智慧手錶的螢幕尺寸比手持裝置小,因此請務必排列顯示元素,以便使用者能夠有效存取,並且有效率地使用可用的螢幕空間。如要讓項目符合螢幕大小,請使用 Material 指南中指定的正確邊框間距和邊界大小。
即使設計符合螢幕大小,使用者執行下列任一操作時,介面元素可能會遭到截斷或裁剪:
- 變更顯示語言。
- 變更文字大小。
- 啟用「粗體文字」系統設定。
測試設計時請務必考量這些事項,確保設計能完美適應不同的使用者環境。
讓互動元素保持完整顯示
如果您的介麵包含互動式元素,請檢查使用者能否完全捲動這些元素,特別是將這些元素放在網頁邊緣時。如果您的應用程式使用 Horologist 程式庫,請使用 responsive() 版面配置工廠。否則,請使用空格字元,並在 ScalingLazyColumn 物件的頂端和底部加上邊界,避免系統一律裁剪第一個和最後一個清單項目。
密集的版面配置使用方塊 (而非資訊卡)
如果您需要更密集的版面配置,請使用 CompactChip,而非資訊卡。資訊卡的顯示區域越大,就越難避免文字遭到截斷及內容裁剪。
考量螢幕尺寸對截斷和裁剪的影響
視 Wear OS 裝置的螢幕大小而定,顯示其他文字和按鈕的空間會比較大:
設計百分比邊界,而非固定邊界
如要建立會配合 Wear OS 裝置的螢幕大小調整內容,請套用百分比邊界,也就是每個邊界的大小與螢幕大小相對應。如果項目位於螢幕頂端或底部,請套用額外的內部邊框間距,盡量避免從螢幕曲線邊緣裁剪內容。相反地,如果內容群組的大小足以容納同一個畫面,頂端和底部的空間會增加。
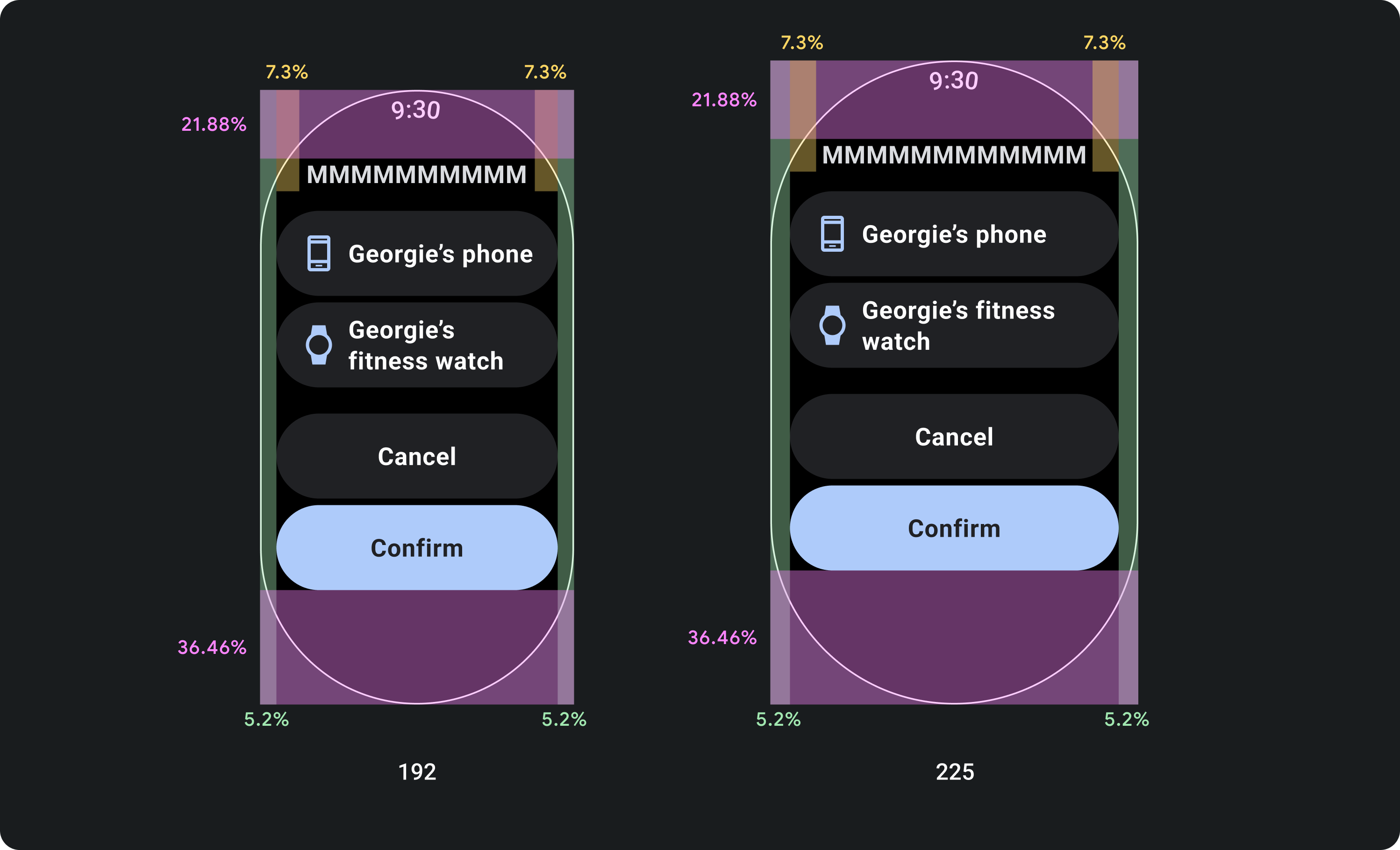
正確做法
錯誤做法
使用較小的螢幕所規定的字元限制
在大多數情況下,大螢幕可在截斷前顯示更多文字和內容。不過,雖然可用的水平空間可能更多,但請一律針對最小的螢幕大小設計,以便在各種裝置上提供一致的體驗。
舉例來說,在較大的螢幕上,按鈕可能會在截斷前保留更多字元空間,但如果這些按鈕是重要的行動號召,對使用者體驗至關重要,那麼請在小型裝置的螢幕上使用足夠簡短 (不截斷的文字)。
或者,如果資訊方塊顯示變數內容 (例如從伺服器擷取的文字),請妥善規劃,可能使文字在較小的螢幕上遭到截斷。

正確做法

