Apps often need to display data in similarly styled containers, such as
containers that hold information about the items in a list. The system provides
the CardView API for you to
show information in cards that have a consistent look across the platform. For
example, cards have a default elevation above their containing view group, so
the system draws shadows below them. Cards provide a way to contain a group of
views while providing a consistent style for the container.
Add the dependencies
The CardView widget is part of AndroidX. To use it in
your project, add the following dependency to your app module's build.gradle
file:
Groovy
dependencies { implementation "androidx.cardview:cardview:1.0.0" }
Kotlin
dependencies { implementation("androidx.cardview:cardview:1.0.0") }
Create cards
To use a CardView, add it to your layout file. Use it as a view group to
contain other views. In the following example, the CardView contains an
ImageView and a few TextViews to display some information to the user:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:padding="16dp"
android:background="#E0F7FA"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<androidx.cardview.widget.CardView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent">
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:padding="4dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/header_image"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:src="@drawable/logo"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title"
style="@style/TextAppearance.MaterialComponents.Headline3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="4dp"
android:text="I'm a title"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/header_image" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/subhead"
style="@style/TextAppearance.MaterialComponents.Subtitle2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="4dp"
android:text="I'm a subhead"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/title" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/body"
style="@style/TextAppearance.MaterialComponents.Body1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="4dp"
android:text="I'm a supporting text. Very Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum."
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/subhead" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</androidx.cardview.widget.CardView>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
The previous code snippet produces something similar to the following, assuming you use the same Android logo image:
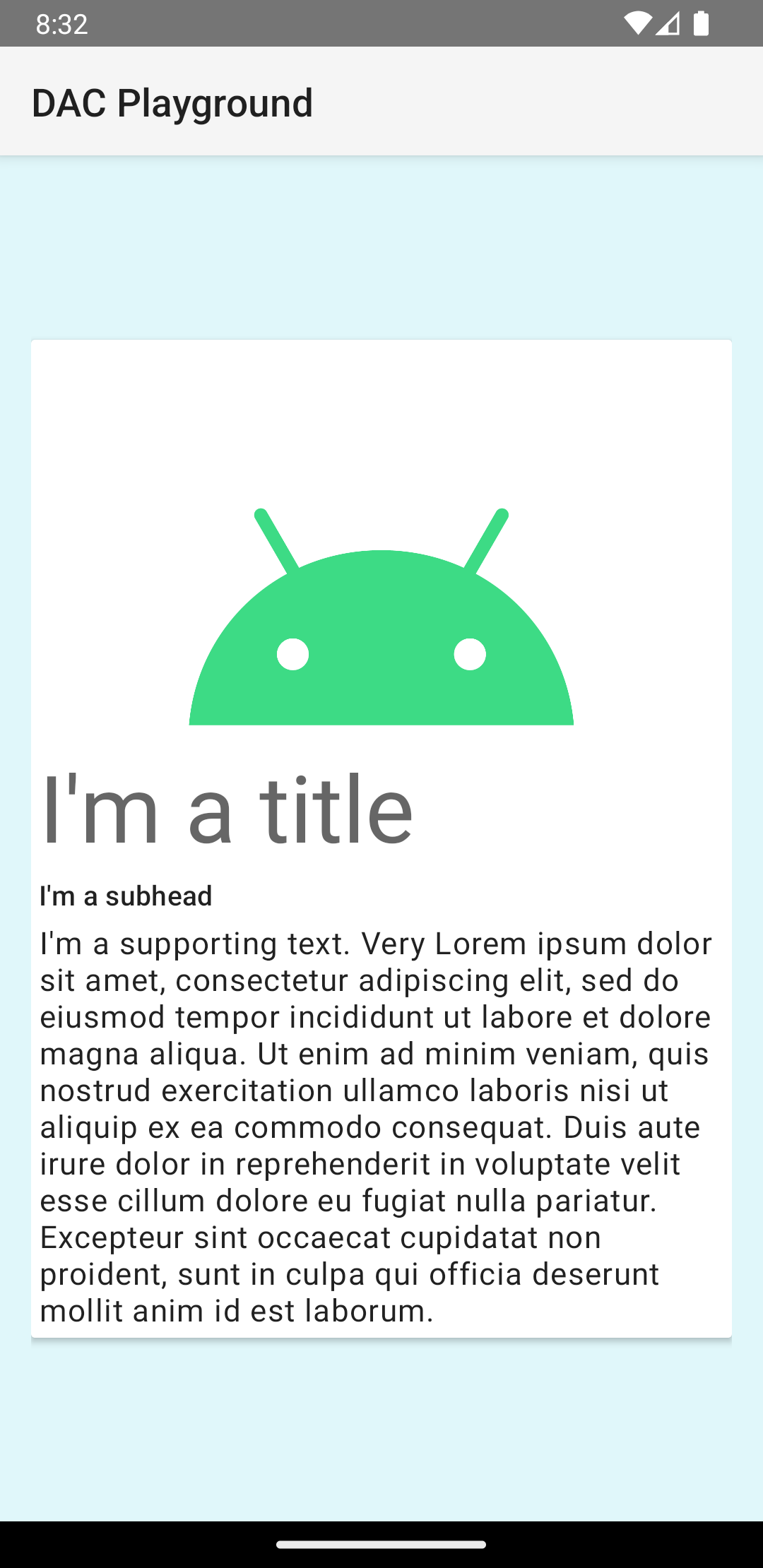
The card in this example is drawn to the screen with a default elevation, which
causes the system to draw a shadow under it. You can provide a custom elevation
for a card with the card_view:cardElevation attribute. A card at a higher
elevation has a more pronounced shadow, and a card at a lower elevation has a
lighter shadow. CardView uses real elevation and dynamic shadows on Android
5.0 (API level 21) and higher.
Use these properties to customize the appearance of the CardView widget:
- To set the corner radius in your layouts, use the
card_view:cardCornerRadiusattribute. - To set the corner radius in your code, use the
CardView.setRadiusmethod. - To set the background color of a card, use the
card_view:cardBackgroundColorattribute.

