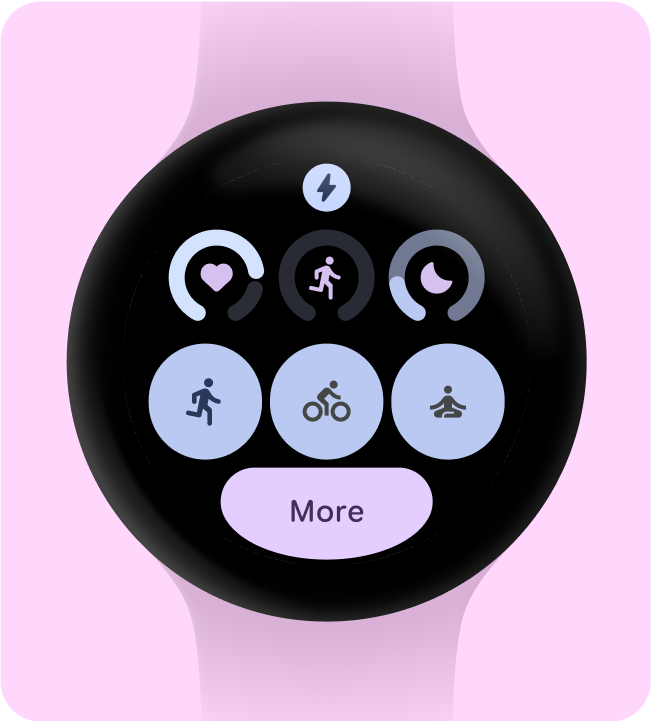
資訊方塊的最佳做法
透過集合功能整理內容
你可以依據偏好儲存及分類內容。

黑底設計
在 Wear OS 上設計黑色背景非常重要,原因有兩個:
- 電池效率:螢幕上每個亮起的像素都會消耗電力。使用黑色背景可減少有效像素數量,延長電池續航力。
- 完美美感:黑色背景可視覺上縮小錶框,營造出延伸至裝置邊緣的連續表面錯覺。在這個空間中加入 UI 元素,可進一步強化這項效果。
check_circle
執行此動作
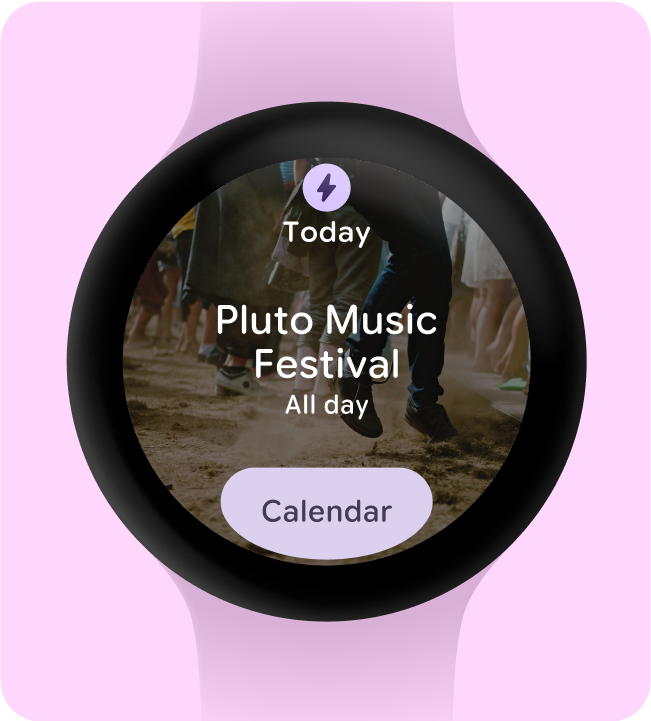
一律將背景顏色設為黑色。
cancel
請勿這麼做
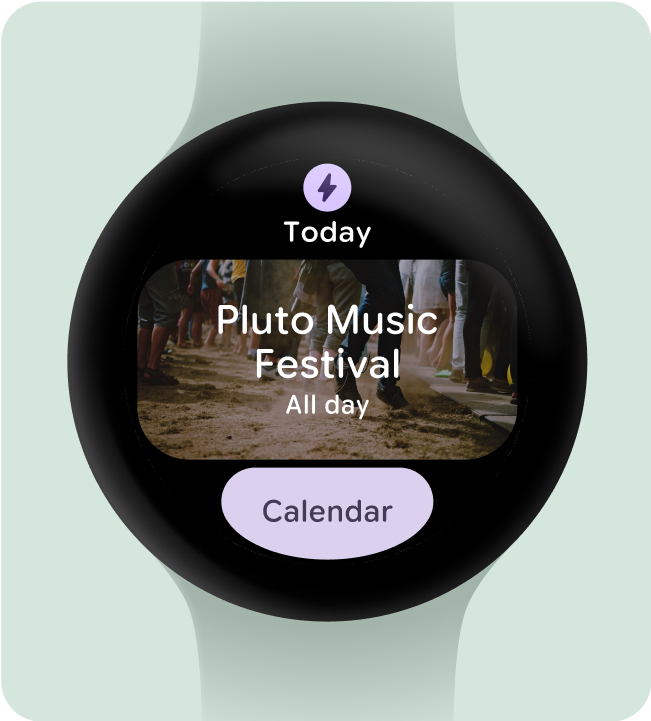
請勿將背景設為全出血圖片或封閉顏色。
只包含必要元素
在使用者捲動資訊方塊輪轉介面時,Wear OS 會自動顯示永久應用程式圖示。應用程式圖示不應設計為資訊方塊的一部分。
如果資訊方塊採用動態主題,請務必提供單色應用程式圖示。請參閱 Android 產品圖示規範,瞭解如何建立品牌的應用程式圖示。
check_circle
執行此動作
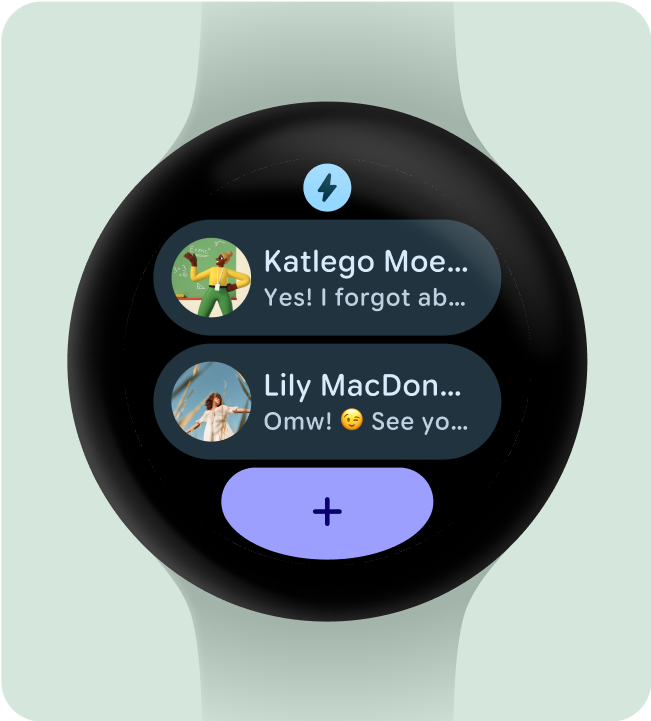
當使用者捲動資訊方塊輪轉介面時,Wear OS 可能會自動顯示應用程式圖示。您不需要在資訊方塊設計中放入應用程式圖示。
cancel
請勿這麼做
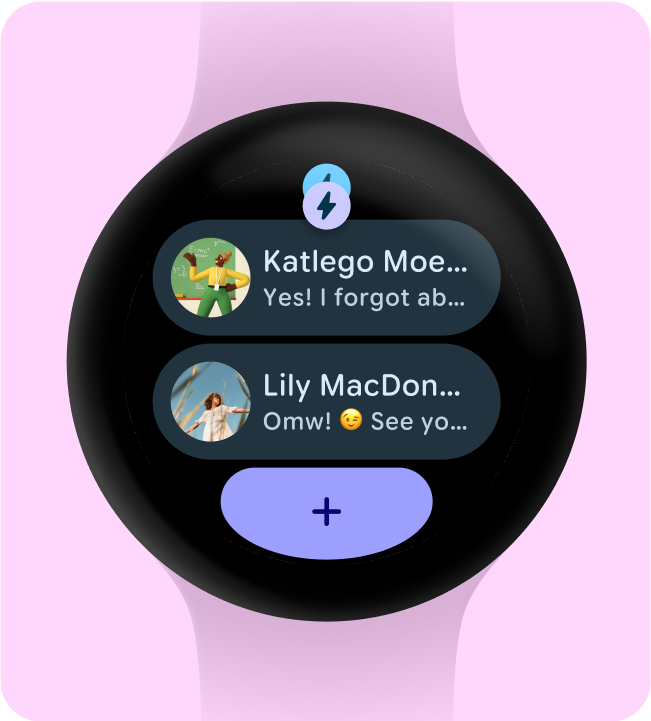
請勿在資訊方塊設計中新增應用程式圖示,因為如果在系統層級顯示,圖示可能會重複顯示/重疊。
隱藏應用程式標題,確保最少輕觸目標
為確保在較小的螢幕上有足夠的空間放置互動元素,如果資訊方塊使用兩列 (以及底部區段),應用程式標題就會隱藏。這可確保資料列的高度足夠 (至少 48dp)。標題可以在較大的螢幕上重新顯示 (225dp 以上)。
check_circle
執行此動作
在小螢幕上,應用程式會隱藏標題,確保兩個資料列的最小高度和輕觸目標為 48dp。
cancel
請勿這麼做
如果您未在小螢幕上隱藏應用程式標題,且有兩行,元件的高度就不會遵循無障礙標準,且小於最小輕觸目標大小。在這個範例中,按鈕的空間小於 48dp,因此會遭到裁剪。
選擇要強調的單一主要用途
為了確保使用者知道如何操作每個資訊方塊 (無論是開啟應用程式、啟動活動,還是瞭解更多資訊),我們需要在其版面配置中加入至少一個互動元素。
check_circle
執行此動作
這個資訊方塊的效果不錯,因為它提供少量選項,並讓使用者可以查看更多選項
cancel
請勿這麼做
這個解決方案對使用者較不實用,因為提供的選項太多,導致使用者無法做出決定
至少包含一個容器
應用程式中的每個資訊方塊都必須包含至少一個容器元素,且可完全點選,連結至應用程式中的對應畫面。資訊方塊的資訊,無論是包含在容器中或單獨顯示,都必須清楚說明連結的內容或可用的動作。
如果使用按鈕,則應遵循標準設計慣例,並清楚標示功能。
check_circle
執行此動作
這個資訊方塊運作良好,因為使用者可以對每項提供的功能採取行動,且這些功能都有明確的輕觸操作元素。
cancel
應避免的做法
這個資訊方塊的效果較差,因為它沒有清楚說明使用者可以輕觸內容查看其他資訊
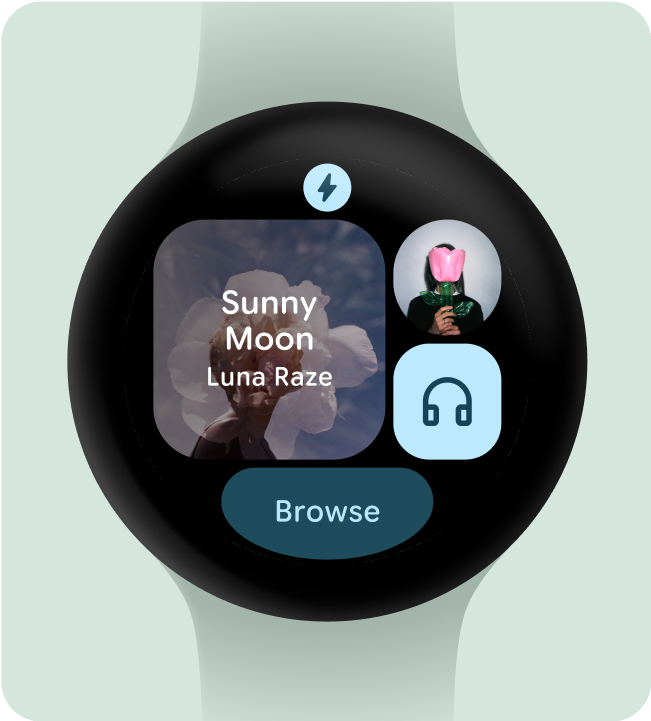
讓使用者立即瞭解動作
手錶上的體驗沒有充足的空間可用來傳達意義,因此最有效的資訊方塊應具備可輕鬆預測的互動元件。
check_circle
執行此動作
成功的資訊方塊會充分利用可用的空間,清楚說明每個動作的結果
cancel
請勿這麼做
這個資訊方塊中的動作不明確,包含專輯封面的容器會將使用者帶往哪裡?是否與「播放」按鈕不同?
視覺化呈現動作優先順序
為了協助使用者瞭解資訊方塊上最重要的動作,請視覺上優先顯示互動式容器。
- 在主要動作按鈕上使用主要顏色。
- 在次要動作中使用次要/三次色
check_circle
執行此動作
這個資訊方塊使用填滿 (具有主要和次要顏色角色) 與透明的三次底部按鈕角色組合,並採用色調填滿樣式
cancel
請勿這麼做
這個資訊方塊包含太多使用填充樣式按鈕的情況,而且所有按鈕都使用主要顏色角色
簡化為較少的容器
資訊方塊應避免使用多個互動元件來觸發特定動作,而是嘗試將整體版面配置簡化為較少的容器。
check_circle
執行此動作
這個資訊方塊會使用多個容器,每個容器都會做為按鈕執行特定動作,例如啟動計時器或建立新的計時器
cancel
請勿這麼做
由於所有資訊都會導向相同位置,因此在此處使用 4 個容器並非必要
使用容器來執行功能
為確保使用者能預測資訊方塊中的每個元件會執行哪些操作,我們不建議使用容器做為裝飾或結構用途,以免點選後沒有任何反應。
check_circle
執行此動作
這個解決方案有效,是因為資訊方塊的唯一動作是建立流程,所有其他內容都會浮動在黑色背景上
cancel
請勿這麼做
這個資訊方塊會讓使用者感到困惑,因為他們似乎可以與所有容器互動
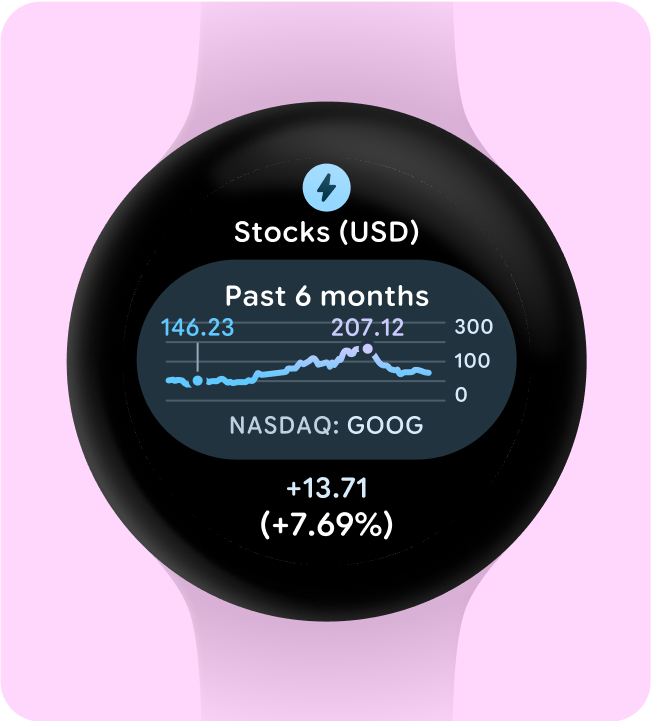
以一目瞭然的方式呈現圖表
一目瞭然是 Wear OS 設計的關鍵。由於螢幕時間有限 (約 7 秒),請以清晰的格式優先顯示重要資訊,讓觀眾一目瞭然。
請記住,手錶可補足手機的功能,讓您快速存取重要詳細資料。
check_circle
執行此動作
以一目了然的方式呈現數值或統計資訊,讓使用者根據需要,輕觸以瞭解應用程式的更多資訊
cancel
請勿這麼做
在資訊方塊上顯示詳細數值或統計資訊
這個頁面中的內容和程式碼範例均受《內容授權》中的授權所規範。Java 與 OpenJDK 是 Oracle 和/或其關係企業的商標或註冊商標。
上次更新時間:2025-07-27 (世界標準時間)。
[[["容易理解","easyToUnderstand","thumb-up"],["確實解決了我的問題","solvedMyProblem","thumb-up"],["其他","otherUp","thumb-up"]],[["缺少我需要的資訊","missingTheInformationINeed","thumb-down"],["過於複雜/步驟過多","tooComplicatedTooManySteps","thumb-down"],["過時","outOfDate","thumb-down"],["翻譯問題","translationIssue","thumb-down"],["示例/程式碼問題","samplesCodeIssue","thumb-down"],["其他","otherDown","thumb-down"]],["上次更新時間:2025-07-27 (世界標準時間)。"],[],[]]