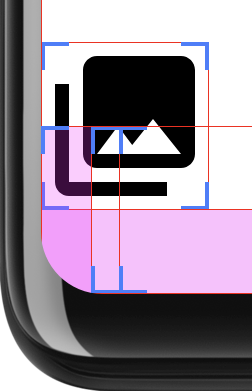
Począwszy od Androida 12 (poziom interfejsu API 31) możesz używać
RoundedCorner i
WindowInsets.getRoundedCorner(int
position), aby otrzymać
promień i punkt środkowy zaokrąglonych rogów ekranu urządzenia. Te interfejsy API
zapobiega zaokrąglaniu elementów interfejsu aplikacji na ekranach
w rogach ekranu. Ten schemat zapewnia
getPrivacyIndicatorBounds()
interfejsu API, który zwraca ograniczony prostokąt każdego widocznego mikrofonu i kamery.
.
Zaimplementowane w aplikacji te interfejsy API nie mają wpływu na urządzenia z niezaokrąglonych ekranów.
Aby wdrożyć tę funkcję, pobierz informacje o elemencie RoundedCorner za pomocą:
WindowInsets.getRoundedCorner(int position) względem granic
aplikacji. Jeśli aplikacja nie zajmuje całego ekranu, interfejs API stosuje wartość
zaokrąglonego narożnika przez oparcie punktu środkowego zaokrąglonego rogu na oknie;
od granic aplikacji.
Ten fragment kodu pokazuje, jak można uniknąć obcięcia interfejsu użytkownika przez aplikację
ustawianie marginesu widoku na podstawie informacji ze strony RoundedCorner. W tym
jest to prawy górny róg.
Kotlin
// Get the top-right rounded corner from WindowInsets. val insets = rootWindowInsets val topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT) ?: return // Get the location of the close button in window coordinates. val location = IntArray(2) closeButton!!.getLocationInWindow(location) val buttonRightInWindow = location[0] + closeButton.width val buttonTopInWindow = location[1] // Find the point on the quarter circle with a 45-degree angle. val offset = (topRight.radius * Math.sin(Math.toRadians(45.0))).toInt() val topBoundary = topRight.center.y - offset val rightBoundary = topRight.center.x + offset // Check whether the close button exceeds the boundary. if (buttonRightInWindow < rightBoundary << buttonTopInWindow > topBoundary) { return } // Set the margin to avoid truncating. val parentLocation = IntArray(2) getLocationInWindow(parentLocation) val lp = closeButton.layoutParams as FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp.rightMargin = Math.max(buttonRightInWindow - rightBoundary, 0) lp.topMargin = Math.max(topBoundary - buttonTopInWindow, 0) closeButton.layoutParams = lp
Java
// Get the top-right rounded corner from WindowInsets. final WindowInsets insets = getRootWindowInsets(); final RoundedCorner topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(POSITION_TOP_RIGHT); if (topRight == null) { return; } // Get the location of the close button in window coordinates. int [] location = new int[2]; closeButton.getLocationInWindow(location); final int buttonRightInWindow = location[0] + closeButton.getWidth(); final int buttonTopInWindow = location[1]; // Find the point on the quarter circle with a 45-degree angle. final int offset = (int) (topRight.getRadius() * Math.sin(Math.toRadians(45))); final int topBoundary = topRight.getCenter().y - offset; final int rightBoundary = topRight.getCenter().x + offset; // Check whether the close button exceeds the boundary. if (buttonRightInWindow < rightBoundary << buttonTopInWindow > topBoundary) { return; } // Set the margin to avoid truncating. int [] parentLocation = new int[2]; getLocationInWindow(parentLocation); FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp = (FrameLayout.LayoutParams) closeButton.getLayoutParams(); lp.rightMargin = Math.max(buttonRightInWindow - rightBoundary, 0); lp.topMargin = Math.max(topBoundary - buttonTopInWindow, 0); closeButton.setLayoutParams(lp);
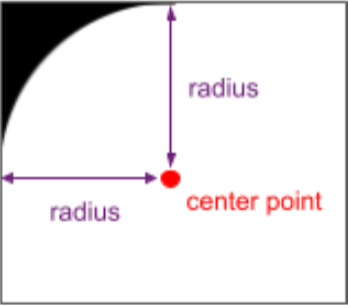
Uważaj na przycinanie
Jeśli interfejs wypełnia cały ekran, zaokrąglone rogi mogą powodować problemy z treścią. przycinanie. Na przykład na ilustracji 2 w rogu ekranu widać ikonę układ rysowany za paskami systemowymi:

Aby tego uniknąć, sprawdź, czy nie ma zaokrąglonych rogów, i zastosuj dopełnienie, aby zachować umieść zawartość aplikacji poza rogi urządzenia, jak widać poniżej przykład:
Kotlin
class InsetsLayout(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet) : FrameLayout(context, attrs) { override fun onLayout(changed: Boolean, left: Int, top: Int, right: Int, bottom: Int) { val insets = rootWindowInsets if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S && insets != null) { applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets) } super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom) } @RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.S) private fun applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets: WindowInsets) { val topLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_LEFT) val topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT) val bottomLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_LEFT) val bottomRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_RIGHT) val leftRadius = max(topLeft?.radius ?: 0, bottomLeft?.radius ?: 0) val topRadius = max(topLeft?.radius ?: 0, topRight?.radius ?: 0) val rightRadius = max(topRight?.radius ?: 0, bottomRight?.radius ?: 0) val bottomRadius = max(bottomLeft?.radius ?: 0, bottomRight?.radius ?: 0) val windowManager = context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE) as WindowManager val windowBounds = windowManager.currentWindowMetrics.bounds val safeArea = Rect( windowBounds.left + leftRadius, windowBounds.top + topRadius, windowBounds.right - rightRadius, windowBounds.bottom - bottomRadius ) val location = intArrayOf(0, 0) getLocationInWindow(location) val leftMargin = location[0] - windowBounds.left val topMargin = location[1] - windowBounds.top val rightMargin = windowBounds.right - right - location[0] val bottomMargin = windowBounds.bottom - bottom - location[1] val layoutBounds = Rect( location[0] + paddingLeft, location[1] + paddingTop, location[0] + width - paddingRight, location[1] + height - paddingBottom ) if (layoutBounds != safeArea && layoutBounds.contains(safeArea)) { setPadding( calculatePadding(leftRadius, leftMargin, paddingLeft), calculatePadding(topRadius, topMargin, paddingTop), calculatePadding(rightRadius, rightMargin, paddingRight), calculatePadding(bottomRadius, bottomMargin, paddingBottom) ) } } private fun calculatePadding(radius1: Int?, radius2: Int?, margin: Int, padding: Int): Int = (max(radius1 ?: 0, radius2 ?: 0) - margin - padding).coerceAtLeast(0) }
Java
public class InsetsLayout extends FrameLayout { public InsetsLayout(@NonNull Context context) { super(context); } public InsetsLayout(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { WindowInsets insets = getRootWindowInsets(); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S && insets != null) { applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets); } super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom); } @RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.S) private void applyRoundedCornerPadding(WindowInsets insets) { RoundedCorner topLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_LEFT); RoundedCorner topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT); RoundedCorner bottomLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_LEFT); RoundedCorner bottomRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_RIGHT); int radiusTopLeft = 0; int radiusTopRight = 0; int radiusBottomLeft = 0; int radiusBottomRight = 0; if (topLeft != null) radiusTopLeft = topLeft.getRadius(); if (topRight != null) radiusTopRight = topRight.getRadius(); if (bottomLeft != null) radiusBottomLeft = bottomLeft.getRadius(); if (bottomRight != null) radiusBottomRight = bottomRight.getRadius(); int leftRadius = Math.max(radiusTopLeft, radiusBottomLeft); int topRadius = Math.max(radiusTopLeft, radiusTopRight); int rightRadius = Math.max(radiusTopRight, radiusBottomRight); int bottomRadius = Math.max(radiusBottomLeft, radiusBottomRight); WindowManager windowManager = (WindowManager) getContext().getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE); Rect windowBounds = windowManager.getCurrentWindowMetrics().getBounds(); Rect safeArea = new Rect( windowBounds.left + leftRadius, windowBounds.top + topRadius, windowBounds.right - rightRadius, windowBounds.bottom - bottomRadius ); int[] location = {0, 0}; getLocationInWindow(location); int leftMargin = location[0] - windowBounds.left; int topMargin = location[1] - windowBounds.top; int rightMargin = windowBounds.right - getRight() - location[0]; int bottomMargin = windowBounds.bottom - getBottom() - location[1]; Rect layoutBounds = new Rect( location[0] + getPaddingLeft(), location[1] + getPaddingTop(), location[0] + getWidth() - getPaddingRight(), location[1] + getHeight() - getPaddingBottom() ); if (!layoutBounds.equals(safeArea) && layoutBounds.contains(safeArea)) { setPadding( calculatePadding(radiusTopLeft, radiusBottomLeft, leftMargin, getPaddingLeft()), calculatePadding(radiusTopLeft, radiusTopRight, topMargin, getPaddingTop()), calculatePadding(radiusTopRight, radiusBottomRight, rightMargin, getPaddingRight()), calculatePadding(radiusBottomLeft, radiusBottomRight, bottomMargin, getPaddingBottom()) ); } } private int calculatePadding(int radius1, int radius2, int margin, int padding) { return Math.max(Math.max(radius1, radius2) - margin - padding, 0); } }
Ten układ określa, czy interfejs obejmuje obszar zaokrąglonych rogów. i dodaje dopełnienie w odpowiednich miejscach. Rysunek 3 przedstawia „Pokaż granice układu” deweloper aby wyraźniej pokazać stosowanie dopełnienia:
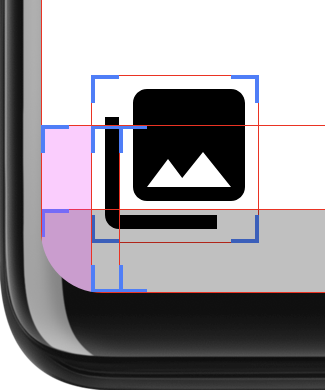
Aby to ustalić, ten układ oblicza dwa prostokąty: safeArea to
obszar w promieniach zaokrąglonych rogów, a layoutBounds to rozmiar
układu bez dopełnienia. Jeśli layoutArea zawiera wszystkie wartości safeArea, to
elementy podrzędne układu mogą być przycięte. W takim przypadku dopełnienie jest
dodano, aby układ pozostał w środku safeArea.
Dzięki sprawdzeniu, czy funkcja layoutBounds w pełni obejmuje obiekt safeArea, unikniesz dodawania
dopełnienie, gdy układ nie obejmuje krawędzi wyświetlacza. Rysunek 4
pokazuje układ, gdy nie jest on narysowany za paskiem nawigacyjnym. W tym przypadku
układ nie rozszerza się wystarczająco daleko, aby zmieścić się w zaokrąglonych rogach,
mieści się w obszarze zajmowanym przez pasek nawigacyjny. Dopełnienie nie jest wymagane.