Compose에는 다양한 내장 애니메이션 메커니즘이 있으며 어떤 것을 선택해야 할지 알기 어려울 수 있습니다. 다음은 일반적인 애니메이션 사용 사례 목록입니다. 사용할 수 있는 다양한 API 옵션의 전체 집합에 관한 자세한 내용은 전체 Compose 애니메이션 문서를 참고하세요.
일반 컴포저블 속성에 애니메이션 적용
Compose는 여러 일반적인 애니메이션 사용 사례를 해결할 수 있는 편리한 API를 제공합니다. 이 섹션에서는 컴포저블의 일반적인 속성을 애니메이션으로 처리하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
나타남 / 사라짐 애니메이션

AnimatedVisibility을 사용하여 컴포저블을 숨기거나 표시합니다. AnimatedVisibility 내부의 하위 요소는 자체 진입 또는 종료 전환에 Modifier.animateEnterExit()를 사용할 수 있습니다.
var visible by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } // Animated visibility will eventually remove the item from the composition once the animation has finished. AnimatedVisibility(visible) { // your composable here // ... }
AnimatedVisibility의 enter 및 exit 매개변수를 사용하면 컴포저블이 표시되고 사라질 때의 동작을 구성할 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 전체 문서를 참고하세요.
컴포저블의 가시성을 애니메이션화하는 또 다른 방법은 animateFloatAsState를 사용하여 시간에 따라 알파를 애니메이션화하는 것입니다.
var visible by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } val animatedAlpha by animateFloatAsState( targetValue = if (visible) 1.0f else 0f, label = "alpha" ) Box( modifier = Modifier .size(200.dp) .graphicsLayer { alpha = animatedAlpha } .clip(RoundedCornerShape(8.dp)) .background(colorGreen) .align(Alignment.TopCenter) ) { }
하지만 알파를 변경하면 컴포저블이 컴포지션에 남아 레이아웃된 공간을 계속 차지한다는 주의사항이 있습니다. 이로 인해 스크린 리더와 기타 접근성 메커니즘에서 화면의 항목을 계속 고려할 수 있습니다. 반면 AnimatedVisibility는 결국 컴포지션에서 항목을 삭제합니다.

배경 색상 애니메이션
val animatedColor by animateColorAsState( if (animateBackgroundColor) colorGreen else colorBlue, label = "color" ) Column( modifier = Modifier.drawBehind { drawRect(animatedColor) } ) { // your composable here }
이 옵션은 Modifier.background()를 사용하는 것보다 성능이 더 좋습니다.
Modifier.background()는 일회성 색상 설정에는 적합하지만 시간이 지남에 따라 색상을 애니메이션으로 표시하면 필요 이상으로 재구성이 많이 발생할 수 있습니다.
배경색에 무한 애니메이션을 적용하려면 애니메이션 반복 섹션을 참고하세요.
컴포저블의 크기 애니메이션
Compose를 사용하면 다양한 방식으로 컴포저블의 크기에 애니메이션을 적용할 수 있습니다. 컴포저블 크기 변경 간 애니메이션에는 animateContentSize()을 사용합니다.
예를 들어 1줄에서 여러 줄로 확장될 수 있는 텍스트가 포함된 상자가 있는 경우 Modifier.animateContentSize()를 사용하여 더 부드러운 전환을 구현할 수 있습니다.
var expanded by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } Box( modifier = Modifier .background(colorBlue) .animateContentSize() .height(if (expanded) 400.dp else 200.dp) .fillMaxWidth() .clickable( interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() }, indication = null ) { expanded = !expanded } ) { }
SizeTransform와 함께 AnimatedContent을 사용하여 크기 변경이 어떻게 이루어져야 하는지 설명할 수도 있습니다.
컴포저블의 위치에 애니메이션 적용
컴포저블의 위치를 애니메이션으로 표시하려면 animateIntOffsetAsState()과 함께 Modifier.offset{ }를 사용합니다.
var moved by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } val pxToMove = with(LocalDensity.current) { 100.dp.toPx().roundToInt() } val offset by animateIntOffsetAsState( targetValue = if (moved) { IntOffset(pxToMove, pxToMove) } else { IntOffset.Zero }, label = "offset" ) Box( modifier = Modifier .offset { offset } .background(colorBlue) .size(100.dp) .clickable( interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() }, indication = null ) { moved = !moved } )
위치나 크기를 애니메이션으로 표시할 때 컴포저블이 다른 컴포저블 위나 아래에 그려지지 않도록 하려면 Modifier.layout{ }를 사용하세요. 이 수정자는 크기 및 위치 변경사항을 상위 요소에 전파하므로 다른 하위 요소에 영향을 미칩니다.
예를 들어 Column 내에서 Box을 이동하고 Box이 이동할 때 다른 하위 요소도 이동해야 하는 경우 다음과 같이 Modifier.layout{ }와 함께 오프셋 정보를 포함합니다.
var toggled by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } val interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() } Column( modifier = Modifier .padding(16.dp) .fillMaxSize() .clickable(indication = null, interactionSource = interactionSource) { toggled = !toggled } ) { val offsetTarget = if (toggled) { IntOffset(150, 150) } else { IntOffset.Zero } val offset = animateIntOffsetAsState( targetValue = offsetTarget, label = "offset" ) Box( modifier = Modifier .size(100.dp) .background(colorBlue) ) Box( modifier = Modifier .layout { measurable, constraints -> val offsetValue = if (isLookingAhead) offsetTarget else offset.value val placeable = measurable.measure(constraints) layout(placeable.width + offsetValue.x, placeable.height + offsetValue.y) { placeable.placeRelative(offsetValue) } } .size(100.dp) .background(colorGreen) ) Box( modifier = Modifier .size(100.dp) .background(colorBlue) ) }
Modifier.layout{ }로 애니메이션 처리하기컴포저블의 패딩 애니메이션 처리

컴포저블의 패딩을 애니메이션으로 처리하려면 animateDpAsState를 Modifier.padding()와 함께 사용합니다.
var toggled by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } val animatedPadding by animateDpAsState( if (toggled) { 0.dp } else { 20.dp }, label = "padding" ) Box( modifier = Modifier .aspectRatio(1f) .fillMaxSize() .padding(animatedPadding) .background(Color(0xff53D9A1)) .clickable( interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() }, indication = null ) { toggled = !toggled } )
컴포저블의 고도 애니메이션
컴포저블의 고도를 애니메이션으로 표시하려면 Modifier.graphicsLayer{ }과 함께 animateDpAsState를 사용하세요. 일회성 고도 변경의 경우 Modifier.shadow()를 사용합니다. 그림자를 애니메이션으로 처리하는 경우 Modifier.graphicsLayer{ } 수정자를 사용하는 것이 더 효율적입니다.
val mutableInteractionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() } val pressed = mutableInteractionSource.collectIsPressedAsState() val elevation = animateDpAsState( targetValue = if (pressed.value) { 32.dp } else { 8.dp }, label = "elevation" ) Box( modifier = Modifier .size(100.dp) .align(Alignment.Center) .graphicsLayer { this.shadowElevation = elevation.value.toPx() } .clickable(interactionSource = mutableInteractionSource, indication = null) { } .background(colorGreen) ) { }
또는 Card 컴포저블을 사용하고 상태별로 고도 속성을 다른 값으로 설정합니다.
텍스트 크기, 변환 또는 회전 애니메이션

텍스트의 크기, 변환 또는 회전을 애니메이션으로 만들 때는 TextStyle의 textMotion 매개변수를 TextMotion.Animated로 설정합니다. 이렇게 하면 텍스트 애니메이션 간 전환이 더 부드러워집니다. Modifier.graphicsLayer{ }를 사용하여 텍스트를 변환하거나 회전하거나 크기를 조정합니다.
val infiniteTransition = rememberInfiniteTransition(label = "infinite transition") val scale by infiniteTransition.animateFloat( initialValue = 1f, targetValue = 8f, animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable(tween(1000), RepeatMode.Reverse), label = "scale" ) Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { Text( text = "Hello", modifier = Modifier .graphicsLayer { scaleX = scale scaleY = scale transformOrigin = TransformOrigin.Center } .align(Alignment.Center), // Text composable does not take TextMotion as a parameter. // Provide it via style argument but make sure that we are copying from current theme style = LocalTextStyle.current.copy(textMotion = TextMotion.Animated) ) }
텍스트 색상 애니메이션
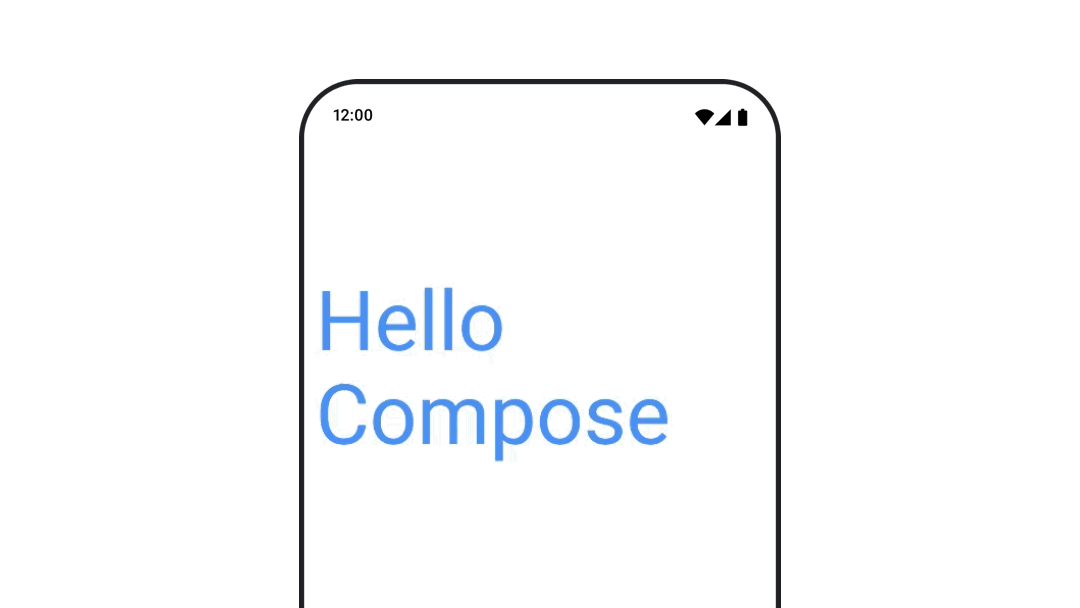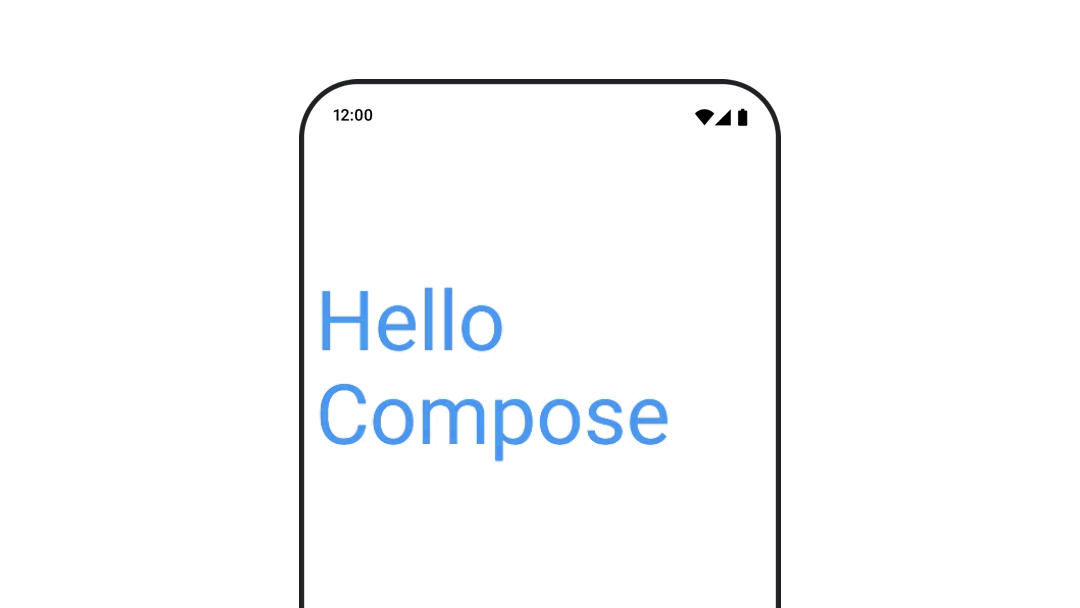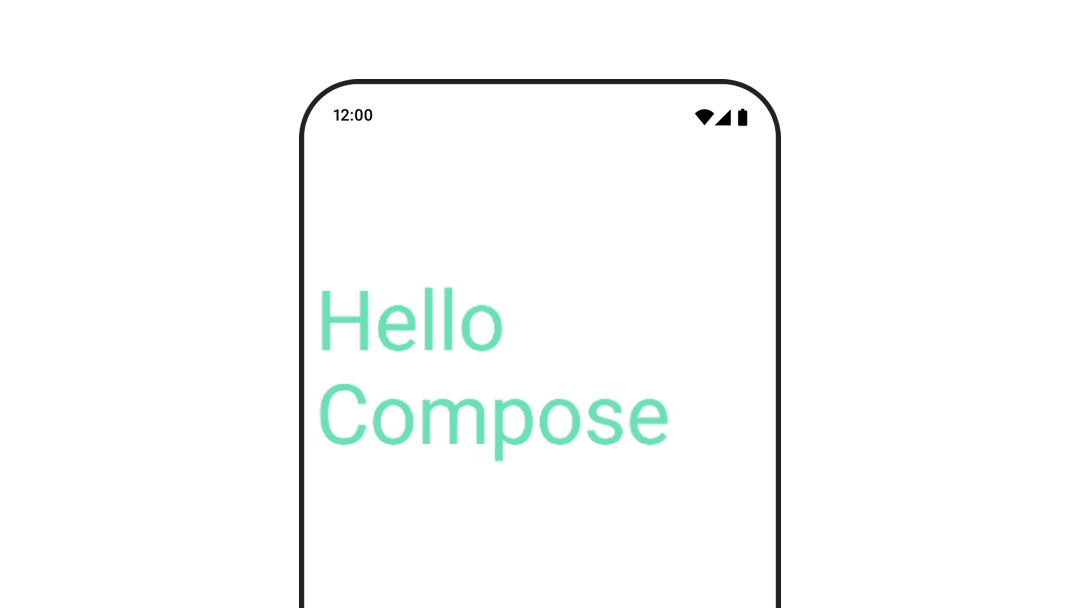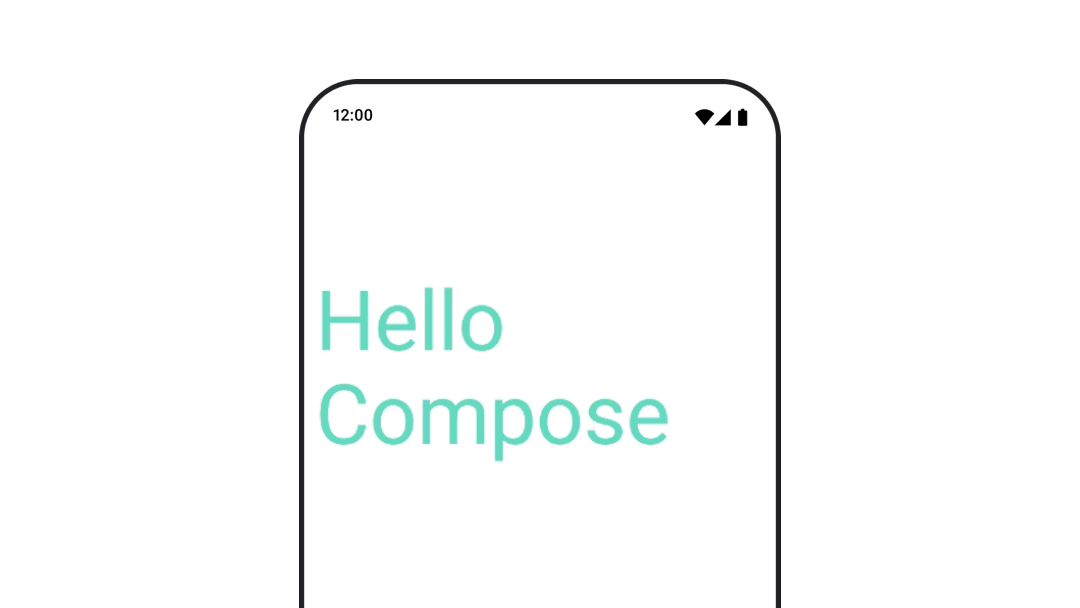
텍스트 색상을 애니메이션으로 표시하려면 BasicText 컴포저블에서 color 람다를 사용하세요.
val infiniteTransition = rememberInfiniteTransition(label = "infinite transition") val animatedColor by infiniteTransition.animateColor( initialValue = Color(0xFF60DDAD), targetValue = Color(0xFF4285F4), animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable(tween(1000), RepeatMode.Reverse), label = "color" ) BasicText( text = "Hello Compose", color = { animatedColor }, // ... )
다양한 유형의 콘텐츠 간 전환
AnimatedContent을 사용하여 여러 컴포저블 간에 애니메이션을 적용합니다. 컴포저블 간에 표준 페이드만 적용하려면 Crossfade을 사용하세요.
var state by remember { mutableStateOf(UiState.Loading) } AnimatedContent( state, transitionSpec = { fadeIn( animationSpec = tween(3000) ) togetherWith fadeOut(animationSpec = tween(3000)) }, modifier = Modifier.clickable( interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() }, indication = null ) { state = when (state) { UiState.Loading -> UiState.Loaded UiState.Loaded -> UiState.Error UiState.Error -> UiState.Loading } }, label = "Animated Content" ) { targetState -> when (targetState) { UiState.Loading -> { LoadingScreen() } UiState.Loaded -> { LoadedScreen() } UiState.Error -> { ErrorScreen() } } }
AnimatedContent는 다양한 종류의 들어가기 및 나가기 전환을 표시하도록 맞춤설정할 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 AnimatedContent 문서를 참고하거나 AnimatedContent에 관한 블로그 게시물을 참고하세요.
여러 대상으로 이동하는 동안 애니메이션 처리
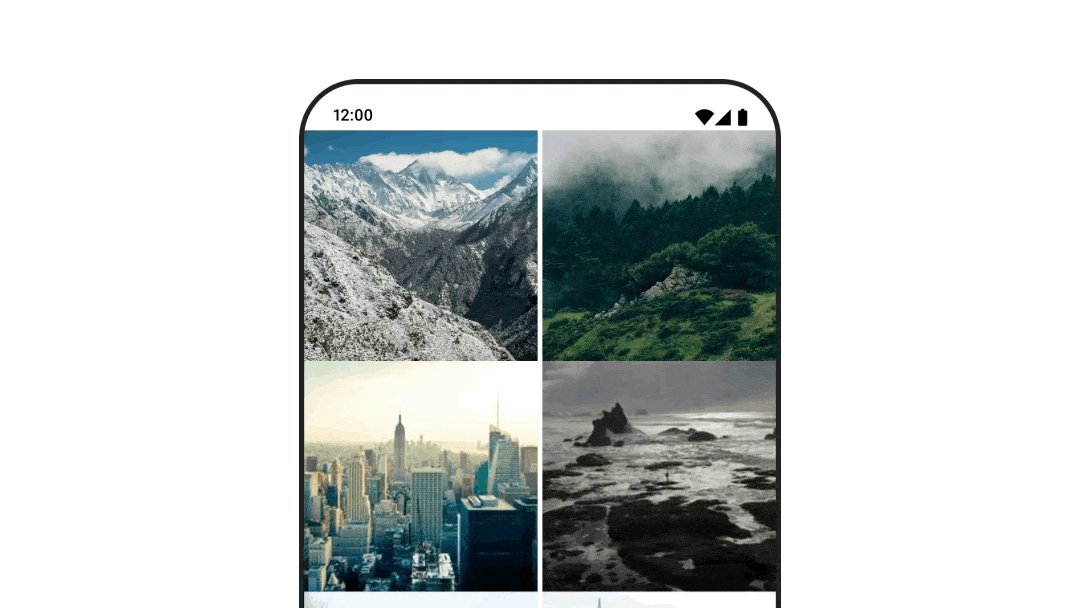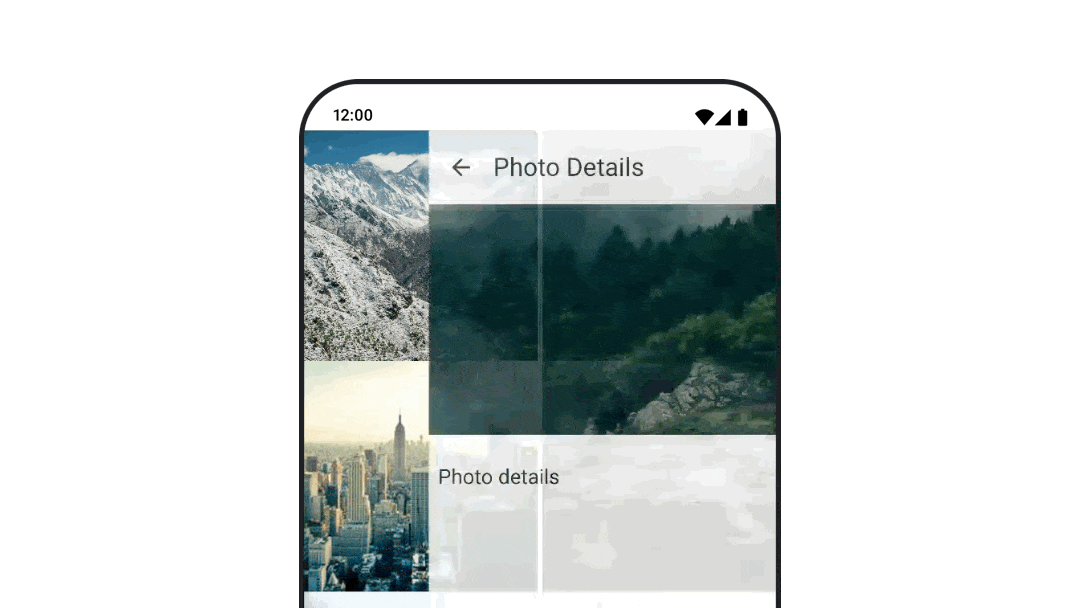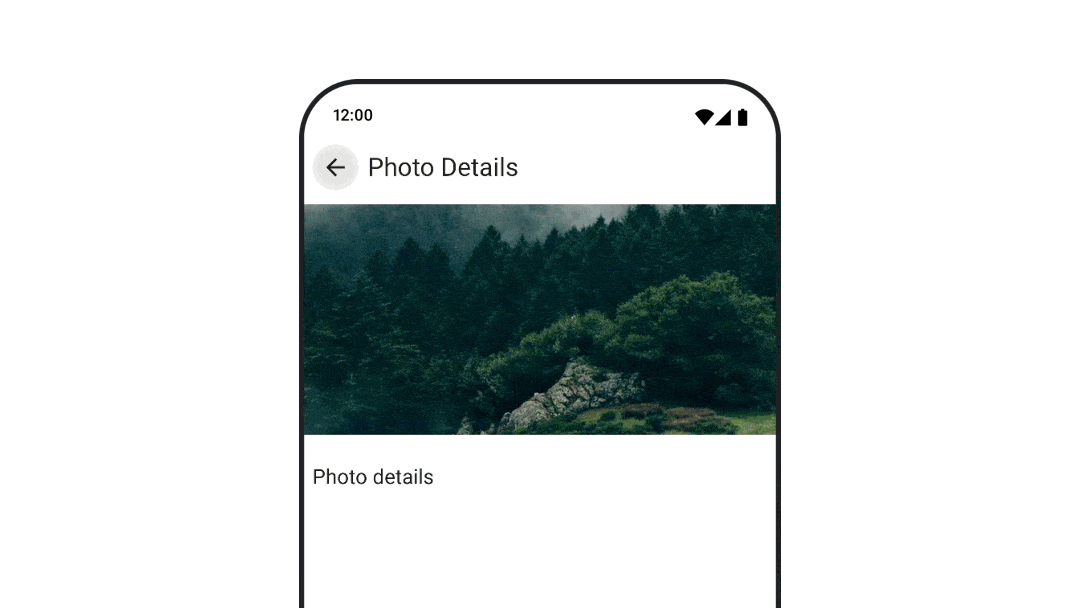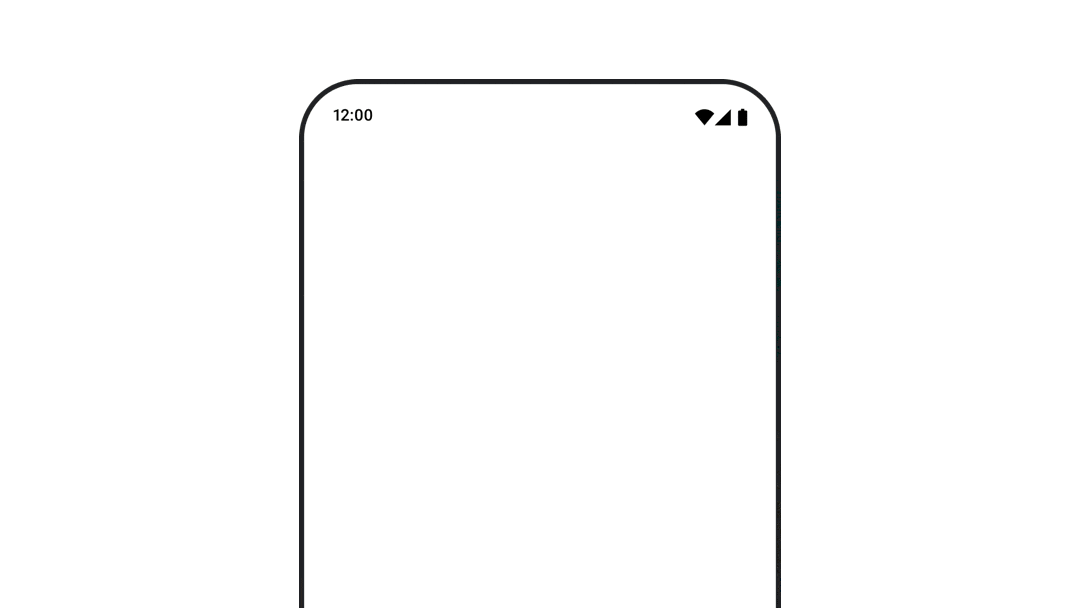
navigation-compose 아티팩트를 사용할 때 컴포저블 간 전환을 애니메이션 처리하려면 컴포저블에서 enterTransition 및 exitTransition를 지정하세요. 최상위 수준 NavHost에서 모든 대상에 사용될 기본 애니메이션을 설정할 수도 있습니다.
val navController = rememberNavController() NavHost( navController = navController, startDestination = "landing", enterTransition = { EnterTransition.None }, exitTransition = { ExitTransition.None } ) { composable("landing") { ScreenLanding( // ... ) } composable( "detail/{photoUrl}", arguments = listOf(navArgument("photoUrl") { type = NavType.StringType }), enterTransition = { fadeIn( animationSpec = tween( 300, easing = LinearEasing ) ) + slideIntoContainer( animationSpec = tween(300, easing = EaseIn), towards = AnimatedContentTransitionScope.SlideDirection.Start ) }, exitTransition = { fadeOut( animationSpec = tween( 300, easing = LinearEasing ) ) + slideOutOfContainer( animationSpec = tween(300, easing = EaseOut), towards = AnimatedContentTransitionScope.SlideDirection.End ) } ) { backStackEntry -> ScreenDetails( // ... ) } }
다양한 종류의 진입 및 종료 전환이 있으며, 이러한 전환은 들어오고 나가는 콘텐츠에 다양한 효과를 적용합니다. 자세한 내용은 문서를 참고하세요.
애니메이션 반복

infiniteRepeatable
animationSpec와 함께 rememberInfiniteTransition를 사용하여 애니메이션을 계속 반복합니다. RepeatModes를 변경하여 앞뒤로 이동하는 방식을 지정합니다.
repeatable을 사용하여 정해진 횟수만큼 반복합니다.
val infiniteTransition = rememberInfiniteTransition(label = "infinite") val color by infiniteTransition.animateColor( initialValue = Color.Green, targetValue = Color.Blue, animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable( animation = tween(1000, easing = LinearEasing), repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse ), label = "color" ) Column( modifier = Modifier.drawBehind { drawRect(color) } ) { // your composable here }
컴포저블이 실행될 때 애니메이션 시작
LaunchedEffect는 컴포저블이 컴포지션에 진입할 때 실행됩니다. 컴포저블이 실행될 때 애니메이션을 시작하므로 이를 사용하여 애니메이션 상태 변경을 유도할 수 있습니다. animateTo 메서드와 함께 Animatable를 사용하여 실행 시 애니메이션을 시작합니다.
val alphaAnimation = remember { Animatable(0f) } LaunchedEffect(Unit) { alphaAnimation.animateTo(1f) } Box( modifier = Modifier.graphicsLayer { alpha = alphaAnimation.value } )
순차적 애니메이션 만들기
Animatable 코루틴 API를 사용하여 순차적 또는 동시 애니메이션을 실행합니다. Animatable에서 animateTo를 연속으로 호출하면 각 애니메이션이 이전 애니메이션이 완료될 때까지 기다린 후 진행됩니다 .
정지 함수이기 때문입니다.
val alphaAnimation = remember { Animatable(0f) } val yAnimation = remember { Animatable(0f) } LaunchedEffect("animationKey") { alphaAnimation.animateTo(1f) yAnimation.animateTo(100f) yAnimation.animateTo(500f, animationSpec = tween(100)) }
동시 애니메이션 만들기
코루틴 API (Animatable#animateTo() 또는 animate) 또는 Transition API를 사용하여 동시 애니메이션을 구현합니다. 코루틴 컨텍스트에서 여러 실행 함수를 사용하면 애니메이션이 동시에 실행됩니다.
val alphaAnimation = remember { Animatable(0f) } val yAnimation = remember { Animatable(0f) } LaunchedEffect("animationKey") { launch { alphaAnimation.animateTo(1f) } launch { yAnimation.animateTo(100f) } }
updateTransition API를 사용하여 동일한 상태로 여러 속성 애니메이션을 동시에 제어할 수 있습니다. 아래 예에서는 상태 변경에 의해 제어되는 두 속성 rect와 borderWidth에 애니메이션을 적용합니다.
var currentState by remember { mutableStateOf(BoxState.Collapsed) } val transition = updateTransition(currentState, label = "transition") val rect by transition.animateRect(label = "rect") { state -> when (state) { BoxState.Collapsed -> Rect(0f, 0f, 100f, 100f) BoxState.Expanded -> Rect(100f, 100f, 300f, 300f) } } val borderWidth by transition.animateDp(label = "borderWidth") { state -> when (state) { BoxState.Collapsed -> 1.dp BoxState.Expanded -> 0.dp } }
애니메이션 성능 최적화
Compose의 애니메이션은 성능 문제를 일으킬 수 있습니다. 이는 애니메이션의 특성 때문입니다. 애니메이션은 움직임의 착시 현상을 만들기 위해 화면의 픽셀을 프레임별로 빠르게 이동하거나 변경합니다.
Compose의 다양한 단계(구성, 레이아웃, 그리기)를 고려하세요. 애니메이션이 레이아웃 단계를 변경하는 경우 영향을 받는 모든 컴포저블이 레이아웃을 다시 지정하고 다시 그려야 합니다. 애니메이션이 그리기 단계에서 발생하면 전체적으로 해야 할 작업이 적으므로 레이아웃 단계에서 애니메이션을 실행하는 것보다 기본적으로 성능이 더 좋습니다.
애니메이션을 적용하는 동안 앱이 최대한 적은 작업을 실행하도록 하려면 가능한 경우 Modifier의 람다 버전을 선택하세요. 이렇게 하면 재구성이 건너뛰고 컴포지션 단계 외부에서 애니메이션이 실행됩니다. 그렇지 않으면 이 수정자는 항상 그리기 단계에서 실행되므로 Modifier.graphicsLayer{ }를 사용하세요. 자세한 내용은 성능 문서의 읽기 지연 섹션을 참고하세요.
애니메이션 시간 변경하기
Compose는 기본적으로 대부분의 애니메이션에 스프링 애니메이션을 사용합니다. 스프링 또는 물리학 기반 애니메이션이 더 자연스럽게 느껴집니다. 또한 고정된 시간이 아닌 객체의 현재 속도를 고려하므로 중단될 수 있습니다.
기본값을 재정의하려면 위에 설명된 모든 애니메이션 API에서 animationSpec을 설정하여 애니메이션 실행 방식을 맞춤설정할 수 있습니다. 특정 기간 동안 실행되도록 하거나 더 탄력적으로 만들 수 있습니다.
다음은 다양한 animationSpec 옵션을 요약한 내용입니다.
spring: 물리학 기반 애니메이션으로, 모든 애니메이션의 기본값입니다. stiffness 또는 dampingRatio를 변경하여 다른 애니메이션 모양과 느낌을 구현할 수 있습니다.tween(between의 약어): 기간 기반 애니메이션으로,Easing함수를 사용하여 두 값 사이를 애니메이션화합니다.keyframes: 애니메이션의 특정 주요 지점에서 값을 지정하는 사양입니다.repeatable:RepeatMode에 지정된 특정 횟수만큼 실행되는 기간 기반 사양입니다.infiniteRepeatable: 영원히 실행되는 기간 기반 사양입니다.snap: 애니메이션 없이 최종 값으로 즉시 스냅합니다.

animationSpecs에 대한 자세한 내용은 전체 문서를 참고하세요.
추가 리소스
Compose의 재미있는 애니메이션에 관한 자세한 예는 다음을 참고하세요.
