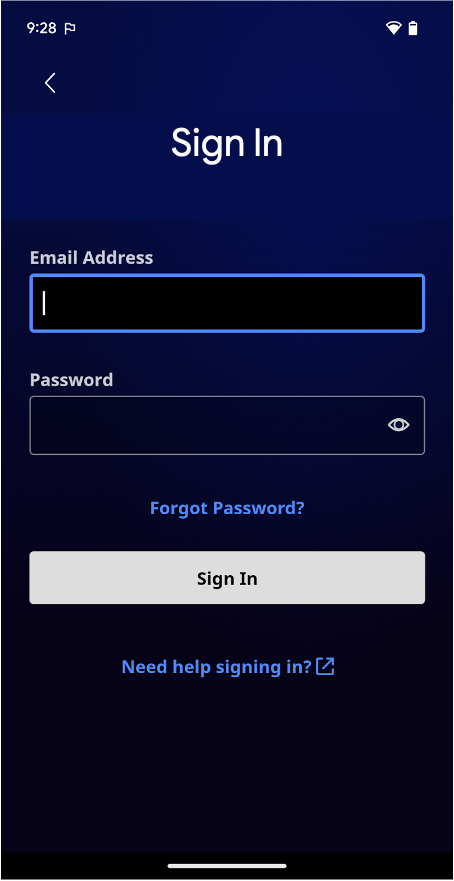
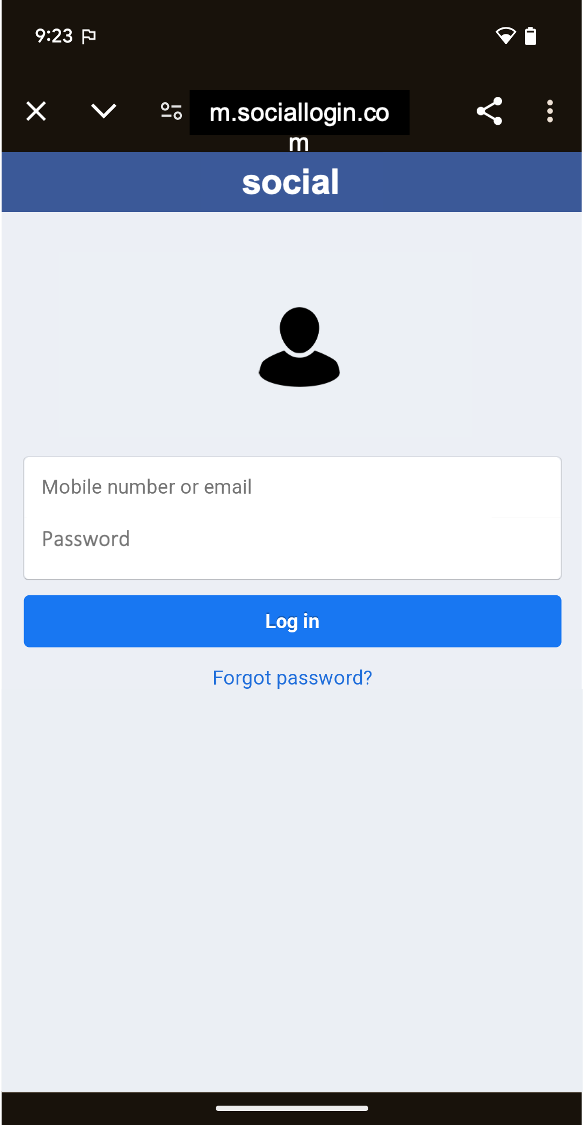
Android позволяет использовать возможности веб-технологий в ваших приложениях. Таким образом, вы можете воспользоваться преимуществами гибкости и эффективности, которые дает возможность отображать определенные типы контента.
Это позволяет легко интегрировать существующий веб-контент в ваше Android-приложение, например, для отображения новостной ленты, интерактивных обучающих материалов, рекламы или даже мини-игры, без необходимости создавать все с нуля. Представьте это как окно в интернет, расположенное внутри вашего приложения. Существует два способа встраивания веб-контента в ваше приложение:
-
WebView: Он отображает управляемый вами веб-контент непосредственно в тексте, где требуется высокая степень гибкости при настройке или обновлении пользовательского интерфейса. -
Custom Tabs: полноценный интерфейс просмотра внутри приложения, работающий в браузере пользователя по умолчанию ( см. поддержку браузеров ). Это удобно, когда пользователь переходит по ссылке и вы хотите, чтобы он оставался в приложении, а не переходил во внешний браузер. Большая часть функций просмотра доступна «из коробки».

Зачем встраивать веб-контент?
Встраивание веб-контента в ваше приложение имеет ряд преимуществ:
- Эффективность : Используйте существующий код вашего веб-сайта. Развивайте существующие веб-технологии и контент.
- Интеграция : Используйте внешний контент от сторонних поставщиков, например, медиафайлы и рекламу, в своем приложении.
- Гибкость : Динамическое обновление контента без ограничений предопределенными пользовательскими интерфейсами и без выпуска обновлений приложения.
Когда следует использовать веб-контент?
Существует три основных сценария использования веб-технологий в вашем Android-приложении:
1. Встраивание веб-контента в ваше приложение в качестве основного или вспомогательного контента : используйте WebView
- Отображайте собственный веб-контент непосредственно в тексте, используя его в качестве основного элемента интерфейса, если вам необходима высокая степень гибкости при настройке или обновлении пользовательского интерфейса.
- Отображайте другой контент, такой как реклама, юридические условия и правила, а также контент третьих лиц, непосредственно в приложении или в виде окна.

2. Просмотр содержимого приложения с помощью Custom Tabs или WebView для более сложных сценариев использования.
- Обеспечьте полноценный просмотр контента внутри приложения, когда пользователи переходят по ссылке и вы хотите, чтобы они оставались в приложении, а не переходили во внешний браузер.
- Примечание: Для устройств с большими экранами, таких как планшеты и складные устройства, существуют дополнительные параметры, позволяющие приложениям эффективно использовать дополнительное пространство:
- Приложения могут открывать веб-ссылки в режиме разделенного экрана, используя функцию запуска многооконного режима рядом с основным . Это позволяет пользователям одновременно работать в многозадачном режиме, переключаясь между вашим приложением и браузером. ИЛИ
-
Custom Tabsесть боковая панель, которая может открываться в рамках той же задачи, но рядом с существующим содержимым приложения.
-
Custom Tabработает в браузере по умолчанию, если браузер поддерживаетCustom Tabs.- Хотя можно использовать
WebViewи обеспечить настраиваемый интерфейс просмотра внутри приложения, мы рекомендуем использоватьCustom Tabsдля стандартного интерфейса браузера и плавного перехода при открытии пользователем веб-ссылки в браузере.
- Хотя можно использовать
3. Процессы входа в систему или аутентификации внутри вашего приложения.
В Android рекомендуется создавать сценарии входа в систему или аутентификации с помощью Credential Manager . Если для этих целей вам по-прежнему необходимо использовать Embedded Web, воспользуйтесь следующими рекомендациями:
- Некоторые приложения используют
WebViewдля обеспечения авторизации пользователей, включая использование имени пользователя и пароля (или ключа доступа), специфичных для данного приложения. Это позволяет разработчикам унифицировать процессы аутентификации на разных платформах. - При использовании сторонних сервисов идентификации или авторизации, например, «Войти с помощью…», лучше всего использовать
Custom Tabs. ЗапускCustom Tabпомогает защитить учетные данные пользователя, изолируя их на стороннем сайте.
Для получения дополнительной информации об использовании WebView для аутентификации см. раздел « Аутентификация пользователей с помощью WebView» . Для запуска Custom Tab см. раздел «Обзор пользовательских вкладок Android» .