Compose 中的 UI 測試使用語意與 UI 階層互動。 「語意」一詞的意思是指定 UI 的意義。在這種情況下,「使用者介面 (或元素)」是指單一組合和全螢幕的任何元素。語意樹狀結構會隨 UI 階層一起產生,並描述該階層。
如要進一步瞭解語意,請參閱「Compose 中的語意」。
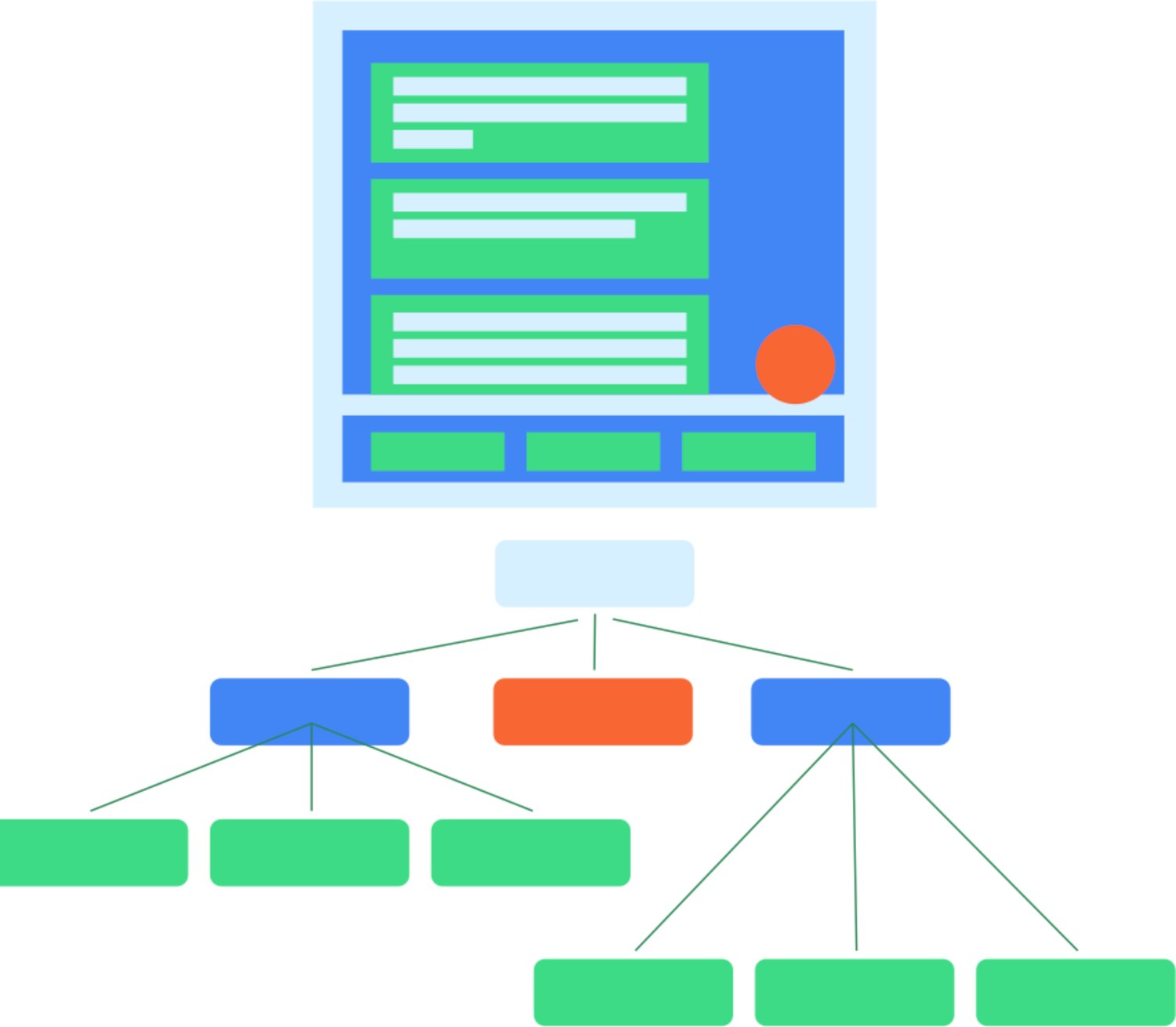
圖 1。一般 UI 階層及其語意樹狀結構。
語意架構主要用於無障礙功能,因此測試能利用語意相關 UI 階層所揭露的資訊。開發人員可自行決定要公開的內容及程度。

圖 2。包含圖示和文字的一般按鈕。
舉例來說,假設有個按鈕像上圖一樣有圖示和文字元素,預設的語意樹狀結構中只會包含「喜歡」文字標籤。這是因為某些可編譯的物件 (例如 Text) 已經對語意樹狀結構公開部分屬性。您可以使用 Modifier 將屬性新增至語意樹狀結構。
MyButton(
modifier = Modifier.semantics { contentDescription = "Add to favorites" }
)
其他資源
- 在 Android 上測試應用程式:這個主要的 Android 測試到達網頁,提供更廣泛的測試基礎知識和技術。
- 測試基礎知識:進一步瞭解測試 Android 應用程式背後的概念。
- 本機測試:您可以在自己的工作站上,在本機執行部分測試。
- 檢測設備測試:建議您也執行檢測設備測試。也就是直接在裝置上執行的測試。
- 持續整合: 持續整合可讓您將測試整合至部署管道。
- 測試不同螢幕大小:使用者可選擇的裝置種類繁多,因此您應測試不同螢幕大小。
- Espresso:雖然 Espresso 是專為以檢視區塊為基礎的 UI 設計,但您仍可運用相關知識,進行部分 Compose 測試。
