A button consists of text or an icon, or both, that communicates what action occurs when the user taps it.
You can create a button in your layout in one of three ways, depending on whether you want a button with text, an icon, or both:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp" android:orientation="vertical" > <Button android:id="@+id/supabutton" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="I'm a button" /> <ImageButton android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:contentDescription="A tiny Android icon" android:src="@drawable/baseline_android_24" app:tint="#ff0000" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:drawableStart="@drawable/baseline_android_24" android:drawablePadding="4dp" android:drawableTint="#ff0000" android:text="I'm a button with an icon" /> </LinearLayout>
The previous code generates something like this:
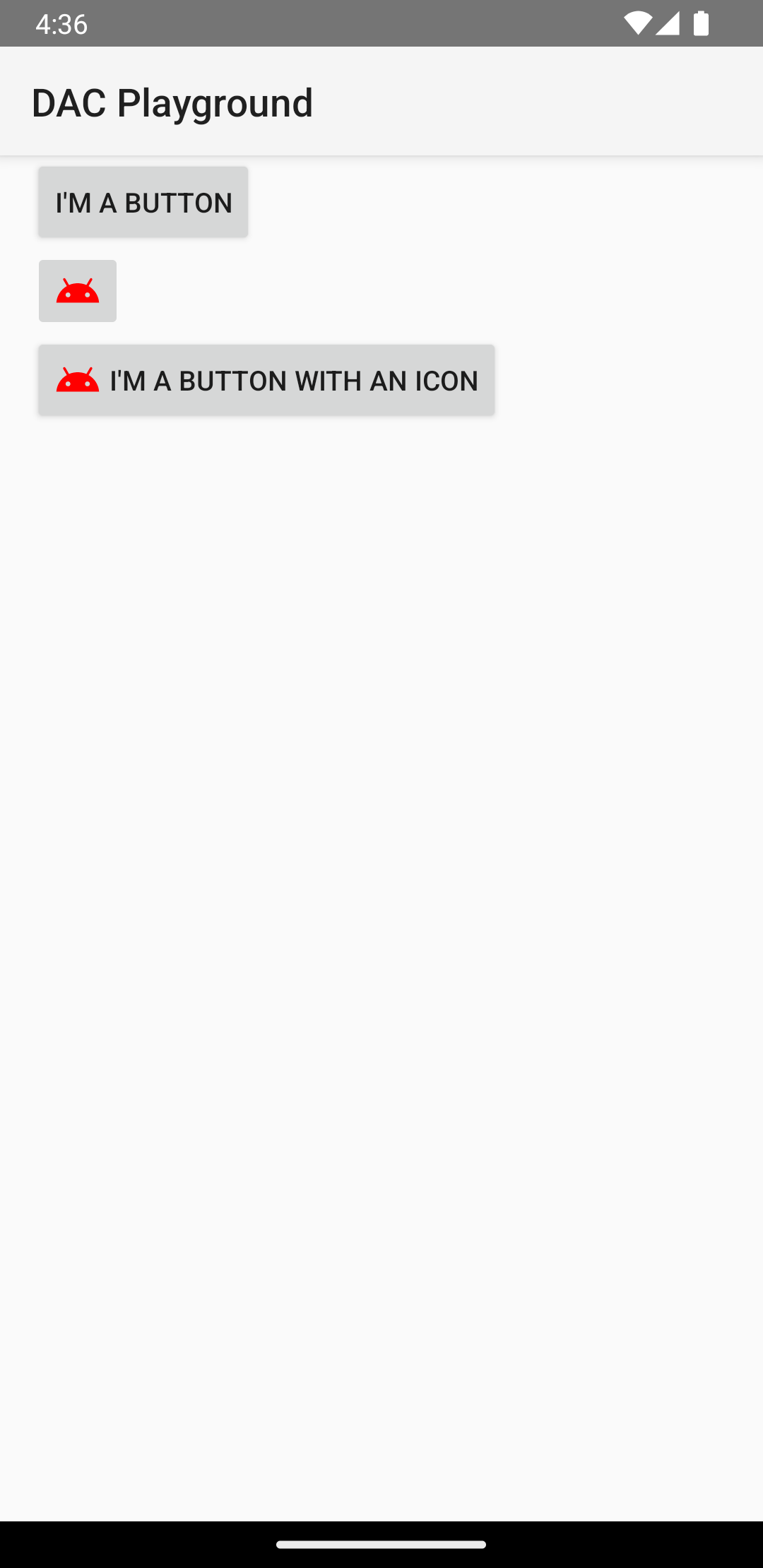
Respond to click events
When the user taps a button, the
Button object receives an
on-click event.
To declare the event handler programmatically, create an
View.OnClickListener
object and assign it to the button by calling
setOnClickListener(View.OnClickListener),
as in the following example:
Kotlin
findViewById<Button>(R.id.supabutton) .setOnClickListener { Log.d("BUTTONS", "User tapped the Supabutton") }
Java
Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.supabutton); button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(View v) { Log.d("BUTTONS", "User tapped the Supabutton"); } });
Style your button
The appearance of your button—the background image and font—varies between devices, because devices by different manufacturers often have different default styles for input controls.
To customize individual buttons with a different background, specify the
android:background attribute
with a drawable or color resource. Alternatively, you can apply a style for the button,
which works in similarly to HTML styles to define multiple style properties such as the background,
font, and size. For more information about applying styles, see
Styles and themes.
Borderless button
One design that can be useful is a "borderless" button. Borderless buttons resemble basic buttons except that they have no borders or background but still change appearance during different states, such as when tapped.
To create a borderless button, apply the
borderlessButtonStyle
style to the button, as in the following example:
<Button android:id="@+id/supabutton" style="?android:attr/borderlessButtonStyle" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="I'm a button" />
Custom background
If you want to truly redefine the appearance of your button, you can specify a custom background. Instead of supplying a simple bitmap or color, however, your background must be a state list resource that changes appearance depending on the button's current state.
You can define the state list in an XML file that defines three images or colors to use for the different button states.
To create a state list drawable for your button background, do the following:
- Create three bitmaps for the button background that represent the default, tapped, and focused button states. To ensure that your images fit buttons of various sizes, create the bitmaps as nine-patch bitmaps.
- Place the bitmaps into your project's
res/drawable/directory. Name each bitmap to reflect the button state it represents, such asbutton_default.9.png,button_pressed.9.png, andbutton_focused.9.png. - Create a new XML file in the
res/drawable/directory. Name it something likebutton_custom.xml. Insert XML like the following:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:drawable="@drawable/button_pressed" android:state_pressed="true" /> <item android:drawable="@drawable/button_focused" android:state_focused="true" /> <item android:drawable="@drawable/button_default" /> </selector>
This defines a single drawable resource that changes its image based on the current state of the button.
- The first
<item>defines the bitmap to use when the button is tapped (activated). - The second
<item>defines the bitmap to use when the button is focused, such as when the button is highlighted using the trackball or directional pad. - The third
<item>defines the bitmap to use when the button is in the default state, neither tapped nor focused.
This XML file represents a single drawable resource. When referenced by a
Buttonfor its background, the image displayed changes based on the button's state. - The first
- Apply the drawable XML file as the button background:
<Button android:id="@+id/button_send" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/button_send" android:onClick="sendMessage" android:background="@drawable/button_custom" />
For more information about this XML syntax, including how to define a button that is disabled,
hovered, or in another state, read about
StateListDrawable.

