Mampu menentukan bentuk yang akan digambar dalam konteks tampilan OpenGL ES adalah langkah pertama dalam membuat grafis canggih untuk aplikasi Anda. Menggambar dengan OpenGL ES bisa sedikit rumit tanpa mengetahui beberapa hal dasar tentang cara OpenGL ES mengharapkan Anda untuk menentukan objek grafis.
Pelajaran ini menjelaskan sistem koordinat OpenGL ES yang relatif terhadap layar perangkat Android, dasar-dasar untuk mendefinisikan bentuk, wajah bentuk, serta mendefinisikan segitiga dan persegi.
Menentukan segitiga
OpenGL ES memungkinkan Anda menentukan objek yang digambar menggunakan koordinat dalam ruang tiga dimensi. Jadi,
sebelum bisa menggambar segitiga, Anda harus menentukan koordinatnya. Di OpenGL, cara yang
umum untuk melakukan
ini untuk mendefinisikan sebuah larik verteks dari angka floating point untuk koordinat. Untuk maksimum
efisiensi, tulis koordinat ini ke dalam ByteBuffer, yang diteruskan ke
Pipeline grafis OpenGL ES untuk pemrosesan.
Kotlin
// number of coordinates per vertex in this array const val COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3 var triangleCoords = floatArrayOf( // in counterclockwise order: 0.0f, 0.622008459f, 0.0f, // top -0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f // bottom right ) class Triangle { // Set color with red, green, blue and alpha (opacity) values val color = floatArrayOf(0.63671875f, 0.76953125f, 0.22265625f, 1.0f) private var vertexBuffer: FloatBuffer = // (number of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(triangleCoords.size * 4).run { // use the device hardware's native byte order order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) // create a floating point buffer from the ByteBuffer asFloatBuffer().apply { // add the coordinates to the FloatBuffer put(triangleCoords) // set the buffer to read the first coordinate position(0) } } }
Java
public class Triangle { private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer; // number of coordinates per vertex in this array static final int COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3; static float triangleCoords[] = { // in counterclockwise order: 0.0f, 0.622008459f, 0.0f, // top -0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f // bottom right }; // Set color with red, green, blue and alpha (opacity) values float color[] = { 0.63671875f, 0.76953125f, 0.22265625f, 1.0f }; public Triangle() { // initialize vertex byte buffer for shape coordinates ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( // (number of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) triangleCoords.length * 4); // use the device hardware's native byte order bb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); // create a floating point buffer from the ByteBuffer vertexBuffer = bb.asFloatBuffer(); // add the coordinates to the FloatBuffer vertexBuffer.put(triangleCoords); // set the buffer to read the first coordinate vertexBuffer.position(0); } }
Secara default, OpenGL ES mengasumsikan sistem koordinat di mana [0,0,0] (X,Y,Z) menentukan pusat
frame GLSurfaceView,
[1,1,0] adalah sudut kanan atas {i>frame<i} dan
[-1,-1,0] adalah sudut kiri bawah bingkai. Untuk ilustrasi sistem koordinat ini, lihat
Developer OpenGL ES
panduan kami.
Perhatikan bahwa koordinat bentuk ini ditentukan dengan urutan berlawanan arah jarum jam. Gambar urutan itu penting karena menentukan sisi mana yang merupakan wajah depan bentuk, yang biasanya yang ingin digambar, dan tampilan belakang, yang dapat Anda pilih untuk tidak digambar menggunakan cull OpenGL ES fitur wajah. Untuk informasi selengkapnya tentang wajah dan pemusnahan, lihat Panduan developer OpenGL ES.
Menentukan persegi
Mendefinisikan segitiga cukup mudah di OpenGL, tetapi bagaimana jika Anda ingin rumit? Misalnya, persegi? Ada sejumlah cara untuk melakukan ini, tetapi jalur umum untuk menggambar model di OpenGL ES adalah dengan menggunakan dua segitiga yang digambar bersama:
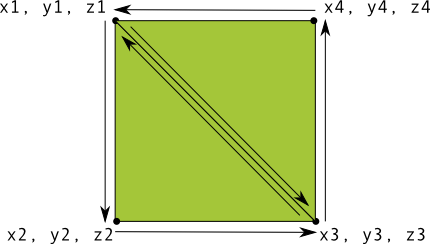
Gambar 1. Menggambar persegi menggunakan dua segitiga.
Sekali lagi, Anda harus menentukan verteks dalam urutan berlawanan arah jarum jam untuk kedua segitiga yang
mewakili bentuk ini, dan memasukkan nilai ke dalam ByteBuffer. Untuk menghindari
dengan mendefinisikan dua koordinat yang dibagikan oleh setiap segitiga dua kali, gunakan daftar gambar untuk memberi tahu
Pipeline grafis OpenGL ES cara menggambar verteks ini. Berikut adalah kode untuk bentuk ini:
Kotlin
// number of coordinates per vertex in this array const val COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3 var squareCoords = floatArrayOf( -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // top left -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom right 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f // top right ) class Square2 { private val drawOrder = shortArrayOf(0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3) // order to draw vertices // initialize vertex byte buffer for shape coordinates private val vertexBuffer: FloatBuffer = // (# of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(squareCoords.size * 4).run { order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) asFloatBuffer().apply { put(squareCoords) position(0) } } // initialize byte buffer for the draw list private val drawListBuffer: ShortBuffer = // (# of coordinate values * 2 bytes per short) ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(drawOrder.size * 2).run { order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) asShortBuffer().apply { put(drawOrder) position(0) } } }
Java
public class Square { private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer; private ShortBuffer drawListBuffer; // number of coordinates per vertex in this array static final int COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3; static float squareCoords[] = { -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // top left -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom right 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f }; // top right private short drawOrder[] = { 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3 }; // order to draw vertices public Square() { // initialize vertex byte buffer for shape coordinates ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( // (# of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) squareCoords.length * 4); bb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); vertexBuffer = bb.asFloatBuffer(); vertexBuffer.put(squareCoords); vertexBuffer.position(0); // initialize byte buffer for the draw list ByteBuffer dlb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( // (# of coordinate values * 2 bytes per short) drawOrder.length * 2); dlb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); drawListBuffer = dlb.asShortBuffer(); drawListBuffer.put(drawOrder); drawListBuffer.position(0); } }
Contoh ini memberi Anda gambaran tentang hal yang diperlukan untuk membuat bentuk yang lebih kompleks dengan OpenGL. Di beberapa umum, Anda menggunakan kumpulan segitiga untuk menggambar objek. Pada pelajaran berikutnya, Anda akan belajar cara menggambar bentuk-bentuk ini di layar.
