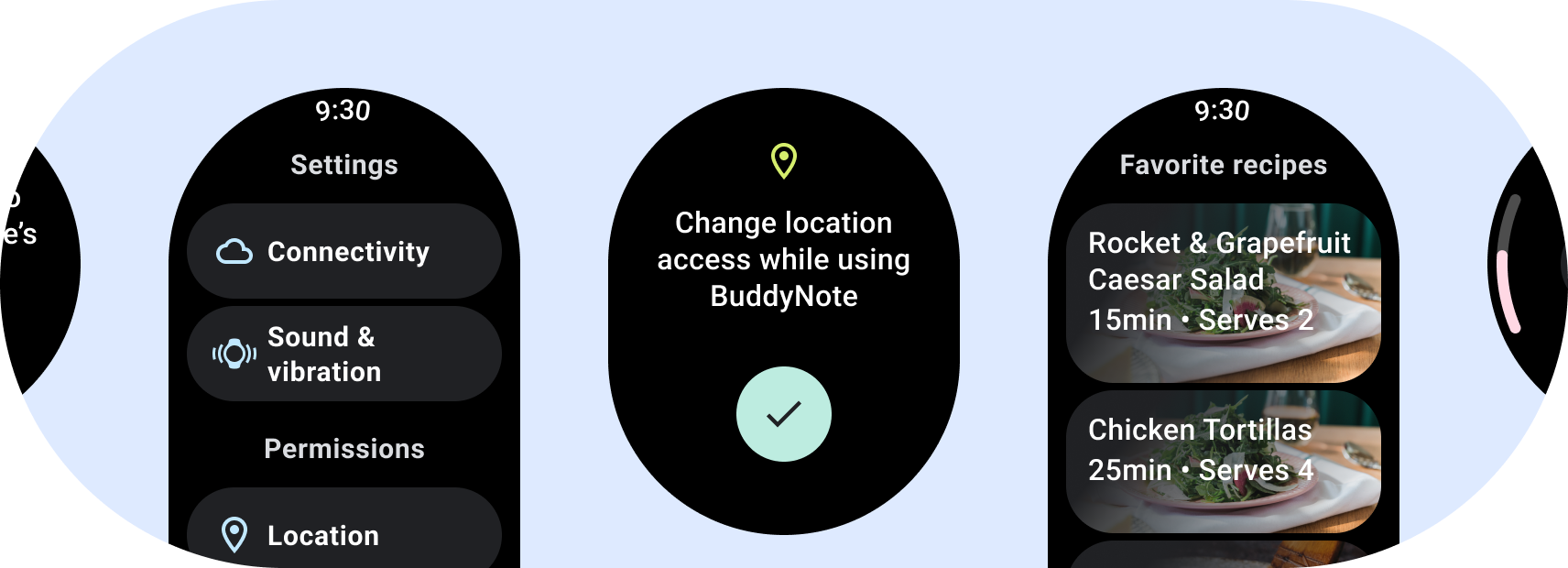
在设计 Wear OS 应用时,请谨慎选择适合的布局 。由于 Wear OS 在圆形显示屏上运行, 规范布局分为两类 您在设计应用时应该考虑的指标
非滚动应用布局
非滚动布局侧重于一目了然的信息,通过 互动很少或根本没有互动。因此,要构建 转换为这些布局:
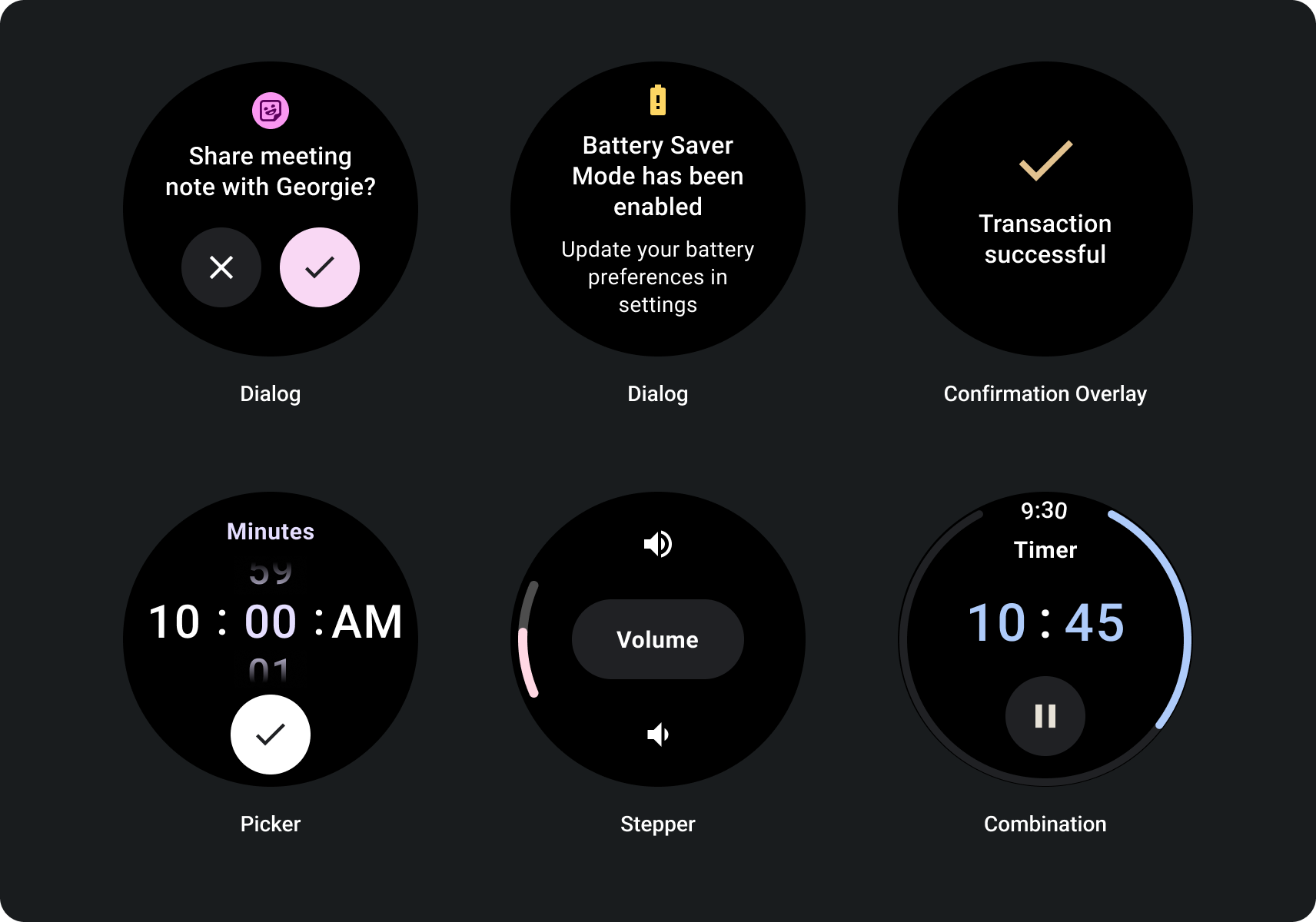
专为响应式非滚动视图而构建
- 针对语言、字体缩放、设备和可变组合进行测试 内容。
- 仅当内容已知或受控时使用不可滚动布局 或者必须使用特定的设计
- 对布局应用建议的上外边距、下外边距和侧边外边距。
- 在内容原本可能出现的位置,以百分比值定义外边距 进行裁剪。
- 合理排列元素,以充分利用空间内的空间 并在不同尺寸的设备之间取得平衡。
滚动应用布局
网页内容包含的信息过多,无法全部显示在一个屏幕上,或 若要支持更长且更具沉浸感的体验,请使用滚动条 视图。
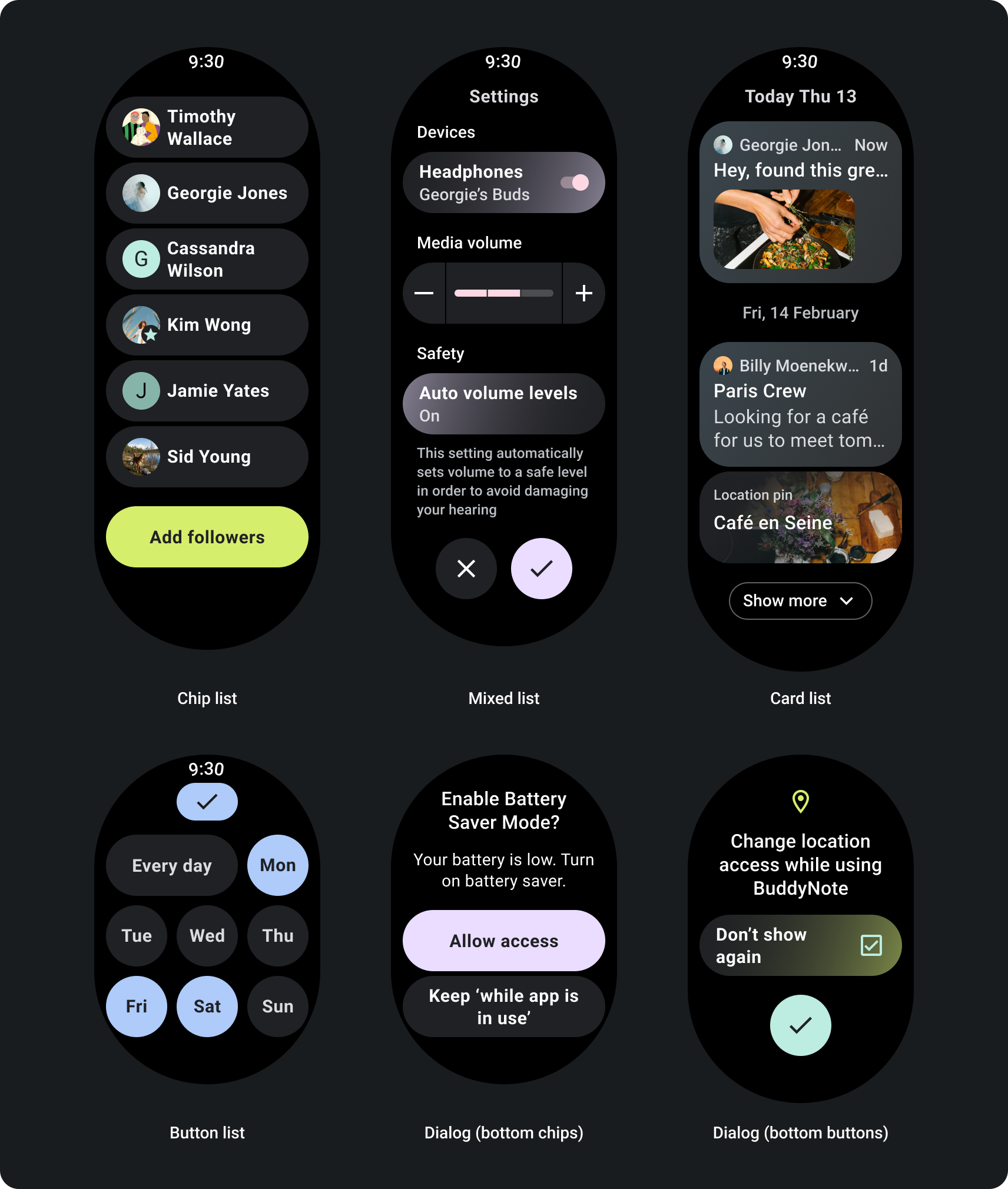
专为自适应滚动视图而构建
- 应用建议的上外边距、下外边距和侧边外边距。
- 以百分比值定义外边距,以防止在 可滚动容器的开头和结尾。
- 在界面元素之间的固定 DP 值中应用外边距。
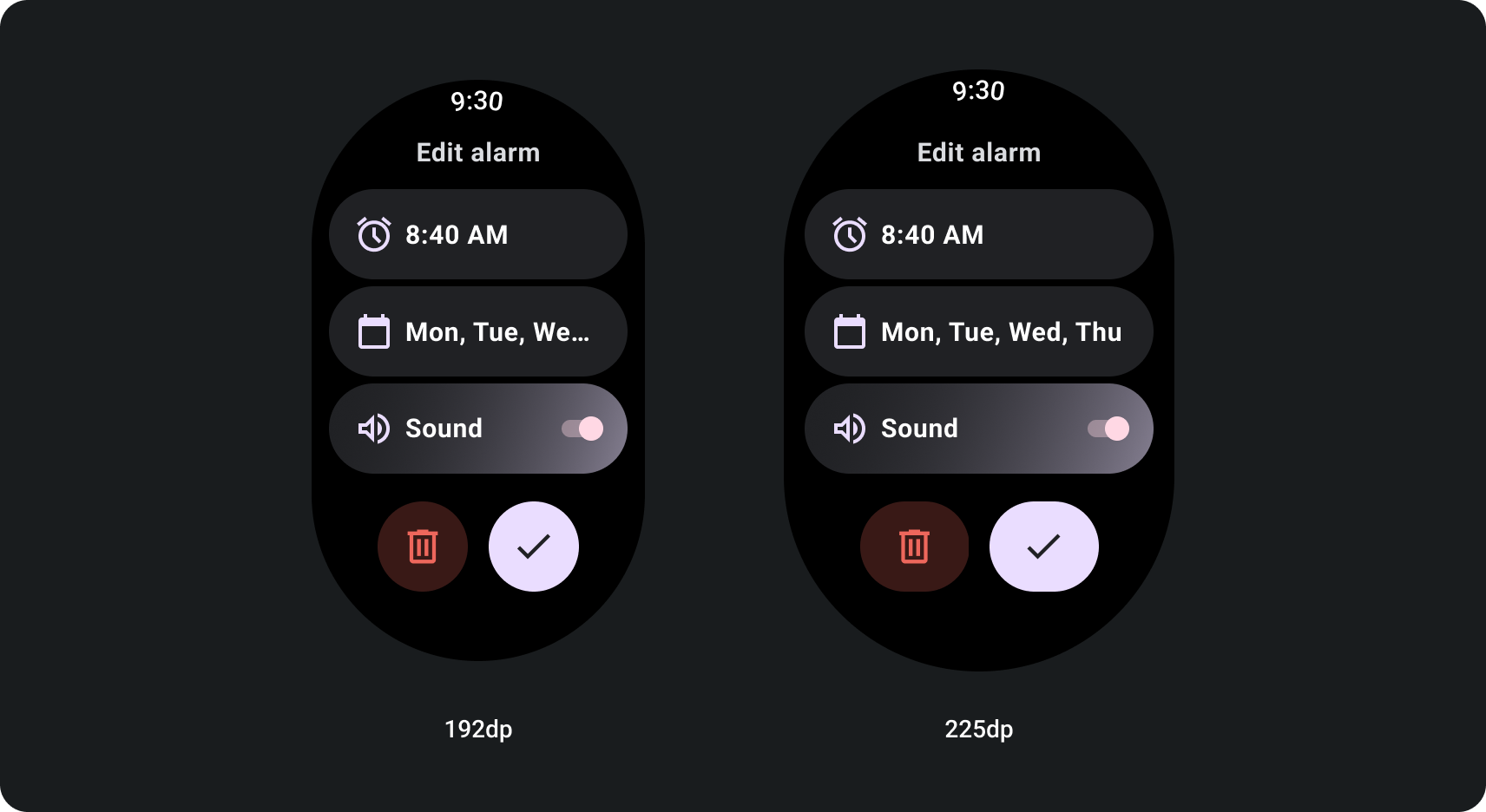
如何使用屏幕尺寸断点针对自适应滚动视图进行构建
采用响应式设计做法的滚动视图通常会适应一系列 屏幕尺寸。但在一些特殊情况下,您可以使用断点 覆盖尺寸并扩充布局,以显示其他选项,改进 或让内容更适合屏幕以下示例 显示了如何在大屏幕上加宽底部两个按钮:
Figma 设计套件
访问设计套件下载页面,探索内置 用于创建不同应用和功能块的组件、选项和建议 遵循最佳做法的设计。

