Le prestazioni di un'app sono scarse se risponde lentamente, mostra animazioni discontinue, si blocca o consuma troppa energia. Per risolvere i problemi di prestazioni è necessario eseguire il profiling dell'app o identificare le aree in cui l'app utilizza in modo inefficiente risorse come la CPU, la memoria, la grafica o la batteria del dispositivo. Questo argomento descrive gli strumenti e le tecniche di Android Studio da utilizzare per risolvere i problemi di prestazioni più comuni.
Per scoprire come eseguire i profiler autonomi senza eseguire l'intero IDE Android Studio (solo Windows o Linux), consulta Eseguire il profiler autonomo.
Requisiti
Per creare il profilo della tua app, ti consigliamo di avere quanto segue:
Un'app con una variante di build di release in cui è attivata la configurazione del manifest
profileable, nota anche come app profilabile. Per impostazione predefinita, per le app questa configurazione è impostata su true. Per controllare o modificare questa configurazione, apri il file manifest oAndroidManifest.xmldell'app e cerca la configurazione del manifestprofileablenella sezione<application>:<profileable android:shell="true" />Un dispositivo di test virtuale o fisico con livello API 29 o versioni successive e Google Play.
Plug-in Android per Gradle 7.3 o versioni successive.
App profilabili e app di cui è possibile eseguire il debug
Un'app con profilo ti consente di eseguire le attività di profilazione più comuni, ma se devi registrare allocazioni Java/Kotlin o acquisire un dump dell'heap, ti consigliamo di utilizzare un'app debuggabile. Un processo dell'app e un dispositivo di debug che eseguono livello API 26 o versioni successive ti consentono anche di visualizzare la sequenza temporale Interazione, che mostra le interazioni utente e gli eventi del ciclo di vita dell'app nelle visualizzazioni delle attività che li forniscono.
Un'app di cui è possibile eseguire il debug si basa sulla variante di compilazione debug della tua app e ti consente di utilizzare strumenti di sviluppo come il debugger. Tuttavia, comporta alcuni costi in termini di prestazioni. Un'app profilabile si basa sulla variante di compilazione release della tua app e abilita un sottoinsieme di attività di profilazione comuni senza il sovraccarico delle prestazioni della compilazione di debug.
Crea ed esegui un'app profilabile
Per compilare ed eseguire un'app profilabile in Android Studio:
- Crea una configurazione di esecuzione/debug se non ne hai già una.
- Seleziona la variante di build della release (Build > Seleziona variante di build).
- Fai clic su Altre azioni
 > Profila "app" con un overhead ridotto
> Profila "app" con un overhead ridotto
 o su Profila "app" con dati completi
o su Profila "app" con dati completi
 ("app" è il nome della configurazione di esecuzione, quindi potrebbe essere diverso per ciascuno). Per scegliere tra le due opzioni, consulta la sezione Requisiti.
L'app si apre sul dispositivo di test e il riquadro Profiler si apre in Android Studio.
("app" è il nome della configurazione di esecuzione, quindi potrebbe essere diverso per ciascuno). Per scegliere tra le due opzioni, consulta la sezione Requisiti.
L'app si apre sul dispositivo di test e il riquadro Profiler si apre in Android Studio.
Se queste istruzioni non funzionano, consulta la sezione Creare ed eseguire manualmente un'app profilabille.
Avvia la profilazione
Per avviare un'attività di profilazione, segui questi passaggi:
Seleziona un processo dall'elenco nella scheda Home del riquadro Profiler. Nella maggior parte dei casi, ti consigliamo di selezionare il processo principale che rappresenta la tua app.
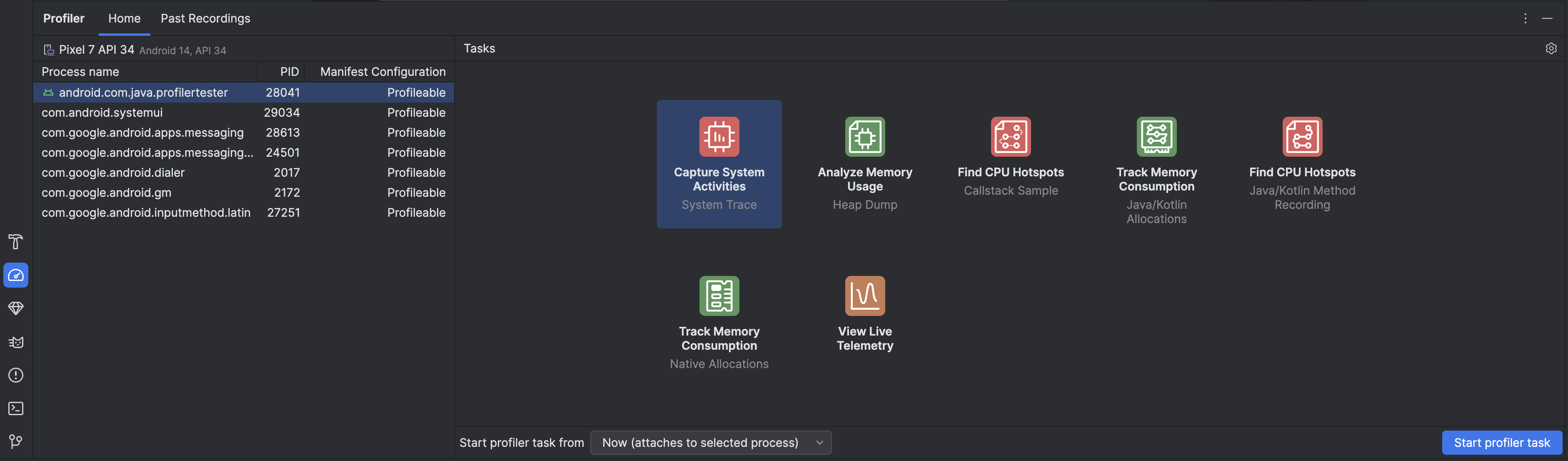
Seleziona un'attività di profilazione dalla sezione Attività. Per ulteriori informazioni sulle attività, consulta le altre pagine di questa sezione. Non tutte le attività di profilazione sono disponibili per ogni processo. Se non sai da dove iniziare, ottieni una panoramica complessiva dell'attività di rendimento controllando la tua app in tempo reale.
Utilizza il menu a discesa Avvia attività di profiler da per selezionare se avviare l'attività di profiler all'avvio o se collegarti al processo durante l'esecuzione. Se stai tentando di migliorare il tempo di avvio dell'app o di acquisire un processo che si verifica durante l'avvio dell'app, devi includere l'avvio. In caso contrario, puoi avviare il profiling nello stato corrente dell'app.
Fai clic su Avvia attività del profiler. L'attività si avvia in una scheda separata.
Interagisci con la tua app in modo che le attività vengano attivate.
Interrompi la registrazione (se applicabile), attendi che venga analizzata e visualizza i risultati.
Confrontare, esportare e importare tracce
Quando interrompi un'attività di profilazione, questa viene salvata automaticamente nella scheda Registrazioni
passate del riquadro Profiler. Puoi utilizzare queste registrazioni salvate per confrontare l'utilizzo delle risorse in diversi scenari. Le registrazioni vengono salvate per la durata della sessione corrente di Android Studio. Se vuoi conservarle più a lungo, esportale facendo clic su Esporta registrazione
 .
Non tutti i tipi di tracce possono essere esportati.
.
Non tutti i tipi di tracce possono essere esportati.
Per importare una traccia, ad esempio da un'esecuzione precedente di Android Studio, fai clic su
Importa registrazione
 nella scheda Registrazioni precedenti e seleziona il file traccia. Puoi anche importare un file trascinandolo nella finestra dell'editor di Android Studio.
nella scheda Registrazioni precedenti e seleziona il file traccia. Puoi anche importare un file trascinandolo nella finestra dell'editor di Android Studio.
Modificare la configurazione della registrazione
Per modificare la configurazione della registrazione delle attività del profiler, fai clic sulle impostazioni del profiler .
Puoi attivare/disattivare due impostazioni principali:
.
Puoi attivare/disattivare due impostazioni principali:
- Per le attività che prevedono il campionamento, l'intervallo di campionamento rappresenta il tempo tra ogni campione. Più breve è l'intervallo specificato, più velocemente si raggiunge il limite di dimensioni del file per i dati registrati.
- Il limite di dimensione del file rappresenta la quantità di dati che può essere scritta sul dispositivo connesso. Quando interrompi la registrazione, Android Studio analizza questi dati e li mostra nella finestra del profiler. Se aumenti il limite e registri una grande quantità di dati, Android Studio impiega molto più tempo per analizzare il file e potrebbe non rispondere.
