Android Studio を使用すると、スマートフォン、タブレット、テレビ、Wear デバイスなどのさまざまなフォーム ファクタ向けの Android アプリの作成が容易になります。このページでは、新しい Android アプリ プロジェクトを開始する方法と既存のプロジェクトをインポートする方法について説明します。
開いているプロジェクトがない場合は、Android Studio のウェルカム画面で [New Project] をクリックして、新しいプロジェクトを作成します。
開いているプロジェクトがある場合は、メインメニューから [File] > [New] > [New Project] を選択して、新しいプロジェクトを作成します。
プロジェクト タイプを選択する
表示される [New Project] 画面で、[Templates] ペインに表示されるデバイスのフォーム ファクタのカテゴリの中から、作成したいプロジェクトのタイプを選択できます。たとえば、図 1 はスマートフォンとタブレットのプロジェクト テンプレートを示しています。
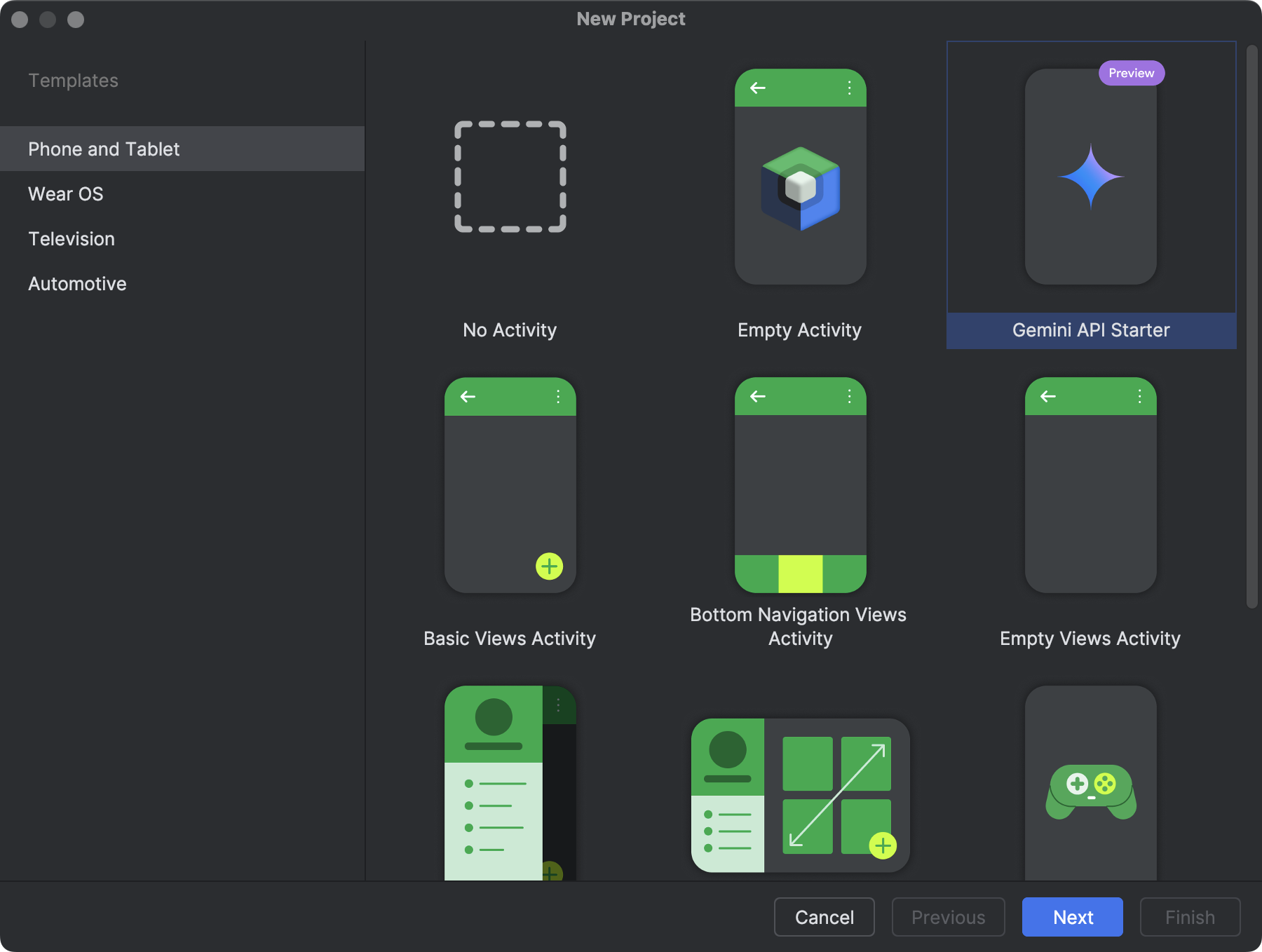
作成したいプロジェクトのタイプを選択すると、プロジェクトの開始に役立つサンプルコードおよびリソースが Android Studio によって追加されます。
プロジェクト タイプを選択して、[Next] をクリックします。
プロジェクトを構成する
プロジェクトを作成するための次のステップは、図 2 に示すように、いくつかの設定を構成することです。ネイティブ C++ プロジェクトを作成する場合は、C / C++ をサポートする新しいプロジェクトを作成するを参照して、構成する必要があるオプションの詳細を確認してください。
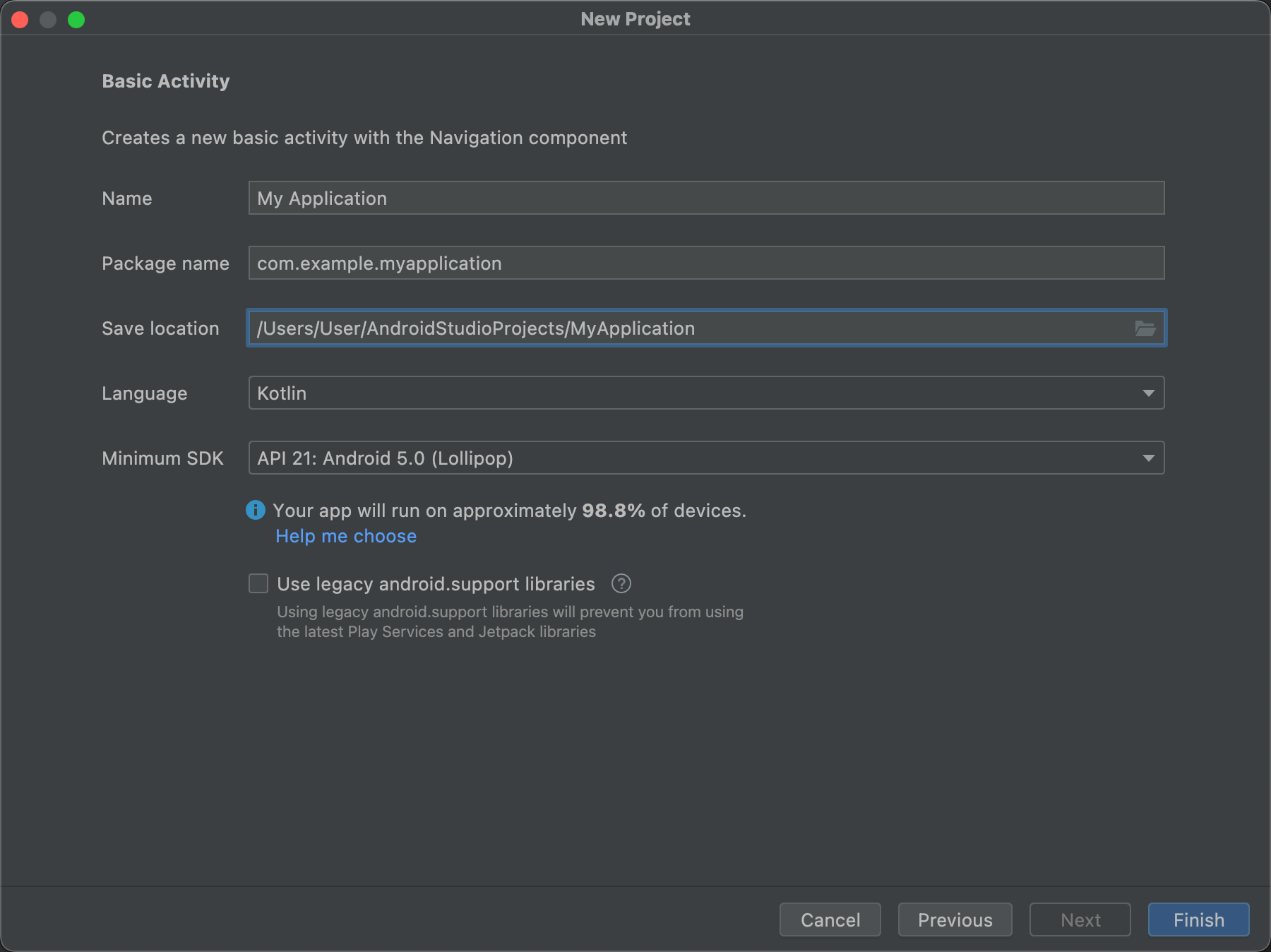
- [Name] にプロジェクト名を指定します。
- [Package name] にパッケージ名を指定します。デフォルトでは、このパッケージ名がプロジェクトの名前空間(プロジェクト リソースへのアクセスに使用されます)とプロジェクトのアプリケーション ID(公開用の ID として使用されます)になります。詳しくは、アプリ モジュールを設定するをご覧ください。
[Save location] にプロジェクトのローカルな保存場所を指定します。
[Language] で Kotlin または Java を選択します。これは、新しいプロジェクトのサンプルコードを作成する際に Android Studio で使用する言語です。プロジェクト内の言語には限定されないことにご注意ください。
[Minimum API level] で、アプリがサポートする最小 API レベルを選択します。低い API レベルを選択すると、利用できる最新の Android API は少なくなりますが、アプリを実行できる Android デバイスの割合は増えます。高い API レベルを選択すると、この逆になります。
判断の参考になる詳細なデータを確認するには、[Help me choose] をクリックします。クリックすると、選択した API レベルの累積分布を示すダイアログが表示され、各種の最小 API レベルを使用した場合の影響を確認できます。
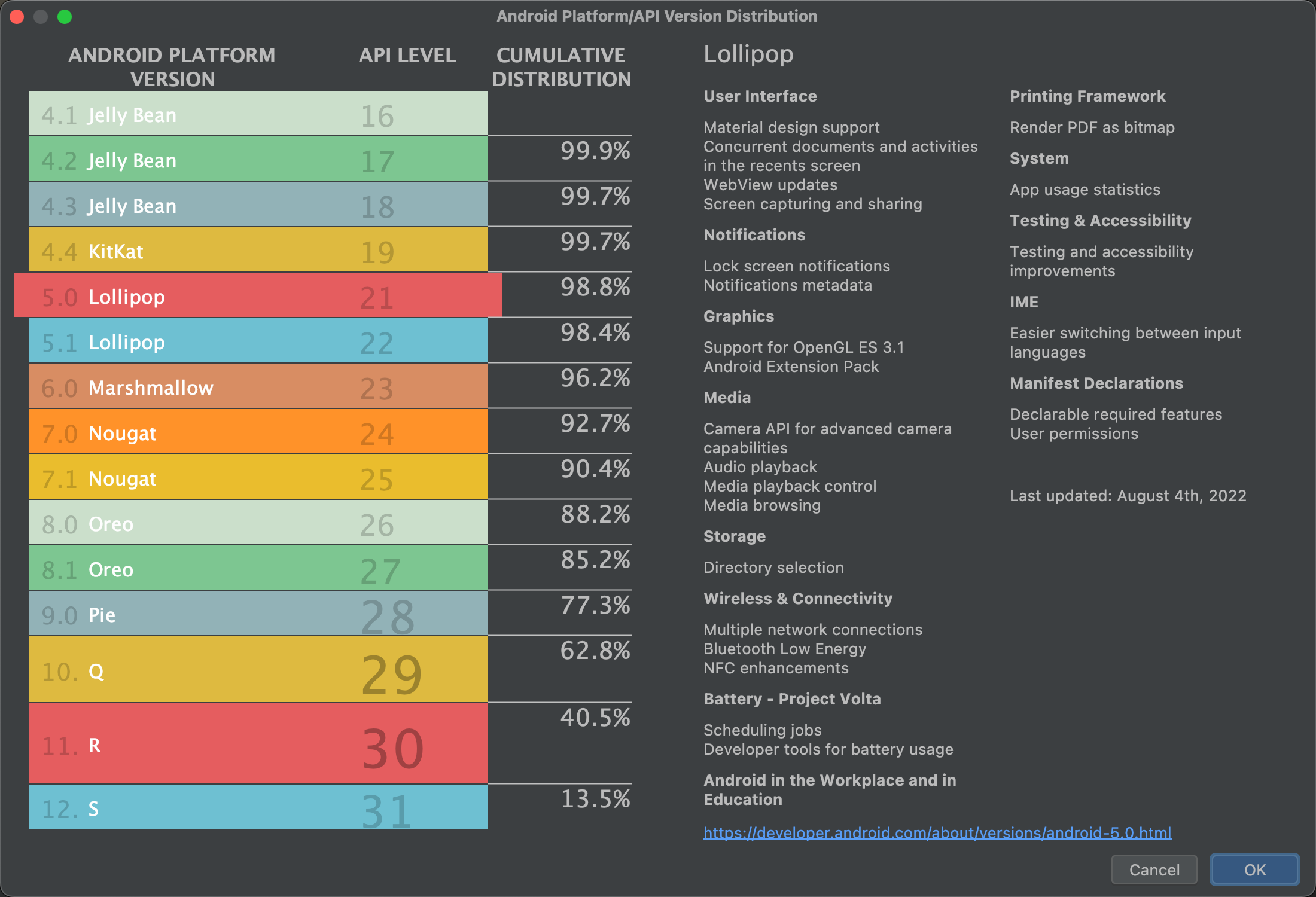
図 3. 各種の API レベルの累積分布を示すヘルプ画面 プロジェクトは、デフォルトで AndroidX ライブラリを使用するように構成されます。このライブラリは Android サポート ライブラリに代わるものです。従来のサポート ライブラリを使用する場合は、[Use legacy android.support libraries] を選択します。ただし、従来のサポート ライブラリはサポートされなくなったため、この設定はおすすめしません。詳しくは、AndroidX の概要をご覧ください。
プロジェクトを作成する準備ができたら、[Finish] をクリックします。
Android Studio により、サンプルとして使用できる基本的なコードとリソースを含む新しいプロジェクトが作成されます。その後、異なるデバイスのフォーム ファクタのサポートを追加することにした場合は、プロジェクトにモジュールを追加できます。モジュール間でコードとリソースを共有する場合は、Android ライブラリを作成することで共有を実現できます。
Android プロジェクトの構造とモジュール タイプについて詳しくは、プロジェクトの概要をご覧ください。Android 開発が初めての方は、最初に Android デベロッパー ガイドをご覧ください。
既存のプロジェクトをインポートする
既存のローカル プロジェクトを Android Studio にインポートする手順は次のとおりです。
- [File] > [New] > [Import Project] をクリックします。
- 表示されるウィンドウで、インポートするプロジェクトのルート ディレクトリに移動します。
- [OK] をクリックします。
新しい IDE ウィンドウでプロジェクトが開き、コンテンツがインデックスに登録されます。
バージョン管理からプロジェクトをインポートする場合は、[File] > [New] > [Project from Version Control] を選択します。バージョン管理からプロジェクトをインポートする方法について詳しくは、IntelliJ のバージョン管理に関する情報をご覧ください。
アプリをビルドして実行する
プロジェクトを作成したら、次は仮想デバイスまたは物理デバイスでビルドして実行します。Android Studio は、簡単に作業を開始できるように、デフォルトの実行構成を設定します。
詳細については、アプリをビルドして実行するをご覧ください。このガイドでは、Android Emulator と物理ハードウェア デバイスでの実行について説明します。
