Một ứng dụng có hiệu suất kém nếu ứng dụng đó phản hồi chậm, hiện ảnh động bị giật, bị treo hoặc ngốn pin. Việc khắc phục các vấn đề về hiệu suất bao gồm cả việc phân tích tài nguyên ứng dụng hoặc xác định các khía cạnh trong đó ứng dụng của bạn sử dụng tài nguyên không hiệu quả (chẳng hạn như CPU, bộ nhớ, đồ hoạ hoặc pin thiết bị). Chủ đề này mô tả các công cụ và kỹ thuật của Android Studio để khắc phục các sự cố hiệu suất thường gặp.
Để tìm hiểu cách chạy trình phân tích tài nguyên độc lập mà không cần chạy toàn bộ IDE Android Studio (chỉ dành cho Windows hoặc Linux), hãy xem phần Chạy trình phân tích tài nguyên độc lập.
Yêu cầu
Để phân tích tài nguyên cho ứng dụng, bạn nên có những thông tin sau:
Ứng dụng có biến thể bản phát hành đã bật cấu hình tệp kê khai
profileable, còn gọi là ứng dụng có thể phân tích. Theo mặc định, các ứng dụng sẽ đặt cấu hình này thành true. Để kiểm tra hoặc thay đổi cấu hình này, hãy mở tệp kê khai hoặc tệpAndroidManifest.xmlcủa ứng dụng rồi tìm trong phần<application>để biết cấu hình tệp kê khaiprofileable:<profileable android:shell="true" />Thiết bị kiểm thử ảo hoặc thực tế chạy API cấp 29 trở lên và đã có Google Play.
Trình bổ trợ Android cho Gradle 7.3 trở lên.
Ứng dụng có thể phân tích so với ứng dụng có thể gỡ lỗi
Ứng dụng có thể định cấu hình cho phép bạn thực hiện hầu hết các tác vụ phân tích tài nguyên phổ biến, nhưng bạn nên sử dụng ứng dụng có thể gỡ lỗi nếu cần ghi lại hoạt động phân bổ Java/Kotlin hoặc chụp tệp báo lỗi. Một quy trình ứng dụng có thể gỡ lỗi và thiết bị chạy API cấp 26 trở lên cũng cho phép bạn xem tiến trình Tương tác, trong đó hiển thị các sự kiện tương tác của người dùng và sự kiện trong vòng đời ứng dụng, trong các chế độ xem tác vụ cung cấp tiến trình đó.
Ứng dụng có thể gỡ lỗi dựa trên biến thể bản dựng debug của ứng dụng và cho phép bạn sử dụng các công cụ phát triển như trình gỡ lỗi; tuy nhiên, ứng dụng này sẽ gây ra một số chi phí về hiệu suất. Ứng dụng có thể phân tích tài nguyên dựa trên biến thể bản dựng release của ứng dụng và cho phép một tập hợp con các tác vụ phân tích tài nguyên phổ biến mà không gây hao tổn hiệu suất của bản gỡ lỗi.
Tạo và chạy một ứng dụng có thể phân tích
Để tạo và chạy một ứng dụng có thể định cấu hình trong Android Studio, hãy làm theo các bước sau:
- Tạo cấu hình chạy/gỡ lỗi nếu bạn chưa có.
- Chọn biến thể bản phát hành (Build > Select Build Variant (Tạo > Chọn biến thể bản dựng)).
- Nhấp vào Thao tác khác
 > Phân tích "ứng dụng" có mức hao tổn thấp
> Phân tích "ứng dụng" có mức hao tổn thấp
 hoặc Phân tích "ứng dụng" có dữ liệu đầy đủ
hoặc Phân tích "ứng dụng" có dữ liệu đầy đủ
 ("ứng dụng" là tên của cấu hình chạy, vì vậy, tên này có thể khác với tên của bạn). Để chọn giữa hai tuỳ chọn này, hãy xem phần Yêu cầu.
Ứng dụng sẽ mở trên thiết bị kiểm thử và ngăn Profiler (Trình phân tích tài nguyên) sẽ mở trong Android Studio.
("ứng dụng" là tên của cấu hình chạy, vì vậy, tên này có thể khác với tên của bạn). Để chọn giữa hai tuỳ chọn này, hãy xem phần Yêu cầu.
Ứng dụng sẽ mở trên thiết bị kiểm thử và ngăn Profiler (Trình phân tích tài nguyên) sẽ mở trong Android Studio.
Nếu bạn không làm theo hướng dẫn này, hãy xem phần Tạo và chạy ứng dụng có thể phân tích tài nguyên theo cách thủ công.
Bắt đầu lập hồ sơ
Để bắt đầu một tác vụ phân tích tài nguyên, hãy làm theo các bước sau:
Chọn một quy trình trong danh sách trên thẻ Trang chủ trong ngăn Trình phân tích tài nguyên. Trong hầu hết các trường hợp, bạn nên chọn quy trình hàng đầu đại diện cho ứng dụng của mình.
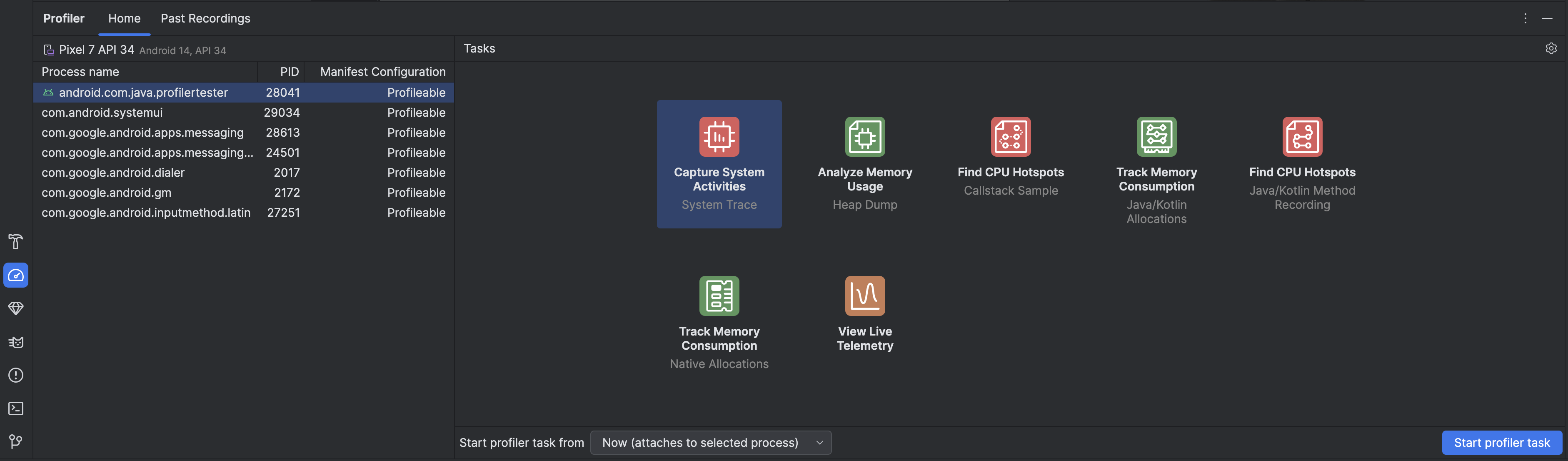
Chọn một tác vụ phân tích tài nguyên trong mục Tasks (Tác vụ). Để biết thêm thông tin về các tác vụ, hãy xem các trang khác trong phần này. Không phải mọi quy trình đều có thể sử dụng mọi tác vụ phân tích tài nguyên. Nếu bạn không biết nên bắt đầu từ đâu, hãy xem tổng quan về hoạt động hiệu suất bằng cách kiểm tra ứng dụng của bạn trực tiếp.
Sử dụng trình đơn thả xuống Start profiler task from (Bắt đầu tác vụ trình phân tích tài nguyên từ) để chọn bắt đầu tác vụ trình phân tích tài nguyên từ khi khởi động hay đính kèm vào quy trình khi đang chạy. Nếu đang cố gắng cải thiện thời gian khởi động ứng dụng hoặc ghi lại một quy trình diễn ra trong quá trình khởi động ứng dụng, bạn nên bao gồm cả quá trình khởi động; nếu không, bạn có thể bắt đầu lập hồ sơ ở trạng thái hiện tại của ứng dụng.
Nhấp vào Bắt đầu tác vụ trình phân tích tài nguyên. Tác vụ sẽ bắt đầu trong thẻ riêng.
Tương tác với ứng dụng để các hoạt động được kích hoạt.
Dừng ghi (nếu có), đợi quá trình phân tích cú pháp và xem kết quả.
So sánh, xuất và nhập dấu vết
Khi bạn dừng một tác vụ phân tích tài nguyên, tác vụ đó sẽ tự động được lưu trong thẻ Bản ghi trước đây trong ngăn Trình phân tích tài nguyên. Bạn có thể sử dụng các bản ghi đã lưu này để so sánh mức sử dụng tài nguyên trong nhiều tình huống. Các bản ghi sẽ được lưu trong suốt phiên Android Studio hiện tại; nếu bạn muốn giữ lại các bản ghi đó lâu hơn, hãy xuất các bản ghi đó bằng cách nhấp vào biểu tượng Export recording (Xuất bản ghi)  .
Không phải loại dấu vết nào cũng có thể xuất.
.
Không phải loại dấu vết nào cũng có thể xuất.
Để nhập dấu vết, chẳng hạn như từ một lần chạy Android Studio trước, hãy nhấp vào biểu tượng Import recording (Nhập bản ghi)  trong thẻ Past Recordings (Bản ghi trước) rồi chọn tệp dấu vết. Bạn cũng có thể nhập tệp bằng cách kéo tệp đó vào cửa sổ trình chỉnh sửa Android Studio.
trong thẻ Past Recordings (Bản ghi trước) rồi chọn tệp dấu vết. Bạn cũng có thể nhập tệp bằng cách kéo tệp đó vào cửa sổ trình chỉnh sửa Android Studio.
Chỉnh sửa cấu hình bản ghi
Để chỉnh sửa cấu hình ghi tác vụ của trình phân tích tài nguyên, hãy nhấp vào chế độ cài đặt trình phân tích tài nguyên  .
Bạn có thể bật/tắt hai chế độ cài đặt chính:
.
Bạn có thể bật/tắt hai chế độ cài đặt chính:
- Đối với các tác vụ liên quan đến hoạt động lấy mẫu, Khoảng thời gian lấy mẫu thể hiện thời gian giữa mỗi mẫu. Khoảng thời gian bạn chỉ định càng ngắn thì bạn càng nhanh đạt được giới hạn kích thước tệp cho dữ liệu được ghi lại.
- Giới hạn kích thước tệp thể hiện lượng dữ liệu có thể ghi vào thiết bị đã kết nối. Khi bạn dừng ghi, Android Studio sẽ phân tích cú pháp dữ liệu này và hiển thị dữ liệu trong cửa sổ trình phân tích tài nguyên. Nếu bạn tăng giới hạn và ghi lại một lượng lớn dữ liệu, Android Studio sẽ mất nhiều thời gian hơn để phân tích cú pháp tệp và có thể không phản hồi.
