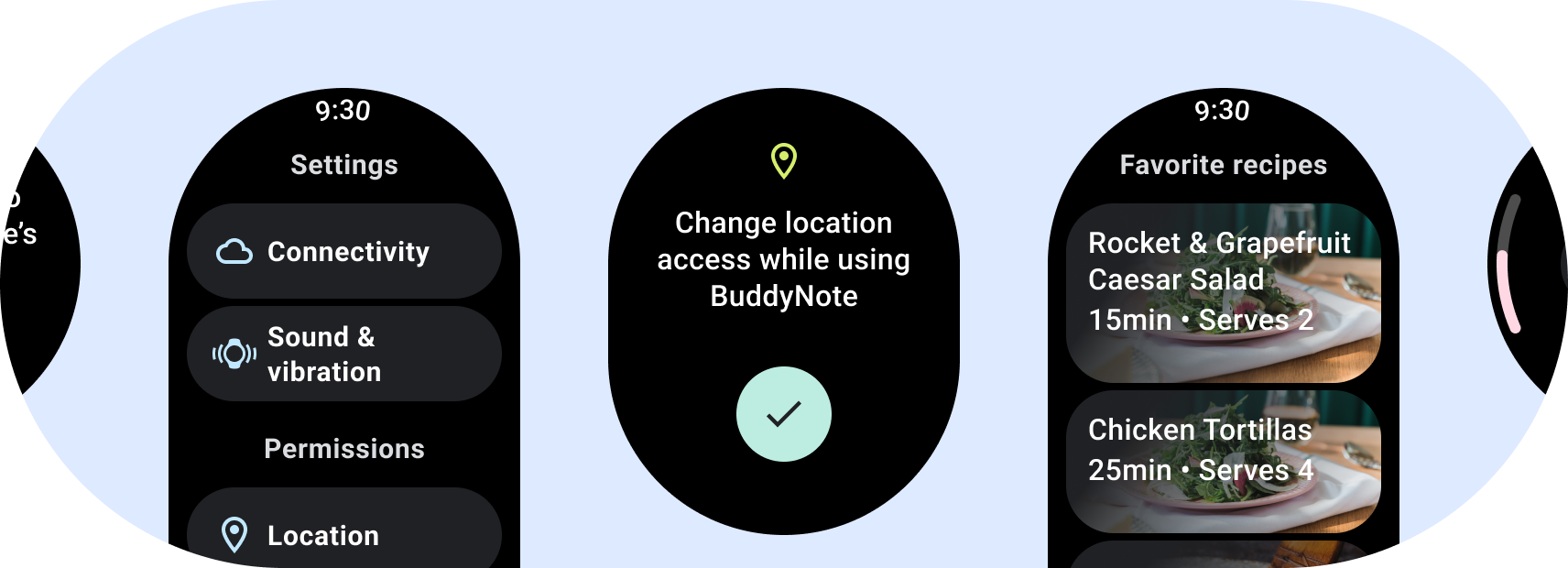
設計 Wear OS 應用程式時,請特別留意您選用的版面配置 每個服務項目因為 Wear OS 可以在圓形螢幕上執行, 標準版面配置有兩種類別 (標準版面配置則適用於手持裝置) 。
非捲動應用程式版面配置
不捲動的版面配置,著重於一目瞭然的資訊,為使用者提供有價值的資訊 或是完全沒有互動因此,建構 回應這些版面配置:
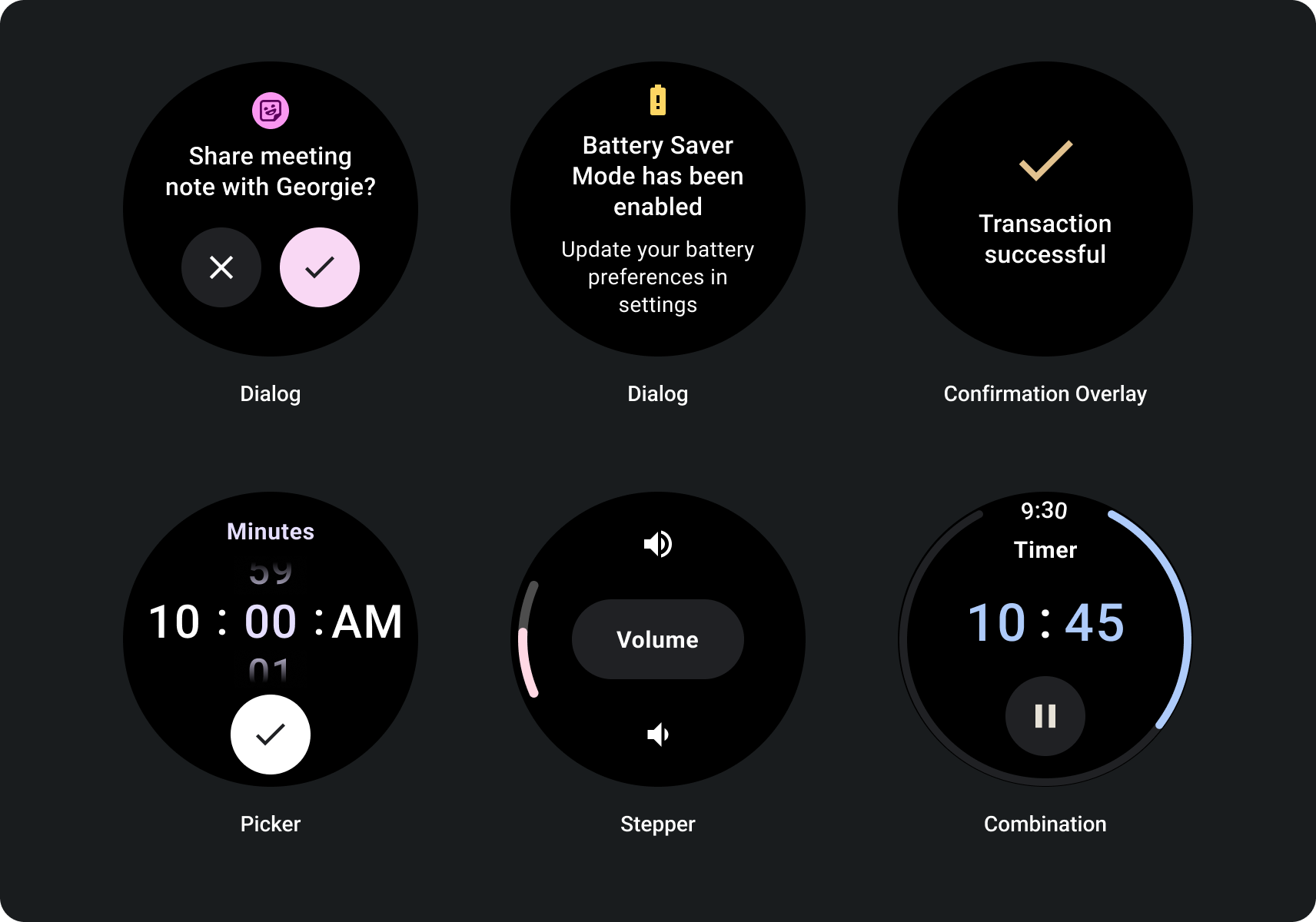
打造回應式非捲動式檢視畫面
- 針對語言、字型縮放、裝置和變數的組合進行測試 內容。
- 只在已知或控制內容時使用無法捲動的版面配置 或者如果必須使用特定設計
- 在版面配置中套用建議頂端、底部和側邊邊界。
- 以百分比值定義其他可能影響內容的位置的利潤 擷取。
- 排列元素,盡可能善用 在不同大小的裝置中維持平衡。
捲動應用程式版面配置
如果網頁包含的資訊多於單一畫面可容納,或 如要支援更長、更身歷其境的歷程,請使用捲動功能 檢視畫面。
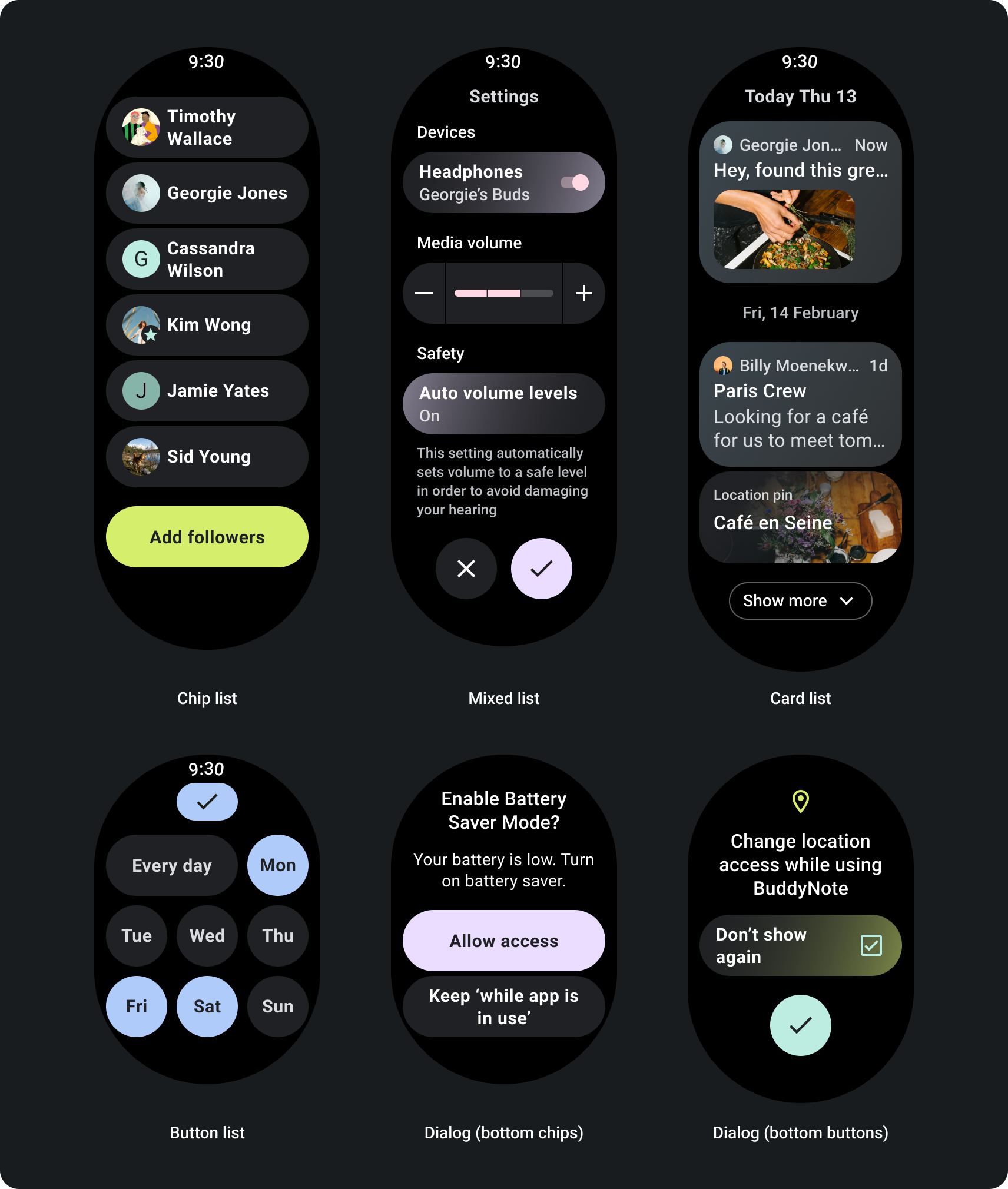
打造回應式捲動檢視畫面
- 套用建議頂端、底部和側邊邊界。
- 在百分比值中定義外邊界,以避免在 可捲動容器的開始和結尾
- 在 UI 元素之間套用固定 DP 值的邊界。
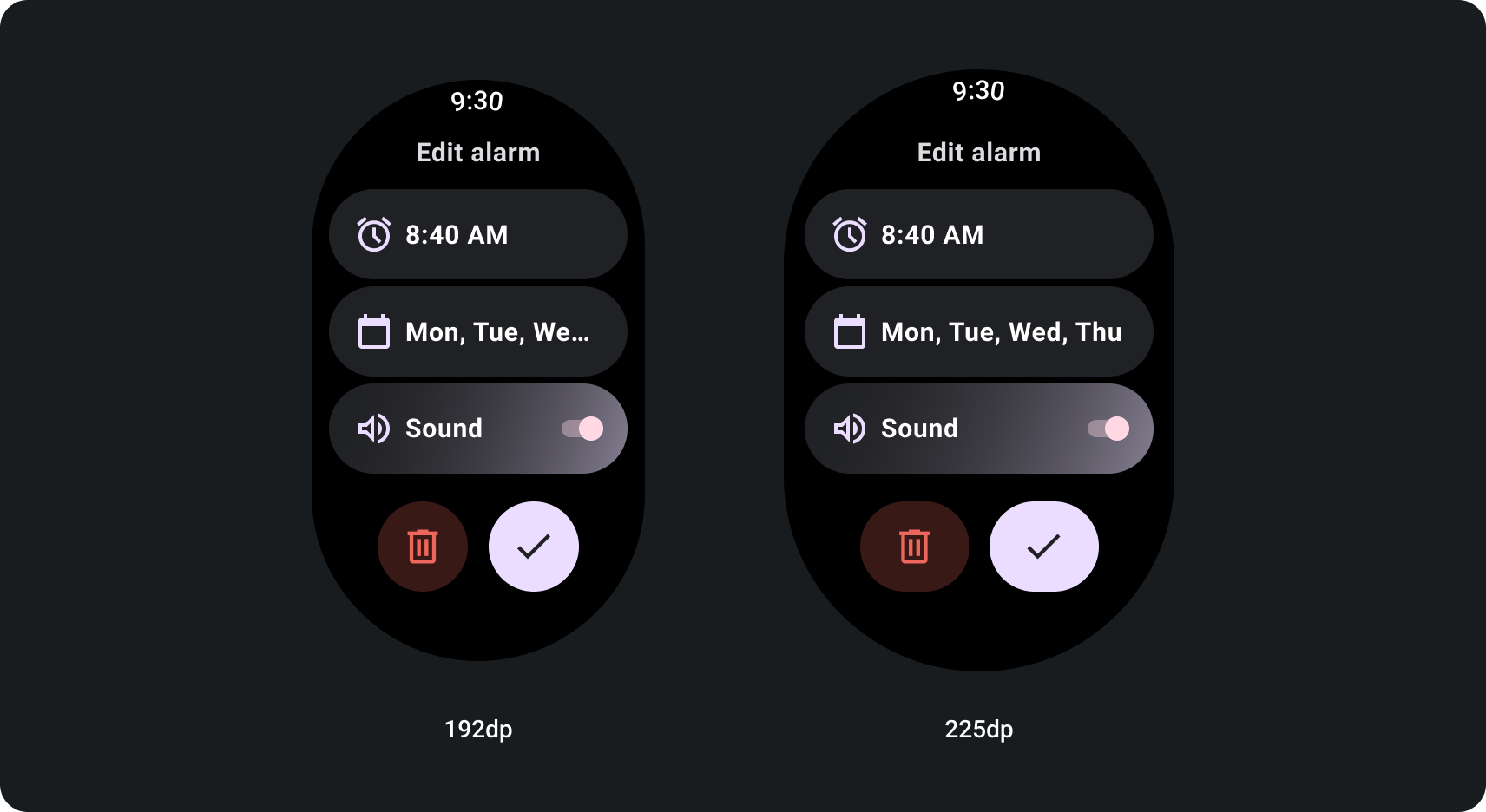
如何使用螢幕大小中斷點建構自動調整式捲動檢視畫面
採用回應式設計做法的捲動檢視畫面,通常會適應多種 螢幕大小但在特殊情況下,您可以使用中斷點 覆寫尺寸並擴增版面配置,以顯示更多選項、改善 方便瀏覽,或是讓內容更符合畫面大小。以下範例 顯示了在較大的螢幕上,如何展開底部的兩個按鈕:
Figma 設計套件
前往設計套件下載頁面,瞭解內建功能的設計版面配置 元件、選項和建議,以建立不同的應用程式和資訊方塊 遵循最佳做法的設計

