Wear OS 手錶可能會有不同的硬體按鈕設定。本指南將說明每種按鈕類型的最佳用途。
按鈕類型
Wear OS 裝置最常見的按鈕類型如下。
OS 按鈕

多功能按鈕

按壓狀態
您可以透過以下方式和 Wear OS 按鈕互動。
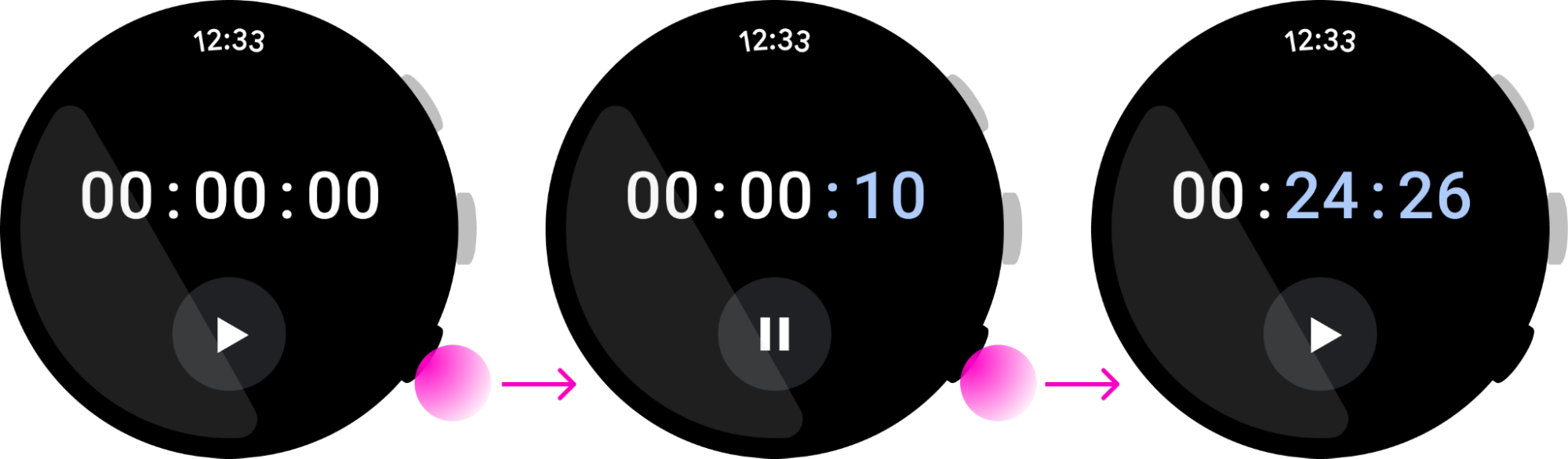
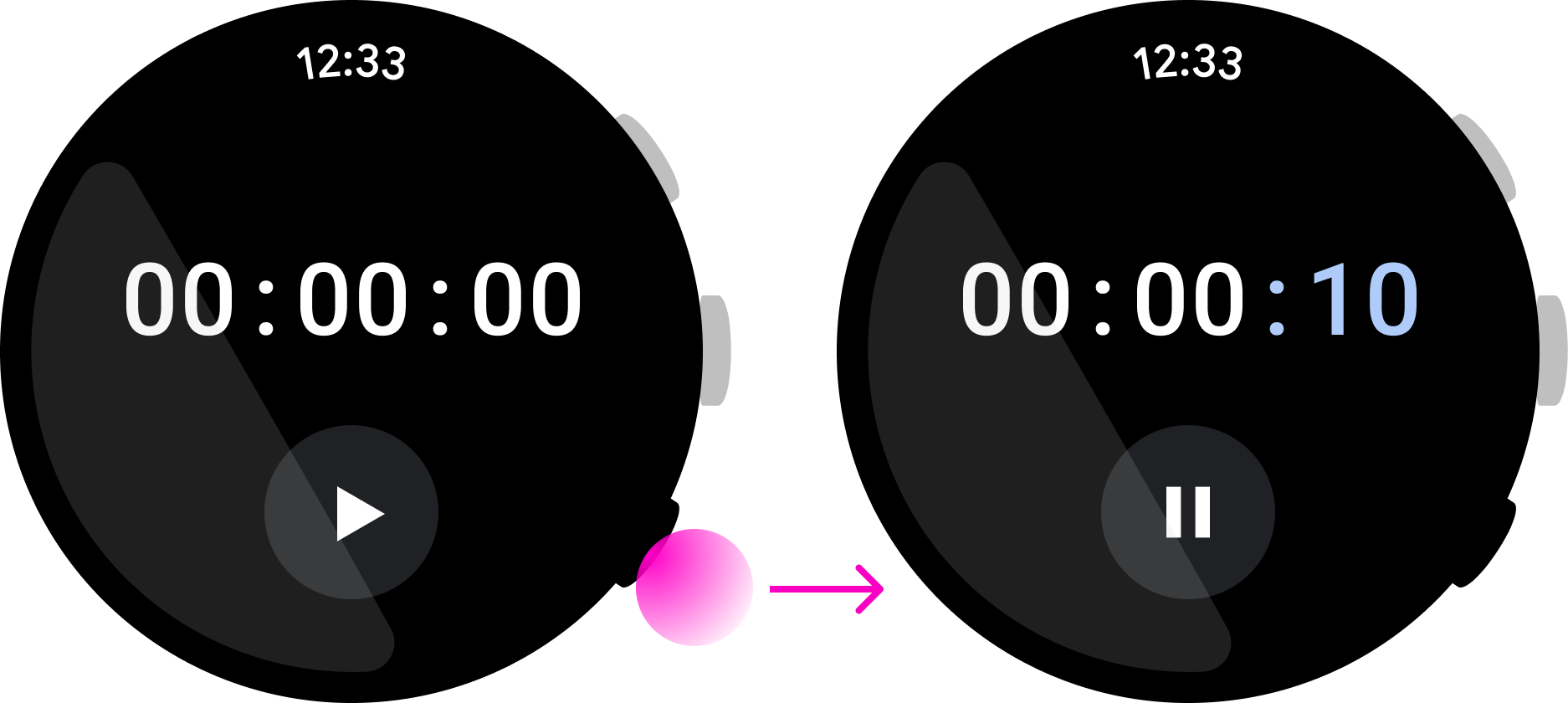
按一下

圖 1. 使用者按下按鈕後快速放開。
按住

圖 2. 使用者按住按鈕達 500 毫秒以上。
多功能按鈕對應
只要符合應用程式的用途,應用程式便能將多功能按鈕指派給各種動作。應用程式不一定要為多功能按鈕指派動作。
如果符合下列任一條件,您便可在應用程式中使用多功能按鈕:
- 應用程式有明顯的二元動作 (如播放/暫停)。
- 使用您的應用程式時多半不需查看螢幕。

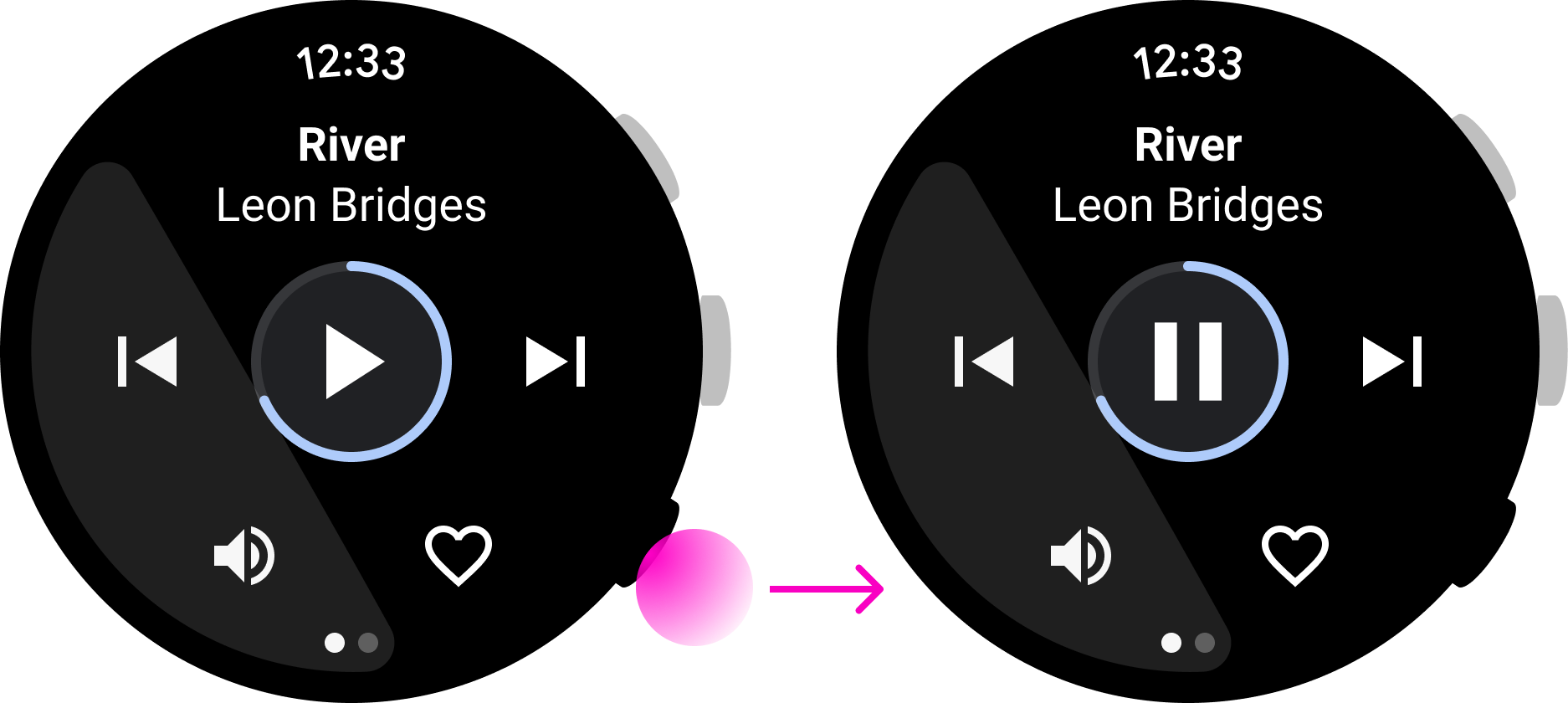
圖 3. 這個健身應用程式將暫停/繼續動作指派給多功能按鈕,使用者不用查看螢幕就能執行動作。
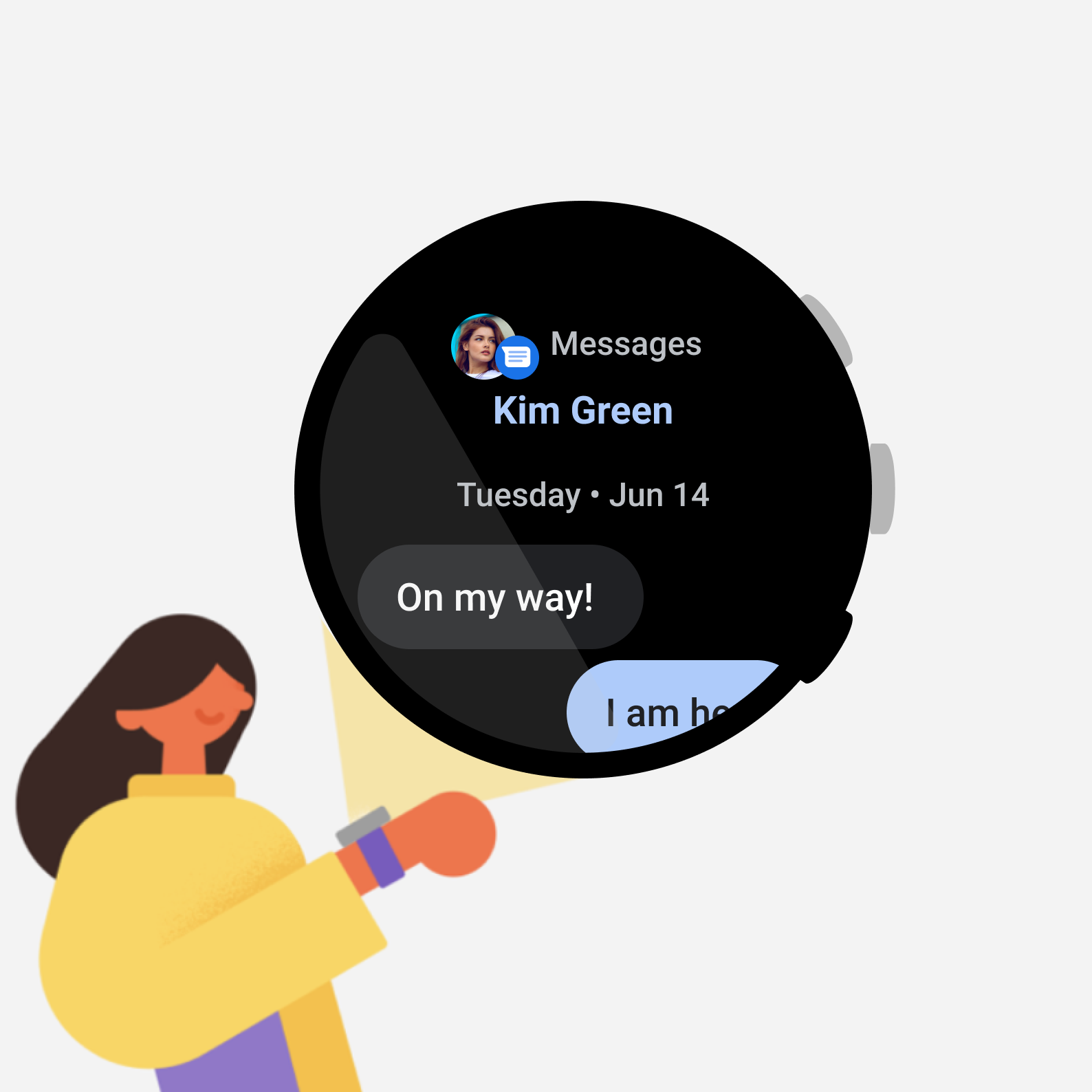
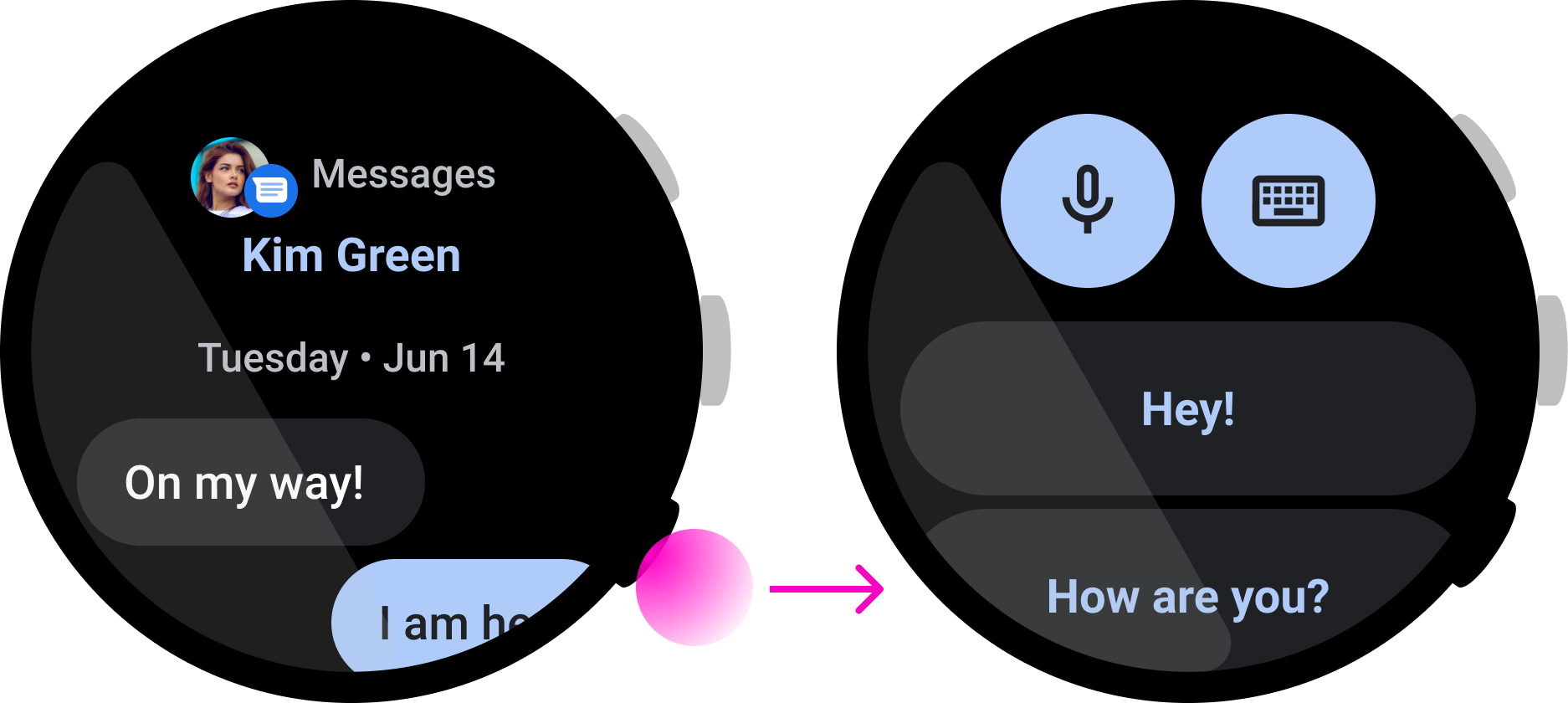
圖 4. 這個訊息應用程式提供回覆動作,這個動作需要進行多個步驟,無法藉由按一下按鈕完成。
二元動作
二元動作可以幫助使用者瞭解按下按鈕後會發生什麼情況。例如碼表上的「開始」和「停止」就構成一種二元動作,也很適合多功能按鈕使用。
使用多功能按鈕做為替代方案
由於某些手錶未設有多功能按鈕,因此請讓使用者得以透過螢幕上的 UI 元素存取多功能按鈕。不過,您也可以把多功能按鈕當成螢幕按鈕的替代方案。
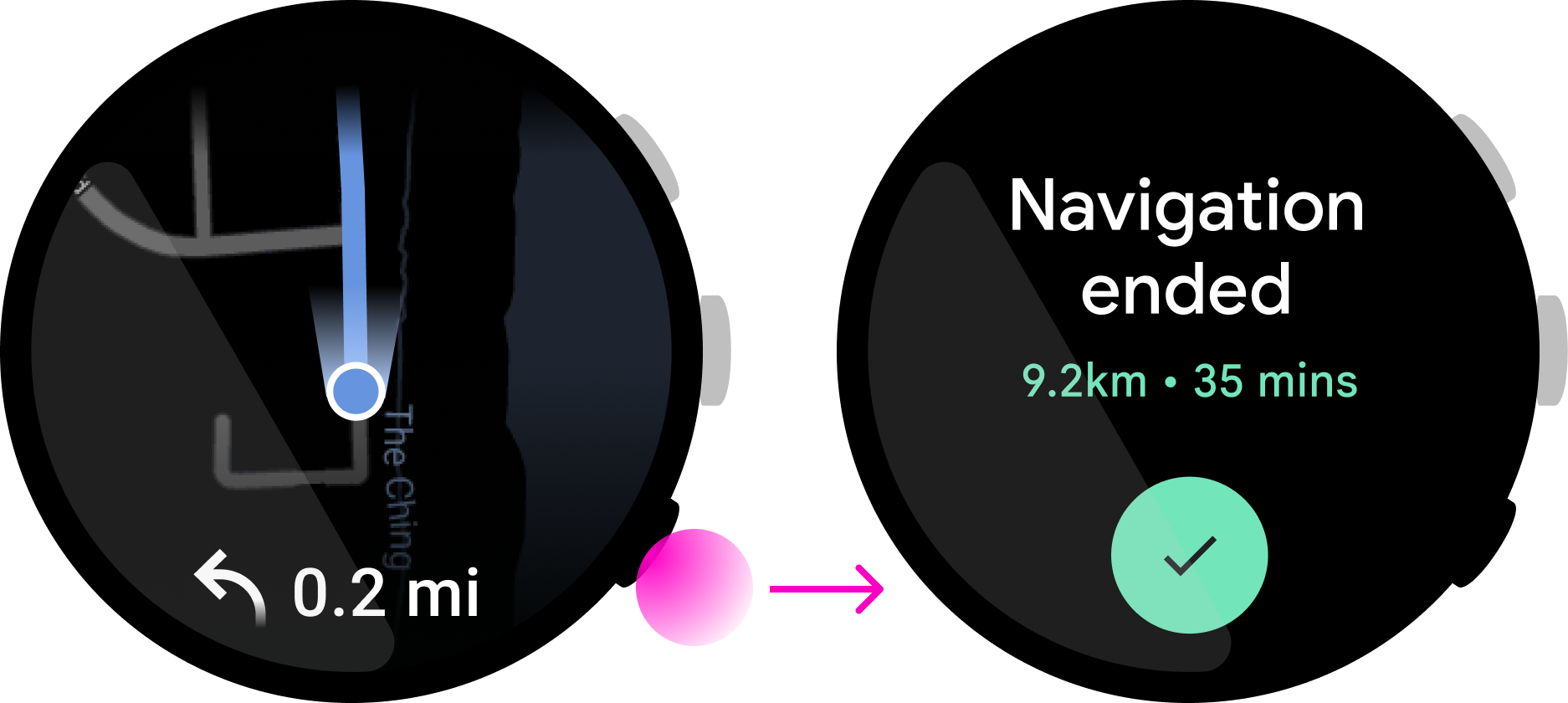
請勿使用多功能按鈕代表螢幕 UI 元素無法執行的動作。
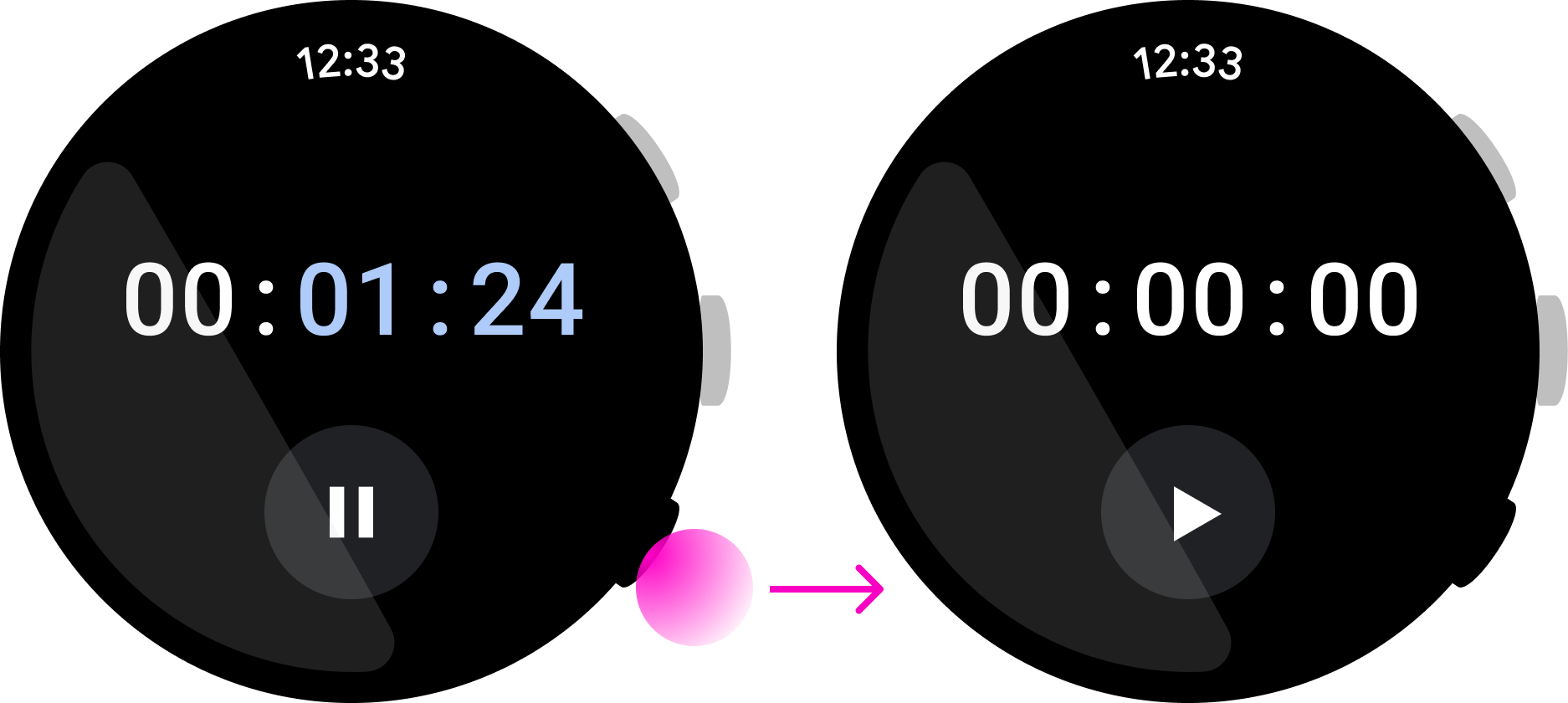
注重簡單明瞭
按下多功能按鈕會立即執行指派的動作。為了避免使用者需要查看螢幕,請用多功能按鈕執行按一下就能完成的動作。
正確做法
錯誤做法
這個音樂應用程式可讓使用者快速暫停播放歌曲,非常適合多功能按鈕使用。不過,這個訊息應用程式在使用者按下按鈕後會開始回覆動作,而使用者可能需要查看訊息之後才能完成動作。因此,這並非適合多功能按鈕的互動方式。
可復原
請讓按鈕動作可以復原。請勿用多功能按鈕觸發破壞性動作,例如刪除資料或停止持續進行的活動。舉例來說,按下這個地圖應用程式的多功能按鈕就會執行「停止導航」動作,這樣可能會導致使用者在重要時刻迷失方向。