่างรูปร่างเริ่มต้น (0) และรูปร่างสิ้นสุด (1)
Box( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val triangle = RoundedPolygon( numVertices = 3, radius = size.minDimension / 2f, centerX = size.width / 2f, centerY = size.height / 2f, rounding = CornerRounding( size.minDimension / 10f, smoothing = 0.1f ) ) val square = RoundedPolygon( numVertices = 4, radius = size.minDimension / 2f, centerX = size.width / 2f, centerY = size.height / 2f ) val morph = Morph(start = triangle, end = square) val morphPath = morph .toPath(progress = 0.5f).asComposePath() onDrawBehind { drawPath(morphPath, color = Color.Black) } } .fillMaxSize() )
ในตัวอย่างข้างต้น ความคืบหน้าอยู่กึ่งกลางระหว่างรูปร่างทั้ง 2 พอดี (สามเหลี่ยมมนและสี่เหลี่ยมจัตุรัส) ทำให้ได้ผลลัพธ์ต่อไปนี้
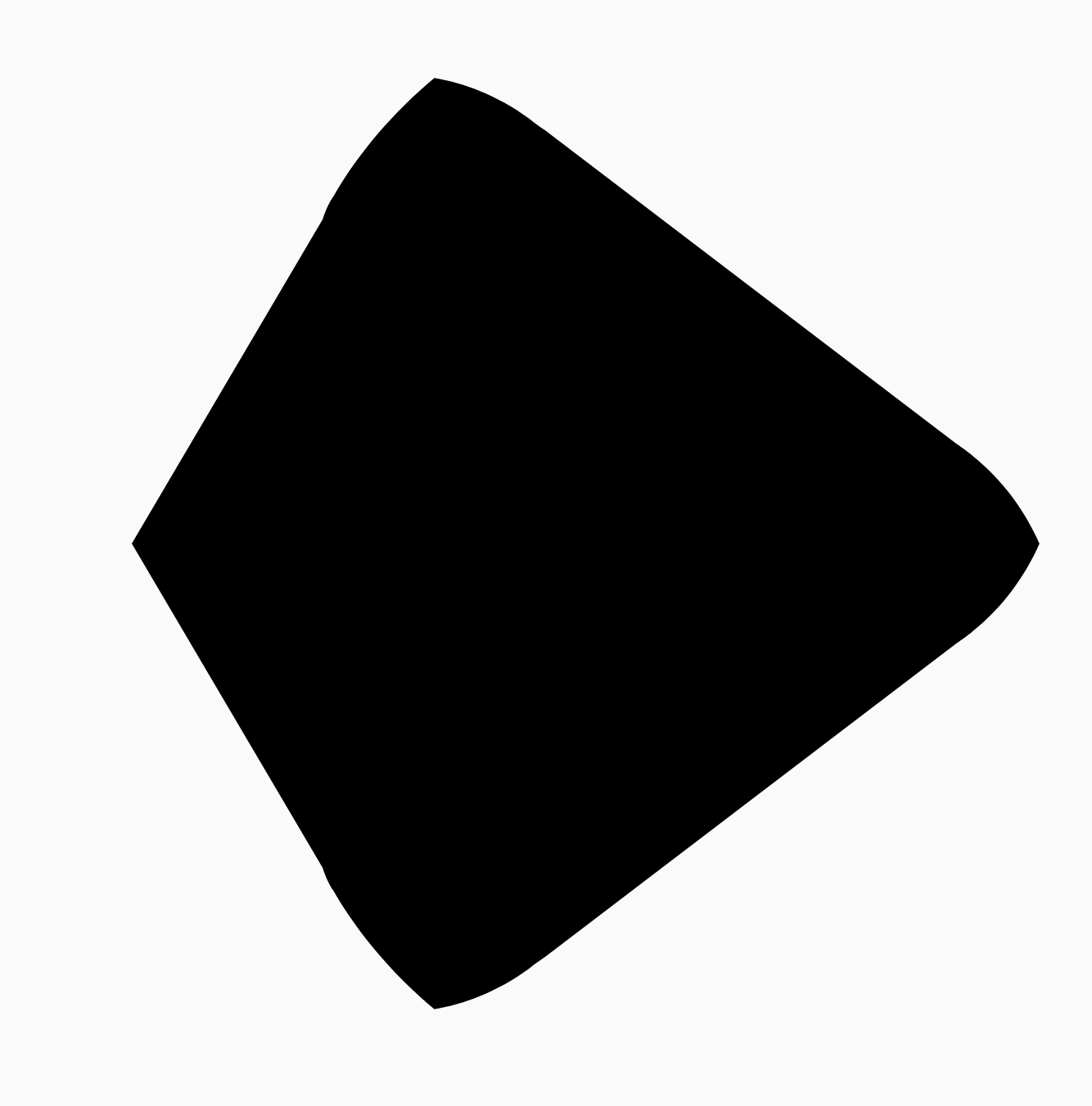
ในสถานการณ์ส่วนใหญ่ การมอร์ฟจะดำเนินการเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของภาพเคลื่อนไหว ไม่ใช่แค่การเรนเดอร์แบบคงที่ หากต้องการสร้างภาพเคลื่อนไหวระหว่าง 2 ค่านี้ คุณสามารถใช้ Animation API มาตรฐานใน Compose เพื่อเปลี่ยนค่าความคืบหน้าเมื่อเวลาผ่านไปได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น คุณสามารถทำให้รูปร่าง 2 รูปนี้เปลี่ยนรูปร่าง ได้อย่างไม่สิ้นสุดดังนี้
val infiniteAnimation = rememberInfiniteTransition(label = "infinite animation") val morphProgress = infiniteAnimation.animateFloat( initialValue = 0f, targetValue = 1f, animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable( tween(500), repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse ), label = "morph" ) Box( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val triangle = RoundedPolygon( numVertices = 3, radius = size.minDimension / 2f, centerX = size.width / 2f, centerY = size.height / 2f, rounding = CornerRounding( size.minDimension / 10f, smoothing = 0.1f ) ) val square = RoundedPolygon( numVertices = 4, radius = size.minDimension / 2f, centerX = size.width / 2f, centerY = size.height / 2f ) val morph = Morph(start = triangle, end = square) val morphPath = morph .toPath(progress = morphProgress.value) .asComposePath() onDrawBehind { drawPath(morphPath, color = Color.Black) } } .fillMaxSize() )
ใช้รูปหลายเหลี่ยมเป็นคลิป
โดยทั่วไปจะใช้ตัวแก้ไข
clip
ใน Compose เพื่อเปลี่ยนวิธีแสดงผล Composable และใช้ประโยชน์จากเงาที่วาดรอบพื้นที่การตัด
fun RoundedPolygon.getBounds() = calculateBounds().let { Rect(it[0], it[1], it[2], it[3]) } class RoundedPolygonShape( private val polygon: RoundedPolygon, private var matrix: Matrix = Matrix() ) : Shape { private var path = Path() override fun createOutline( size: Size, layoutDirection: LayoutDirection, density: Density ): Outline { path.rewind() path = polygon.toPath().asComposePath() matrix.reset() val bounds = polygon.getBounds() val maxDimension = max(bounds.width, bounds.height) matrix.scale(size.width / maxDimension, size.height / maxDimension) matrix.translate(-bounds.left, -bounds.top) path.transform(matrix) return Outline.Generic(path) } }
จากนั้นคุณจะใช้รูปหลายเหลี่ยมเป็นคลิปได้ ดังที่แสดงในข้อมูลโค้ดต่อไปนี้
val hexagon = remember { RoundedPolygon( 6, rounding = CornerRounding(0.2f) ) } val clip = remember(hexagon) { RoundedPolygonShape(polygon = hexagon) } Box( modifier = Modifier .clip(clip) .background(MaterialTheme.colorScheme.secondary) .size(200.dp) ) { Text( "Hello Compose", color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.onSecondary, modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.Center) ) }
ซึ่งจะส่งผลดังนี้
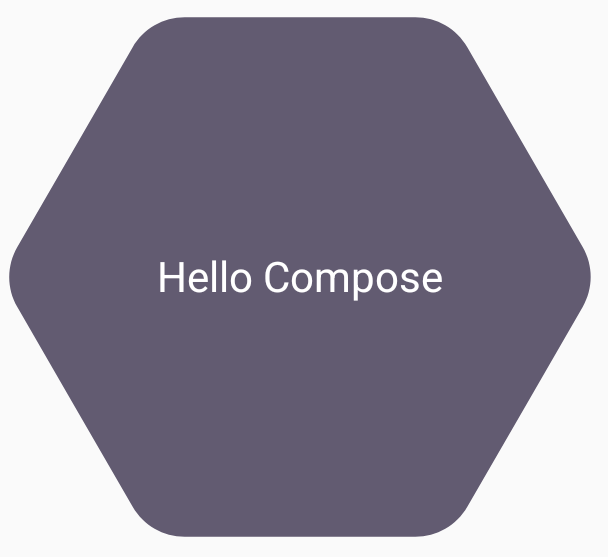
ซึ่งอาจไม่แตกต่างจากสิ่งที่แสดงผลก่อนหน้านี้มากนัก แต่จะช่วยให้ใช้ประโยชน์จากฟีเจอร์อื่นๆ ใน Compose ได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น เทคนิคนี้สามารถใช้เพื่อครอบตัดรูปภาพและใช้เงารอบๆ บริเวณที่ครอบตัดได้
val hexagon = remember { RoundedPolygon( 6, rounding = CornerRounding(0.2f) ) } val clip = remember(hexagon) { RoundedPolygonShape(polygon = hexagon) } Box( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(), contentAlignment = Alignment.Center ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.drawable.dog), contentDescription = "Dog", contentScale = ContentScale.Crop, modifier = Modifier .graphicsLayer { this.shadowElevation = 6.dp.toPx() this.shape = clip this.clip = true this.ambientShadowColor = Color.Black this.spotShadowColor = Color.Black } .size(200.dp) ) }

ปุ่มเปลี่ยนรูปร่างเมื่อคลิก
คุณใช้graphics-shapeไลบรารีเพื่อสร้างปุ่มที่เปลี่ยนรูปร่างระหว่าง
2 รูปร่างเมื่อกดได้ ก่อนอื่น ให้สร้าง MorphPolygonShape ที่ขยาย Shape
ปรับขนาดและแปลให้เหมาะสม โปรดทราบว่าการส่งผ่าน
ความคืบหน้าจะช่วยให้รูปร่างเคลื่อนไหวได้
class MorphPolygonShape( private val morph: Morph, private val percentage: Float ) : Shape { private val matrix = Matrix() override fun createOutline( size: Size, layoutDirection: LayoutDirection, density: Density ): Outline { // Below assumes that you haven't changed the default radius of 1f, nor the centerX and centerY of 0f // By default this stretches the path to the size of the container, if you don't want stretching, use the same size.width for both x and y. matrix.scale(size.width / 2f, size.height / 2f) matrix.translate(1f, 1f) val path = morph.toPath(progress = percentage).asComposePath() path.transform(matrix) return Outline.Generic(path) } }
หากต้องการใช้รูปร่างมอร์ฟนี้ ให้สร้างรูปหลายเหลี่ยม 2 รูป ได้แก่ shapeA และ shapeB สร้างและ
จดจำMorph จากนั้นใช้การมอร์ฟกับปุ่มเป็นเส้นขอบคลิป
โดยใช้ interactionSource เมื่อกดเป็นแรงขับเคลื่อนเบื้องหลัง
ภาพเคลื่อนไหว
val shapeA = remember { RoundedPolygon( 6, rounding = CornerRounding(0.2f) ) } val shapeB = remember { RoundedPolygon.star( 6, rounding = CornerRounding(0.1f) ) } val morph = remember { Morph(shapeA, shapeB) } val interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() } val isPressed by interactionSource.collectIsPressedAsState() val animatedProgress = animateFloatAsState( targetValue = if (isPressed) 1f else 0f, label = "progress", animationSpec = spring(dampingRatio = 0.4f, stiffness = Spring.StiffnessMedium) ) Box( modifier = Modifier .size(200.dp) .padding(8.dp) .clip(MorphPolygonShape(morph, animatedProgress.value)) .background(Color(0xFF80DEEA)) .size(200.dp) .clickable(interactionSource = interactionSource, indication = null) { } ) { Text("Hello", modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.Center)) }
ซึ่งจะทำให้เกิดภาพเคลื่อนไหวต่อไปนี้เมื่อแตะช่อง

ทำให้การเปลี่ยนรูปร่างเคลื่อนไหวอย่างไม่มีที่สิ้นสุด
หากต้องการทำให้รูปร่างมอร์ฟเคลื่อนไหวอย่างต่อเนื่อง ให้ใช้
rememberInfiniteTransition
ด้านล่างนี้คือตัวอย่างรูปโปรไฟล์ที่เปลี่ยนรูปร่าง (และหมุน) ได้ไม่สิ้นสุดเมื่อเวลาผ่านไป
แนวทางนี้ใช้การปรับเล็กน้อยกับ
MorphPolygonShape ที่แสดงด้านบน
class CustomRotatingMorphShape( private val morph: Morph, private val percentage: Float, private val rotation: Float ) : Shape { private val matrix = Matrix() override fun createOutline( size: Size, layoutDirection: LayoutDirection, density: Density ): Outline { // Below assumes that you haven't changed the default radius of 1f, nor the centerX and centerY of 0f // By default this stretches the path to the size of the container, if you don't want stretching, use the same size.width for both x and y. matrix.scale(size.width / 2f, size.height / 2f) matrix.translate(1f, 1f) matrix.rotateZ(rotation) val path = morph.toPath(progress = percentage).asComposePath() path.transform(matrix) return Outline.Generic(path) } } @Preview @Composable private fun RotatingScallopedProfilePic() { val shapeA = remember { RoundedPolygon( 12, rounding = CornerRounding(0.2f) ) } val shapeB = remember { RoundedPolygon.star( 12, rounding = CornerRounding(0.2f) ) } val morph = remember { Morph(shapeA, shapeB) } val infiniteTransition = rememberInfiniteTransition("infinite outline movement") val animatedProgress = infiniteTransition.animateFloat( initialValue = 0f, targetValue = 1f, animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable( tween(2000, easing = LinearEasing), repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse ), label = "animatedMorphProgress" ) val animatedRotation = infiniteTransition.animateFloat( initialValue = 0f, targetValue = 360f, animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable( tween(6000, easing = LinearEasing), repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse ), label = "animatedMorphProgress" ) Box( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(), contentAlignment = Alignment.Center ) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.drawable.dog), contentDescription = "Dog", contentScale = ContentScale.Crop, modifier = Modifier .clip( CustomRotatingMorphShape( morph, animatedProgress.value, animatedRotation.value ) ) .size(200.dp) ) } }
โค้ดนี้จะให้ผลลัพธ์ที่สนุกสนานดังนี้

รูปหลายเหลี่ยมแบบกำหนดเอง
หากรูปร่างที่สร้างจากรูปหลายเหลี่ยมด้านเท่ามุมเท่าไม่ครอบคลุมกรณีการใช้งานของคุณ คุณสามารถ สร้างรูปร่างที่กำหนดเองมากขึ้นด้วยรายการจุดยอด เช่น คุณอาจต้องการสร้างรูปหัวใจดังนี้
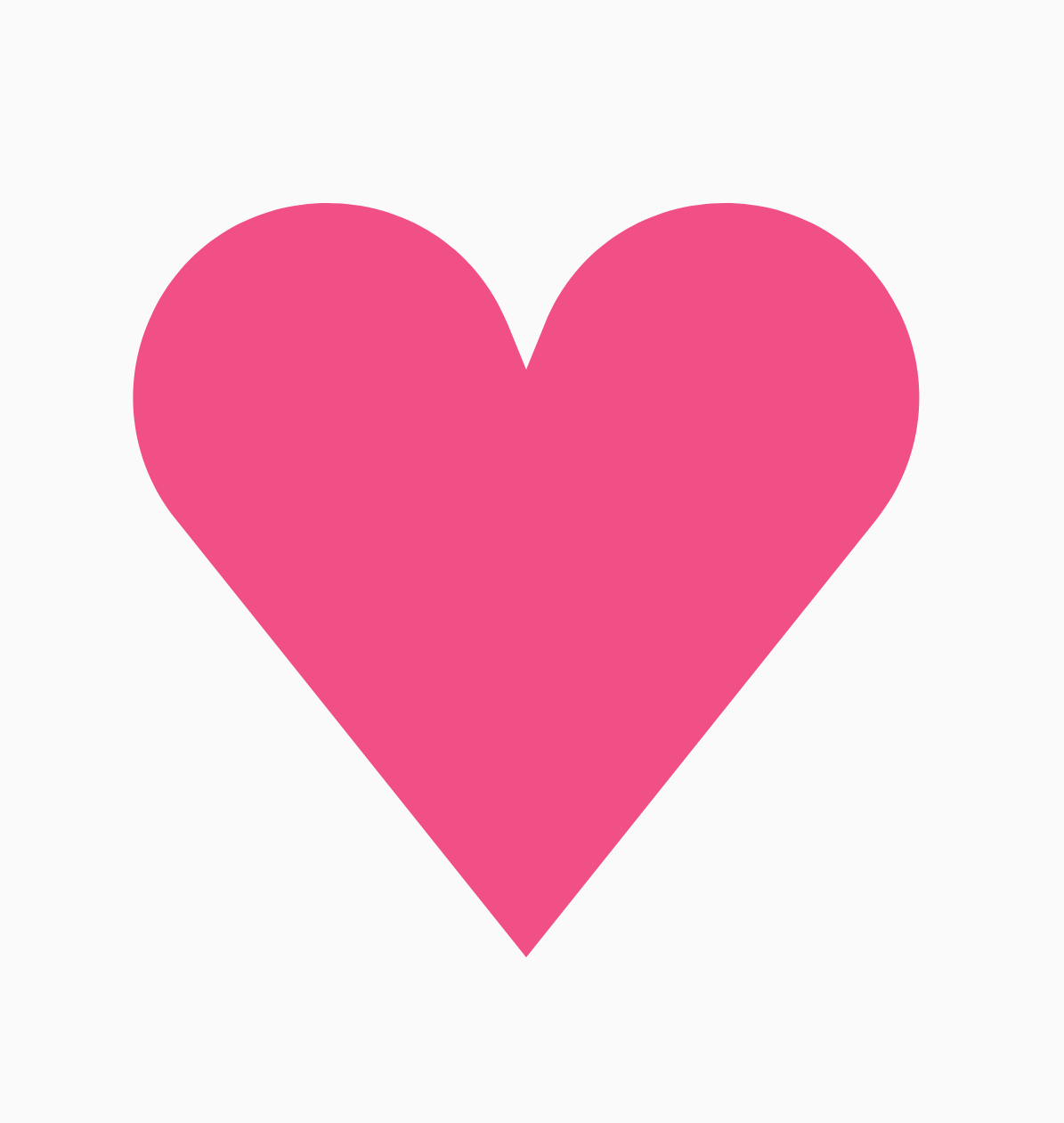
คุณระบุจุดยอดแต่ละจุดของรูปร่างนี้ได้โดยใช้RoundedPolygon
โอเวอร์โหลดที่ใช้พิกัด x, y เป็นอาร์เรย์ของจำนวนทศนิยม
หากต้องการแบ่งรูปหลายเหลี่ยมหัวใจ ให้สังเกตว่าระบบพิกัดเชิงขั้วสำหรับ
การระบุจุดทำให้การดำเนินการนี้ง่ายกว่าการใช้ระบบพิกัดคาร์ทีเซียน (x,y)
โดยที่ 0° เริ่มทางด้านขวามือและดำเนินการตามเข็มนาฬิกา โดยมี
270° อยู่ที่ตำแหน่ง 12 นาฬิกา ดังนี้
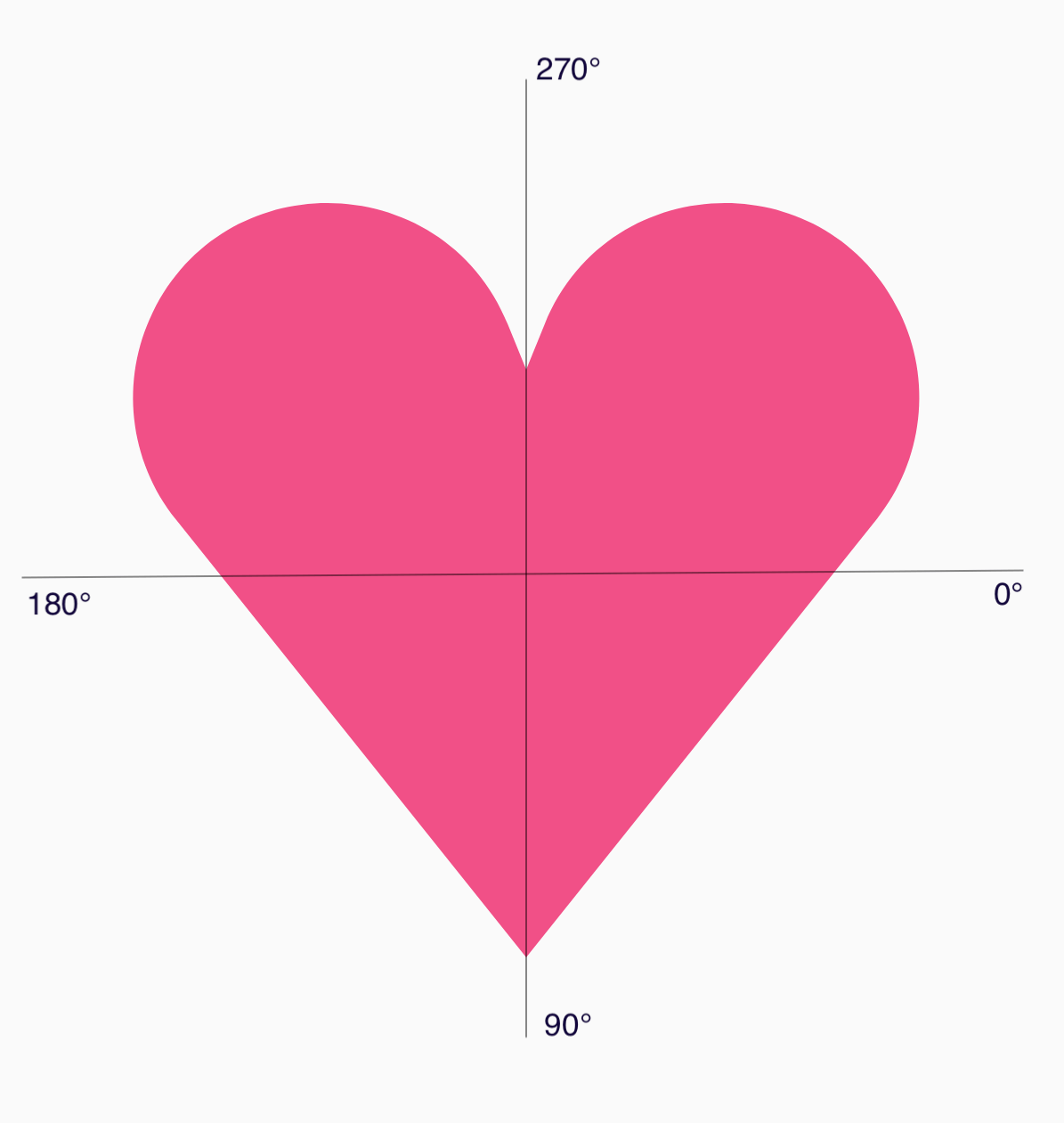
ตอนนี้คุณกำหนดรูปร่างได้ง่ายขึ้นโดยระบุมุม (𝜭) และรัศมีจากจุดกึ่งกลางที่แต่ละจุด
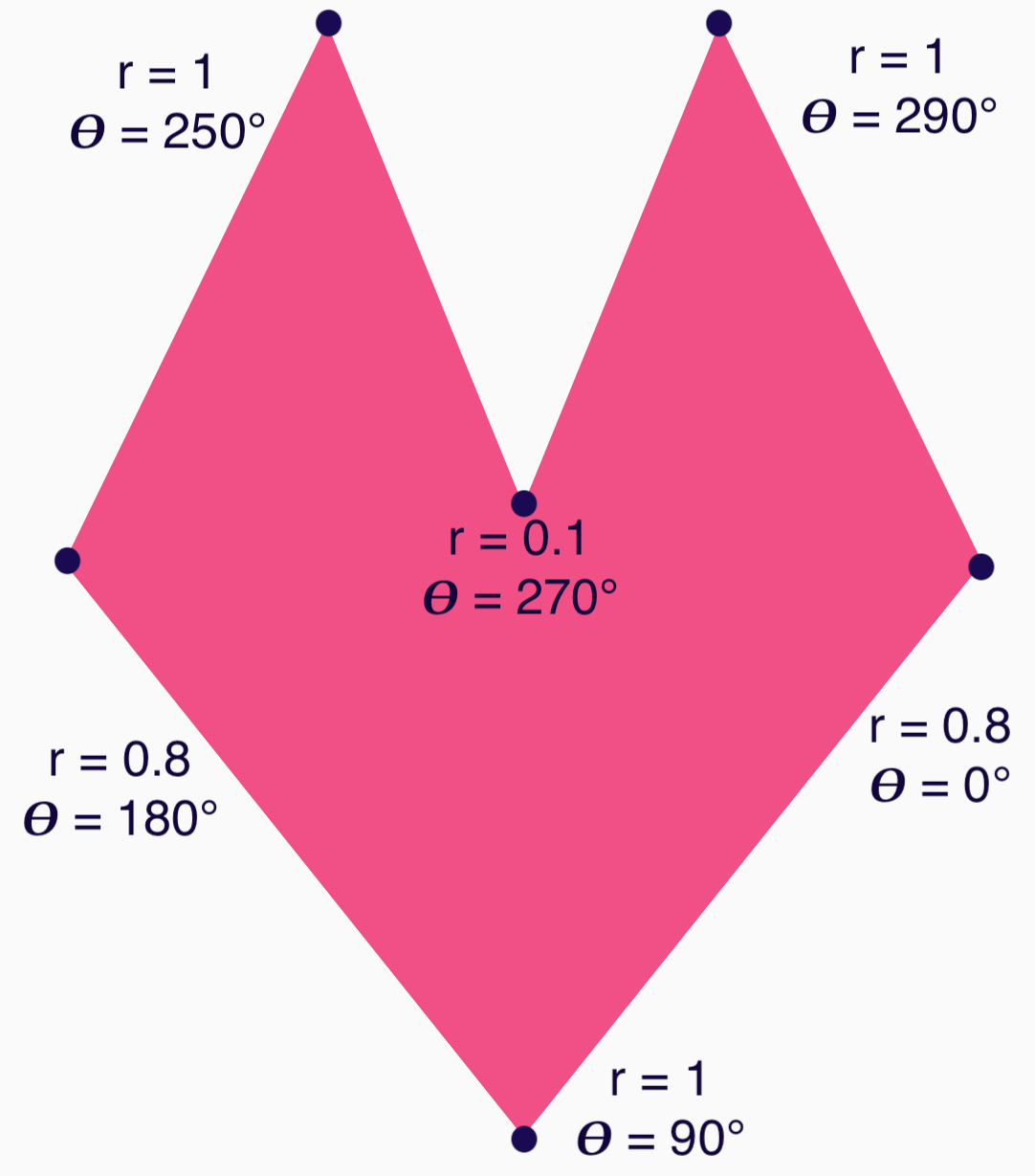
ตอนนี้คุณสร้างจุดยอดและส่งไปยังฟังก์ชัน RoundedPolygon ได้แล้ว
val vertices = remember { val radius = 1f val radiusSides = 0.8f val innerRadius = .1f floatArrayOf( radialToCartesian(radiusSides, 0f.toRadians()).x, radialToCartesian(radiusSides, 0f.toRadians()).y, radialToCartesian(radius, 90f.toRadians()).x, radialToCartesian(radius, 90f.toRadians()).y, radialToCartesian(radiusSides, 180f.toRadians()).x, radialToCartesian(radiusSides, 180f.toRadians()).y, radialToCartesian(radius, 250f.toRadians()).x, radialToCartesian(radius, 250f.toRadians()).y, radialToCartesian(innerRadius, 270f.toRadians()).x, radialToCartesian(innerRadius, 270f.toRadians()).y, radialToCartesian(radius, 290f.toRadians()).x, radialToCartesian(radius, 290f.toRadians()).y, ) }
ต้องแปลงจุดยอดเป็นพิกัดคาร์ทีเซียนโดยใช้ฟังก์ชันต่อไปนี้
radialToCartesian
internal fun Float.toRadians() = this * PI.toFloat() / 180f internal val PointZero = PointF(0f, 0f) internal fun radialToCartesian( radius: Float, angleRadians: Float, center: PointF = PointZero ) = directionVectorPointF(angleRadians) * radius + center internal fun directionVectorPointF(angleRadians: Float) = PointF(cos(angleRadians), sin(angleRadians))
โค้ดก่อนหน้าจะให้จุดยอดดิบสำหรับหัวใจ แต่คุณต้องปัดมุมที่เฉพาะเจาะจงเพื่อรับรูปร่างหัวใจที่เลือก มุมที่ 90° และ
270° จะไม่มีการปัด แต่มุมอื่นๆ จะมีการปัด หากต้องการปัดมุมแต่ละมุม
ตามที่กำหนดเอง ให้ใช้พารามิเตอร์ perVertexRounding
val rounding = remember { val roundingNormal = 0.6f val roundingNone = 0f listOf( CornerRounding(roundingNormal), CornerRounding(roundingNone), CornerRounding(roundingNormal), CornerRounding(roundingNormal), CornerRounding(roundingNone), CornerRounding(roundingNormal), ) } val polygon = remember(vertices, rounding) { RoundedPolygon( vertices = vertices, perVertexRounding = rounding ) } Box( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val roundedPolygonPath = polygon.toPath().asComposePath() onDrawBehind { scale(size.width * 0.5f, size.width * 0.5f) { translate(size.width * 0.5f, size.height * 0.5f) { drawPath(roundedPolygonPath, color = Color(0xFFF15087)) } } } } .size(400.dp) )
ซึ่งจะส่งผลให้เกิดหัวใจสีชมพู ดังนี้

หากรูปร่างก่อนหน้าไม่ครอบคลุม Use Case ของคุณ ให้พิจารณาใช้Path
คลาสเพื่อวาดรูปร่างที่กำหนดเอง หรือโหลดไฟล์ ImageVector จากดิสก์
graphics-shapesไลบรารีไม่ได้มีไว้สำหรับใช้กับรูปร่างใดๆ
แต่มีไว้เพื่อลดความซับซ้อนในการสร้างรูปหลายเหลี่ยมแบบโค้งมนและ
ภาพเคลื่อนไหวแบบมอร์ฟระหว่างรูปเหล่านั้นโดยเฉพาะ
แหล่งข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
ดูข้อมูลและตัวอย่างเพิ่มเติมได้ที่แหล่งข้อมูลต่อไปนี้
- บล็อก: The Shape of Things to Come - Shapes
- บล็อก: การเปลี่ยนรูปร่างใน Android
- การสาธิตรูปร่างใน Github
