Bu derste, yeni API'leri yansıtan ancak eski cihazları destekleyen bir uygulamanın nasıl oluşturulacağı açıklanmaktadır.
Alternatif bir çözüm karar verme
Yeni kullanıcı arayüzü özelliklerini geriye dönük uyumlu şekilde kullanmanın en zor görevi, eski platform sürümleri için eski (yedek) bir çözüme karar vermek ve bu çözümü uygulamaktır. Çoğu durumda, bu yeni kullanıcı arayüzü bileşenlerinin amacını yerine getirmek, eski kullanıcı arayüzü çerçevesi özelliklerini kullanarak mümkündür. Örnek:
-
İşlem çubukları, özel başlık çubukları veya etkinlik düzeninizde görünümler olarak resim düğmeleri içeren yatay bir
LinearLayoutkullanılarak uygulanabilir. Taşma işlemleri, cihazın Menü düğmesi altında sunulabilir. -
İşlem çubuğu sekmeleri, düğmeler içeren yatay bir
LinearLayoutveyaTabWidgetkullanıcı arayüzü öğesi kullanılarak uygulanabilir. -
NumberPickerveSwitchwidget'ları, sırasıylaSpinnerveToggleButtonwidget'ları kullanılarak uygulanabilir. -
ListPopupWindowvePopupMenuwidget'ları,PopupWindowwidget'ları kullanılarak uygulanabilir.
Yeni kullanıcı arayüzü bileşenlerini eski cihazlara geri taşımak için genellikle herkese uygun tek bir çözüm yoktur. Kullanıcı deneyimine dikkat edin: Eski cihazlarda kullanıcılar yeni tasarım kalıplarına ve kullanıcı arayüzü bileşenlerine aşina olmayabilir. Aynı işlevin bilindik öğeler kullanılarak nasıl sunulacağı üzerine biraz düşünün. Uygulama ekosisteminde (işlem çubuğu gibi) yeni kullanıcı arayüzü bileşenleri belirginse veya etkileşim modeli son derece basit ve sezgiselse (ör. ViewPager kullanarak kaydırmalı görünümler) çoğu zaman bu durum daha az önem taşır.
Sekmeleri eski API'lerle uygulayın
İşlem çubuğu sekmelerinin daha eski bir uygulamasını oluşturmak için TabWidget ve TabHost kullanabilirsiniz (ancak alternatif olarak yatay olarak düzenlenmiş Button widget'ları da kullanılabilir). Bu uygulama, Android 2.0 (Eclair)'den daha sonra kullanıma sunulan API'leri kullandığından bu uygulamayı TabHelperEclair ve CompatTabEclair adlı sınıflarda uygulayın.
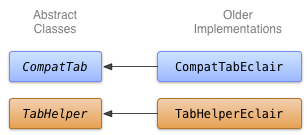
Şekil 1. Sekmelerin Eclair uygulaması için sınıf şeması.
Bu depolama alanını yönetmek için kullanılabilecek bir ActionBar.Tab nesnesi olmadığından, CompatTabEclair uygulaması, sekme metni ve simge gibi sekme özelliklerini örnek değişkenlerinde depolar:
Kotlin
class CompatTabEclair internal constructor(val activity: FragmentActivity, tag: String) : CompatTab(tag) { // Store these properties in the instance, // as there is no ActionBar.Tab object. private var text: CharSequence? = null ... override fun setText(resId: Int): CompatTab { // Our older implementation simply stores this // information in the object instance. text = activity.resources.getText(resId) return this } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
Java
public class CompatTabEclair extends CompatTab { // Store these properties in the instance, // as there is no ActionBar.Tab object. private CharSequence text; ... public CompatTab setText(int resId) { // Our older implementation simply stores this // information in the object instance. text = activity.getResources().getText(resId); return this; } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
TabHelperEclair uygulaması,
TabHost.TabSpec oluşturmak için TabHost widget'ı
nesneleri ve sekme göstergelerini kullanabilirsiniz:
Kotlin
class TabHelperEclair internal constructor(activity: FragmentActivity) : TabHelper(activity) { private var tabHost: TabHost? = null ... override fun setUp() { // Our activity layout for pre-Honeycomb devices // must contain a TabHost. tabHost = tabHost ?: mActivity.findViewById<TabHost>(android.R.id.tabhost).apply { setup() } } override fun addTab(tab: CompatTab) { ... tabHost?.newTabSpec(tab.tag)?.run { setIndicator(tab.getText()) // And optional icon ... tabHost?.addTab(this) } } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }
Java
public class TabHelperEclair extends TabHelper { private TabHost tabHost; ... protected void setUp() { if (tabHost == null) { // Our activity layout for pre-Honeycomb devices // must contain a TabHost. tabHost = (TabHost) mActivity.findViewById( android.R.id.tabhost); tabHost.setup(); } } public void addTab(CompatTab tab) { ... TabSpec spec = tabHost .newTabSpec(tag) .setIndicator(tab.getText()); // And optional icon ... tabHost.addTab(spec); } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }
Artık CompatTab ve TabHelper olmak üzere iki uygulamanız var: Android 3.0 veya sonraki sürümleri çalıştıran cihazlarda çalışan ve yeni API'ler kullanan bir uygulama, Android 2.0 veya sonraki sürümleri çalıştıran cihazlarda çalışan ve daha eski API'leri kullanan cihazlar. Bir sonraki derste, bu uygulamaları uygulamanızda nasıl kullanacağınızı öğreneceksiniz.
