Tutorial ini membahas cara membuat penerapan yang mencerminkan API baru namun mendukung perangkat lama.
Menentukan solusi pengganti
Tugas yang paling menantang dalam menggunakan fitur UI baru dengan cara yang kompatibel dengan versi sebelumnya adalah menentukan dan menerapkan solusi lama (fallback) untuk versi platform lama. Dalam banyak kasus, tujuan komponen UI baru ini dapat dicapai dengan fitur framework UI lama. Contoh:
-
Panel tindakan dapat diterapkan menggunakan
LinearLayouthorizontal yang berisi tombol gambar, baik sebagai panel judul kustom atau sebagai tampilan dalam tata letak aktivitas Anda. Tindakan tambahan dapat ditampilkan pada tombol Menu perangkat. -
Tab panel dapat diimplementasikan menggunakan tindakan horizontal
LinearLayoutberisi tombol, atau menggunakan elemen UITabWidget. -
Widget
NumberPickerdanSwitchmasing-masing dapat diimplementasikan menggunakan widgetSpinnerdanToggleButton. -
Widget
ListPopupWindowdanPopupMenudapat diimplementasikan menggunakan widgetPopupWindow.
Biasanya, tidak ada solusi serbaguna untuk melakukan backport komponen UI baru ke perangkat lama. Perhatikan pengalaman pengguna: pada perangkat lama, pengguna mungkin tidak mengenal pola desain dan komponen UI baru. Pertimbangkan cara agar fungsi yang sama dapat disampaikan menggunakan elemen yang sudah dikenal. Dalam banyak kasus, hal ini kurang menjadi perhatian, jika komponen UI baru lebih terlihat dalam ekosistem aplikasi (seperti panel tindakan), atau di mana model interaksinya sangat sederhana dan intuitif (seperti tampilan geser menggunakan ViewPager).
Menerapkan tab menggunakan API lama
Untuk membuat implementasi tab panel tindakan lama, Anda dapat menggunakan TabWidget dan TabHost (meskipun dapat menggunakan widget Button yang ditampilkan secara horizontal). Implementasikan widget tersebut di class bernama TabHelperEclair dan CompatTabEclair, karena implementasi ini menggunakan API yang diperkenalkan setidaknya pada Android 2.0 (Eclair).
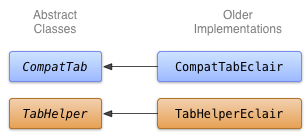
Gambar 1. Diagram class untuk implementasi Eclair pada tab.
Implementasi CompatTabEclair menyimpan properti tab seperti teks tab dan ikon dalam variabel instance, karena tidak ada objek ActionBar.Tab yang tersedia untuk menangani penyimpanan ini:
Kotlin
class CompatTabEclair internal constructor(val activity: FragmentActivity, tag: String) : CompatTab(tag) { // Store these properties in the instance, // as there is no ActionBar.Tab object. private var text: CharSequence? = null ... override fun setText(resId: Int): CompatTab { // Our older implementation simply stores this // information in the object instance. text = activity.resources.getText(resId) return this } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
Java
public class CompatTabEclair extends CompatTab { // Store these properties in the instance, // as there is no ActionBar.Tab object. private CharSequence text; ... public CompatTab setText(int resId) { // Our older implementation simply stores this // information in the object instance. text = activity.getResources().getText(resId); return this; } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
Implementasi TabHelperEclair menggunakan metode di
Widget TabHost untuk membuat TabHost.TabSpec
objek dan indikator tab:
Kotlin
class TabHelperEclair internal constructor(activity: FragmentActivity) : TabHelper(activity) { private var tabHost: TabHost? = null ... override fun setUp() { // Our activity layout for pre-Honeycomb devices // must contain a TabHost. tabHost = tabHost ?: mActivity.findViewById<TabHost>(android.R.id.tabhost).apply { setup() } } override fun addTab(tab: CompatTab) { ... tabHost?.newTabSpec(tab.tag)?.run { setIndicator(tab.getText()) // And optional icon ... tabHost?.addTab(this) } } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }
Java
public class TabHelperEclair extends TabHelper { private TabHost tabHost; ... protected void setUp() { if (tabHost == null) { // Our activity layout for pre-Honeycomb devices // must contain a TabHost. tabHost = (TabHost) mActivity.findViewById( android.R.id.tabhost); tabHost.setup(); } } public void addTab(CompatTab tab) { ... TabSpec spec = tabHost .newTabSpec(tag) .setIndicator(tab.getText()); // And optional icon ... tabHost.addTab(spec); } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }
Sekarang Anda memiliki dua implementasi CompatTab dan TabHelper: satu yang berfungsi pada perangkat yang menjalankan Android 3.0 atau yang lebih baru dan menggunakan API baru, dan satu lagi yang berfungsi pada perangkat yang menjalankan Android 2.0 atau yang lebih baru dan menggunakan API lama. Tutorial berikutnya membahas penggunaan implementasi ini dalam aplikasi Anda.
