Si vous utilisez une mise en page basée sur View, trois options principales s'offrent à vous pour implémenter des boutons d'activation/de désactivation. Nous vous recommandons d'utiliser le composant SwitchMaterial de la bibliothèque Material Components :
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<com.google.android.material.switchmaterial.SwitchMaterial
android:id="@+id/material_switch"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/material_switch"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Les anciennes applications peuvent toujours utiliser l'ancien composant AppCompat SwitchCompat, comme illustré dans l'exemple suivant:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.SwitchCompat
android:id="@+id/switchcompat"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/switchcompat"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
L'exemple suivant montre AppCompatToggleButton, un autre ancien composant dont l'UI est sensiblement différente :
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/toggle_button_label"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/toggle"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="packed"
app:layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf="@id/toggle"
android:text="@string/toggle_button" />
<androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatToggleButton
android:id="@+id/toggle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/toggle_button_label"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Ces trois composants offrent le même comportement, mais ont un aspect différent. Les différences entre SwitchMaterial et SwitchCompat sont subtiles, mais AppCompatToggleButton est sensiblement différent :
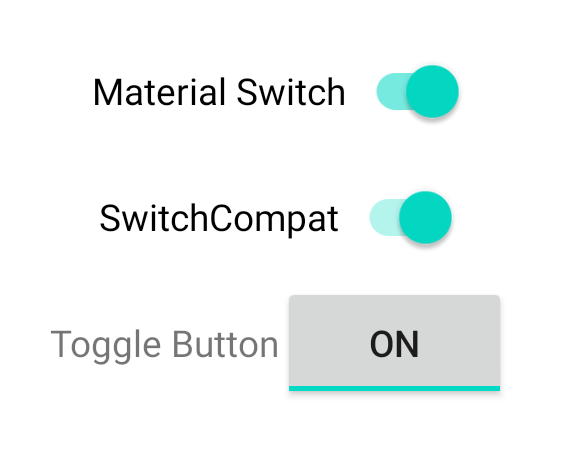
Gérer les changements d'état
SwitchMaterial, SwitchCompat et AppCompatToggleButton sont toutes des sous-classes de CompoundButton, ce qui leur donne un mécanisme commun pour gérer les modifications d'état de vérification. Vous allez implémenter une instance de CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener et l'ajouter au bouton, comme illustré dans l'exemple suivant:
Kotlin
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) val binding: SwitchLayoutBinding = SwitchLayoutBinding.inflate(layoutInflater) setContentView(binding.root) binding.materialSwitch.setOnCheckedChangeListener { _, isChecked -> if (isChecked) { // The switch is checked. } else { // The switch isn't checked. } } } }
Java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); SwitchLayoutBinding binding = SwitchLayoutBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater()); setContentView(binding.getRoot()); binding.materialSwitch.setOnCheckedChangeListener((buttonView, isChecked) -> { if (isChecked) { // The switch is checked. } else { // The switch isn't checked. } }); } }
CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener est une interface à méthode abstraite unique (ou interface SAM). Vous pouvez donc l'implémenter en tant que lambda. Le lambda est appelé chaque fois que l'état coché change, et la valeur de la valeur booléenne isChecked transmise au lambda indique le nouvel état coché.

