برگه Top Down فهرستی از تماسها را نشان میدهد که در آن گسترش یک روش یا گره تابع، فراخوانهای آن را نشان میدهد. شکل 2 یک نمودار از بالا به پایین برای نمودار تماس زیر را نشان می دهد. هر فلش در نمودار از تماس گیرنده به تماس گیرنده اشاره می کند.
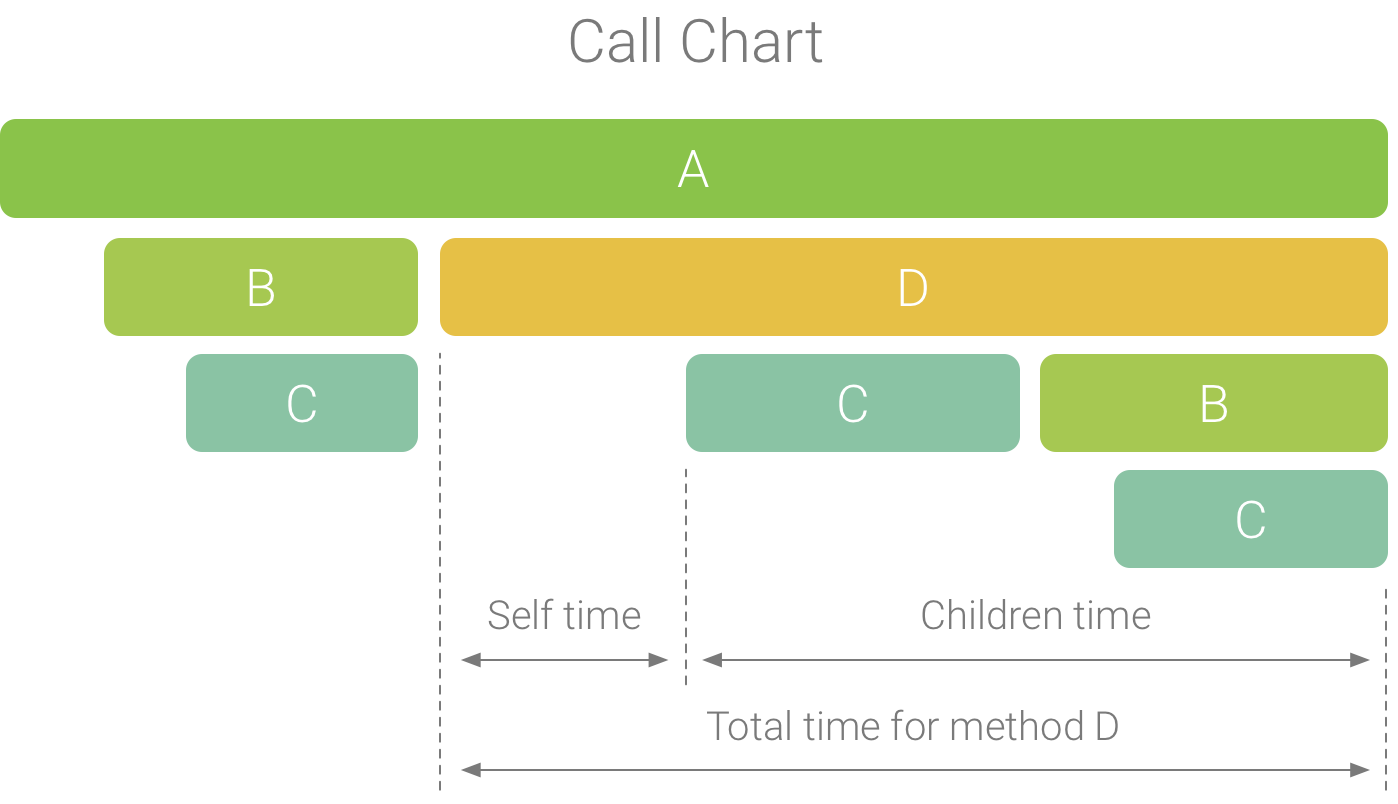
شکل 1. نمودار فراخوانی مثالی که خود، فرزندان و زمان کل را برای روش D نشان می دهد.
همانطور که در شکل 2 نشان داده شده است، گسترش گره برای روش A در تب بالا به پایین، فراخوان های آن، روش های B و D را نشان می دهد. پس از آن، گسترش گره برای روش D، فراخوان های آن، مانند روش های B و C را نشان می دهد. شبیه به Flame. برگه نمودار ، درخت از بالا به پایین اطلاعات ردیابی را برای روشهای یکسانی که پشته تماس یکسانی را به اشتراک میگذارند جمعآوری میکند. یعنی تب Flame chart یک نمایش گرافیکی از تب Top Down را ارائه می دهد.
برگه Top Down اطلاعات زیر را برای کمک به توصیف زمان صرف شده در CPU در هر تماس ارائه می دهد (زمان ها نیز به صورت درصدی از زمان کل رشته در محدوده انتخاب شده نشان داده می شوند):
- Self: زمانی که فراخوانی متد یا تابع صرف اجرای کد خود می شود و نه فراخوانی آن، همانطور که در شکل 1 برای روش D نشان داده شده است.
- فرزندان: زمانی که متد یا فراخوانی تابع صرف اجرای فراخوانهای خود و نه کد خود میشود، همانطور که در شکل 1 برای روش D نشان داده شده است.
- مجموع: مجموع زمان خود و فرزندان روش. این نشان دهنده کل زمانی است که برنامه برای اجرای یک تماس صرف کرده است، همانطور که در شکل 1 برای روش D نشان داده شده است.
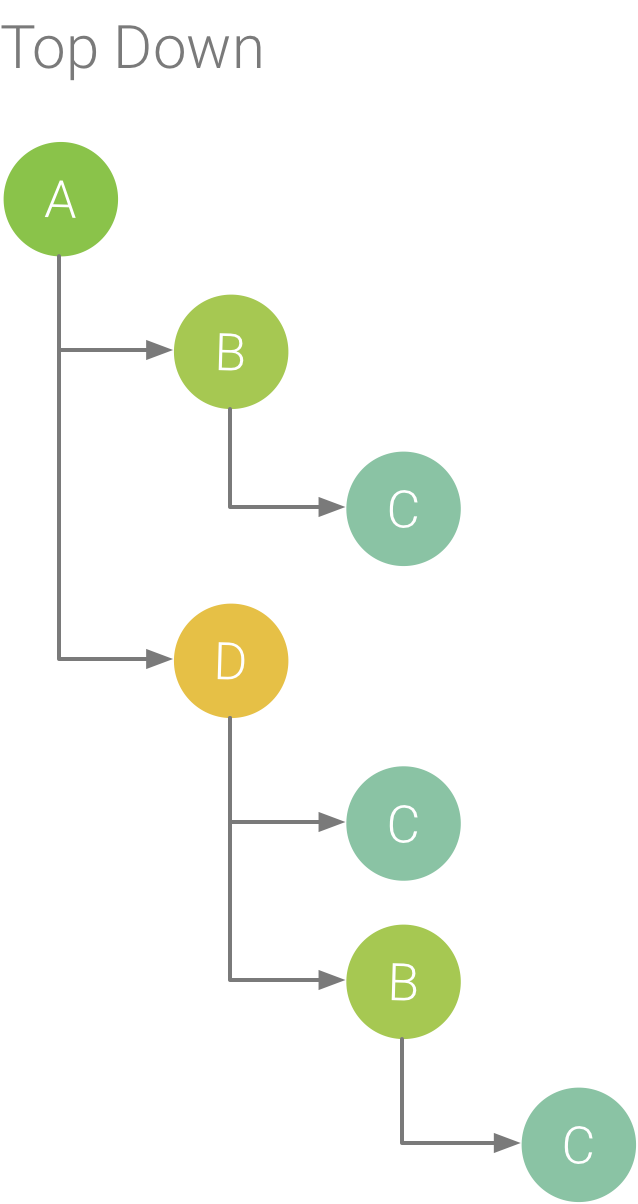
شکل 2. درخت از بالا به پایین.
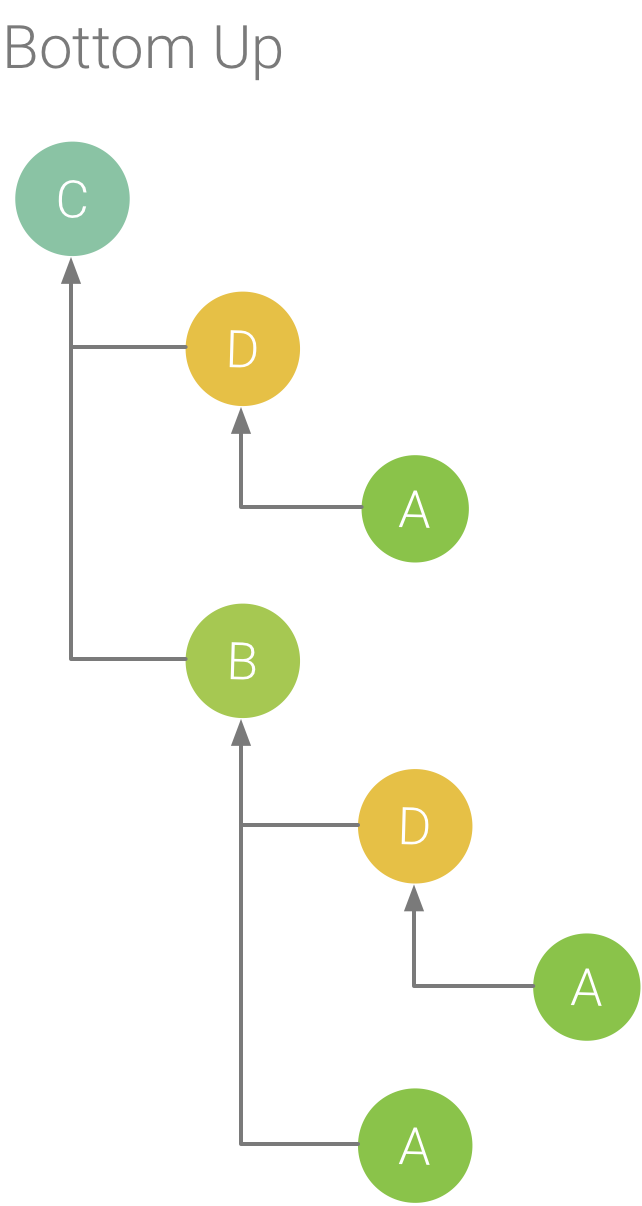
شکل 3. درخت پایین به بالا برای روش C از شکل 5.
تب Bottom Up فهرستی از تماسها را نشان میدهد که در آن با گسترش یک تابع یا گره روش، تماسگیرندگان آن نمایش داده میشود. با استفاده از ردیابی مثال نشان داده شده در شکل 2، شکل 3 یک درخت از پایین به بالا برای روش C ارائه می کند. باز کردن گره برای روش C در درخت پایین به بالا، هر یک از فراخواننده های منحصر به فرد آن، روش های B و D را نمایش می دهد. توجه داشته باشید که، اگرچه B C را فراخوانی می کند. دو بار، B فقط یک بار هنگام گسترش گره برای روش C در درخت پایین به بالا ظاهر می شود. پس از آن، گسترش گره برای B، فراخوان دهنده آن، روش های A و D را نمایش می دهد.
تب Bottom Up برای مرتبسازی روشها یا توابع بر اساس مواردی که بیشترین (یا کمترین) زمان CPU را مصرف میکنند مفید است. میتوانید هر گره را بررسی کنید تا مشخص کنید کدام تماسگیرندگان بیشترین زمان CPU را برای فراخوانی آن روشها یا توابع صرف میکنند. در مقایسه با درخت از بالا به پایین، اطلاعات زمان بندی برای هر روش یا تابع در درخت پایین به بالا به متد بالای هر درخت (گره بالا) اشاره دارد. زمان CPU نیز به عنوان درصدی از زمان کل رشته در طول آن ضبط نشان داده می شود. جدول زیر به توضیح چگونگی تفسیر اطلاعات زمان بندی برای گره بالا و فراخوان دهنده های آن (گره های فرعی) کمک می کند.
| خود | بچه ها | مجموع | |
|---|---|---|---|
| روش یا تابع در بالای درخت پایین به بالا (گره بالا) | کل زمانی را که متد یا تابع صرف اجرای کد خود کرده است و نه فراخواننده هایش را نشان می دهد. در مقایسه با درخت از بالا به پایین، این اطلاعات زمان بندی مجموعه ای از تماس های این روش یا تابع در طول مدت ضبط را نشان می دهد. | کل زمانی را که متد یا تابع صرف اجرای فراخوان های خود کرده است و نه کد خود را نشان می دهد. در مقایسه با درخت بالا به پایین، این اطلاعات زمانبندی مجموع تماسهای این روش یا فراخوانهای تابع را در طول مدت ضبط نشان میدهد. | مجموع زمان خود و زمان فرزندان. |
| تماس گیرندگان (گره های فرعی) | مجموع زمان خود تماس گیرنده را هنگام فراخوانی توسط تماس گیرنده نشان می دهد. با استفاده از درخت پایین به بالا در شکل 6 به عنوان مثال، زمان خود برای روش B برابر است با مجموع زمان های خود برای هر اجرای روش C هنگامی که توسط B فراخوانی می شود. | مجموع زمان فرزندان تماس گیرنده را هنگام فراخوانی توسط تماس گیرنده نشان می دهد. با استفاده از درخت پایین به بالا در شکل 6 به عنوان مثال، زمان فرزندان برای روش B برابر است با مجموع دفعات فرزندان برای هر اجرای روش C هنگامی که توسط B فراخوانی می شود. | مجموع زمان خود و زمان فرزندان. |
توجه: برای یک ضبط مشخص، زمانی که نمایهساز به حد مجاز اندازه فایل برسد، Android Studio جمعآوری دادههای جدید را متوقف میکند (اما این کار ضبط را متوقف نمیکند). این معمولاً هنگام اجرای ردیابیهای ابزاردار خیلی سریعتر اتفاق میافتد، زیرا این نوع ردیابی در مقایسه با ردیابی نمونهبرداری شده، دادههای بیشتری را در زمان کوتاهتری جمعآوری میکند. اگر زمان بازرسی را به دورهای از ضبط که پس از رسیدن به حد مجاز رخ داده است افزایش دهید، دادههای زمانبندی در صفحه ردیابی تغییر نمیکند (زیرا داده جدیدی در دسترس نیست). علاوه بر این، زمانی که فقط بخشی از ضبط را انتخاب می کنید که داده ای در دسترس ندارد، پنجره ردیابی NaN را برای اطلاعات زمان نمایش می دهد.

