Cette leçon explique comment sous-classer les classes abstraites CompatTab et TabHelper, et utiliser de nouvelles API. Votre application peut utiliser cette implémentation sur les appareils exécutant une version de plate-forme compatible.
Implémenter des onglets à l'aide des nouvelles API
Les classes concrètes pour CompatTab et TabHelper qui utilisent des API plus récentes constituent une implémentation de proxy. Étant donné que les classes abstraites définies dans la leçon précédente reflètent les nouvelles API (structure de classe, signatures de méthode, etc.), les classes concrètes qui utilisent ces nouvelles API servent simplement de proxy pour les appels de méthode et leurs résultats.
Vous pouvez utiliser directement des API plus récentes dans ces classes concrètes (et ne pas planter sur les appareils plus anciens) en raison du chargement de classe différé. Les classes sont chargées et initialisées lors du premier accès : instanciation de la classe ou accès à l'un de ses champs ou méthodes statiques pour la première fois. Ainsi, tant que vous n'instanciez pas les implémentations spécifiques à Honeycomb sur des appareils antérieurs à Honeycomb, la VM Dalvik ne génère aucune exception VerifyError.
Une bonne convention d'attribution de noms pour cette implémentation consiste à ajouter le niveau d'API ou le nom de code de version de la plate-forme correspondant aux API requises par les classes concrètes. Par exemple, l'implémentation des onglets natifs peut être fournie par les classes CompatTabHoneycomb et TabHelperHoneycomb, car elles reposent sur des API disponibles dans Android 3.0 (niveau d'API 11) ou version ultérieure.
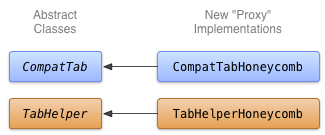
Figure 1 : Schéma de classe pour l'implémentation Honeycomb des onglets.
Implémenter CompatTabHoneycomb
CompatTabHoneycomb est l'implémentation de la classe abstraite CompatTab que TabHelperHoneycomb utilise pour référencer des onglets individuels. CompatTabHoneycomb sert simplement de proxy pour tous les appels de méthode vers l'objet ActionBar.Tab qu'il contient.
Commencez à implémenter CompatTabHoneycomb à l'aide des nouvelles API ActionBar.Tab:
Kotlin
class CompatTabHoneycomb internal constructor(val activity: Activity, tag: String) : CompatTab(tag) { ... // The native tab object that this CompatTab acts as a proxy for. private var mTab: ActionBar.Tab = // Proxy to new ActionBar.newTab API activity.actionBar.newTab() override fun setText(@StringRes textId: Int): CompatTab { // Proxy to new ActionBar.Tab.setText API mTab.setText(textId) return this } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
Java
public class CompatTabHoneycomb extends CompatTab { // The native tab object that this CompatTab acts as a proxy for. ActionBar.Tab mTab; ... protected CompatTabHoneycomb(FragmentActivity activity, String tag) { ... // Proxy to new ActionBar.newTab API mTab = activity.getActionBar().newTab(); } public CompatTab setText(int resId) { // Proxy to new ActionBar.Tab.setText API mTab.setText(resId); return this; } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
Implémenter TabHelperHoneycomb
TabHelperHoneycomb est l'implémentation de la classe abstraite TabHelper qui sert de proxy pour les appels de méthode à un ActionBar réel, obtenu à partir du Activity qu'il contient.
Implémentez TabHelperHoneycomb, pour transmettre les appels de méthode à l'API ActionBar:
Kotlin
class TabHelperHoneycomb internal constructor(activity: FragmentActivity) : TabHelper(activity) { private var mActionBar: ActionBar? = null override fun setUp() { mActionBar = mActionBar ?: mActivity.actionBar.apply { navigationMode = ActionBar.NAVIGATION_MODE_TABS } } override fun addTab(tab: CompatTab) { // Tab is a CompatTabHoneycomb instance, so its // native tab object is an ActionBar.Tab. mActionBar?.addTab(tab.getTab() as ActionBar.Tab) } }
Java
public class TabHelperHoneycomb extends TabHelper { ActionBar actionBar; ... protected void setUp() { if (actionBar == null) { actionBar = activity.getActionBar(); actionBar.setNavigationMode( ActionBar.NAVIGATION_MODE_TABS); } } public void addTab(CompatTab tab) { ... // Tab is a CompatTabHoneycomb instance, so its // native tab object is an ActionBar.Tab. actionBar.addTab((ActionBar.Tab) tab.getTab()); } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }
