防止文本截断和内容裁剪
使用集合让一切井井有条
根据您的偏好保存内容并对其进行分类。
与手持设备相比,智能手表的屏幕尺寸较小,因此以用户可访问且高效利用可用屏幕空间的方式排列和显示元素至关重要。为了让您的内容适合屏幕,请根据 Material 准则指定正确的内边距和外边距。
即使您的设计适合屏幕,当用户执行以下任一操作时,界面的元素也可能会被截断或裁剪:
- 更改显示语言。
- 更改文字大小。
- 启用粗体文字系统设置。
测试您的设计时一定要考虑到这些因素,以确保它们无缝适应不同的用户环境。
让互动元素完全可见
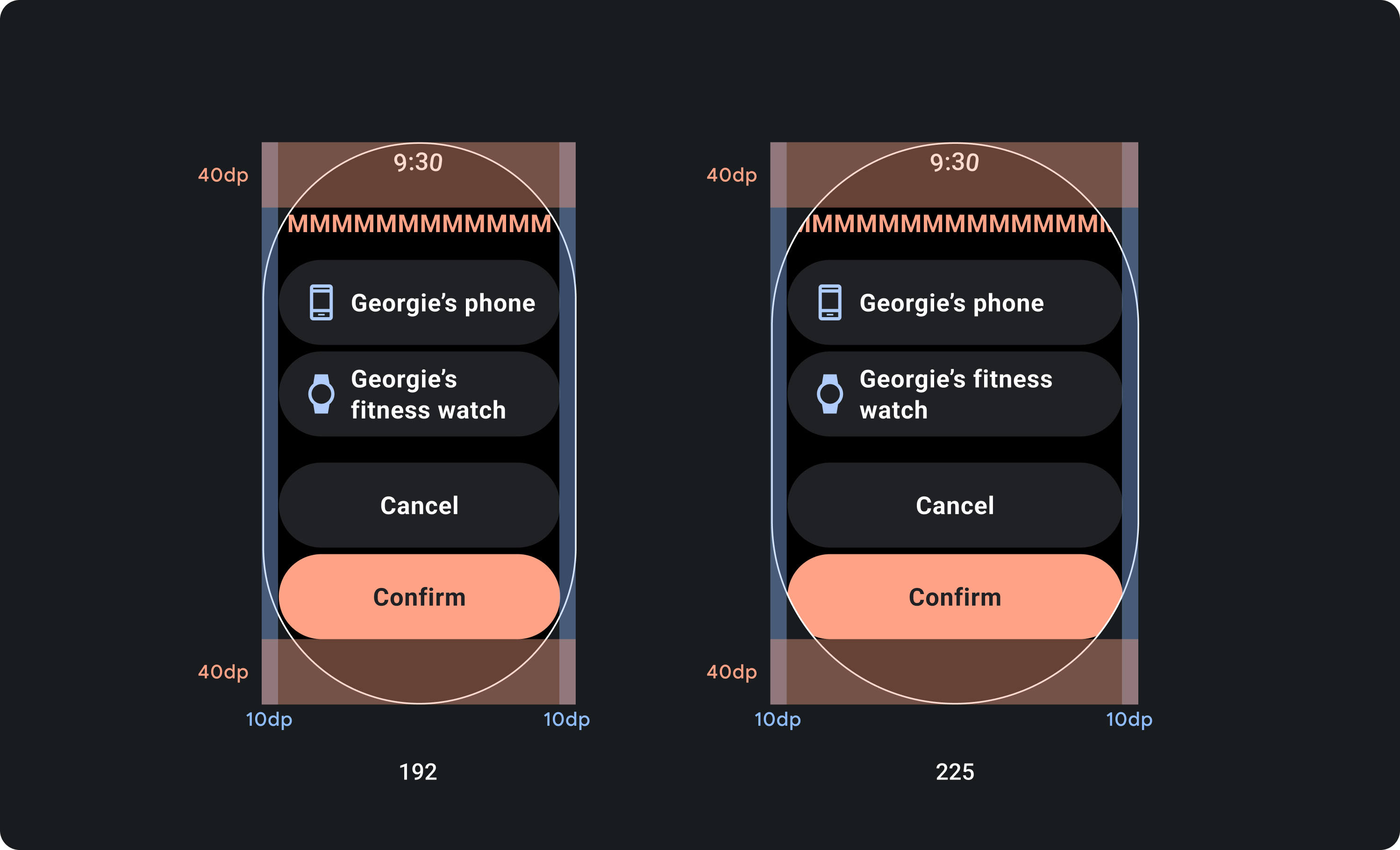
如果界面包含互动元素,请检查用户是否可以将这些元素完全滚动到用户视野范围内,尤其是当这些元素位于页面边缘时。如果您的应用使用 Horologist 库,请使用 responsive() 布局工厂。否则,请使用分隔符并为 ScalingLazyColumn 对象的顶部和底部添加外边距,以防止第一个和最后一个列表项始终被裁剪。
使用条状标签而非卡片实现密集布局
如果您需要更密集的布局,请使用 CompactChip 而不是卡片。卡片表面区域越大,防止文本被截断和内容被裁剪的难度就越大。
考虑屏幕尺寸对截断和裁剪的影响
根据 Wear OS 设备的屏幕尺寸,您可以留出较小或较大的空间来显示其他文本和按钮:
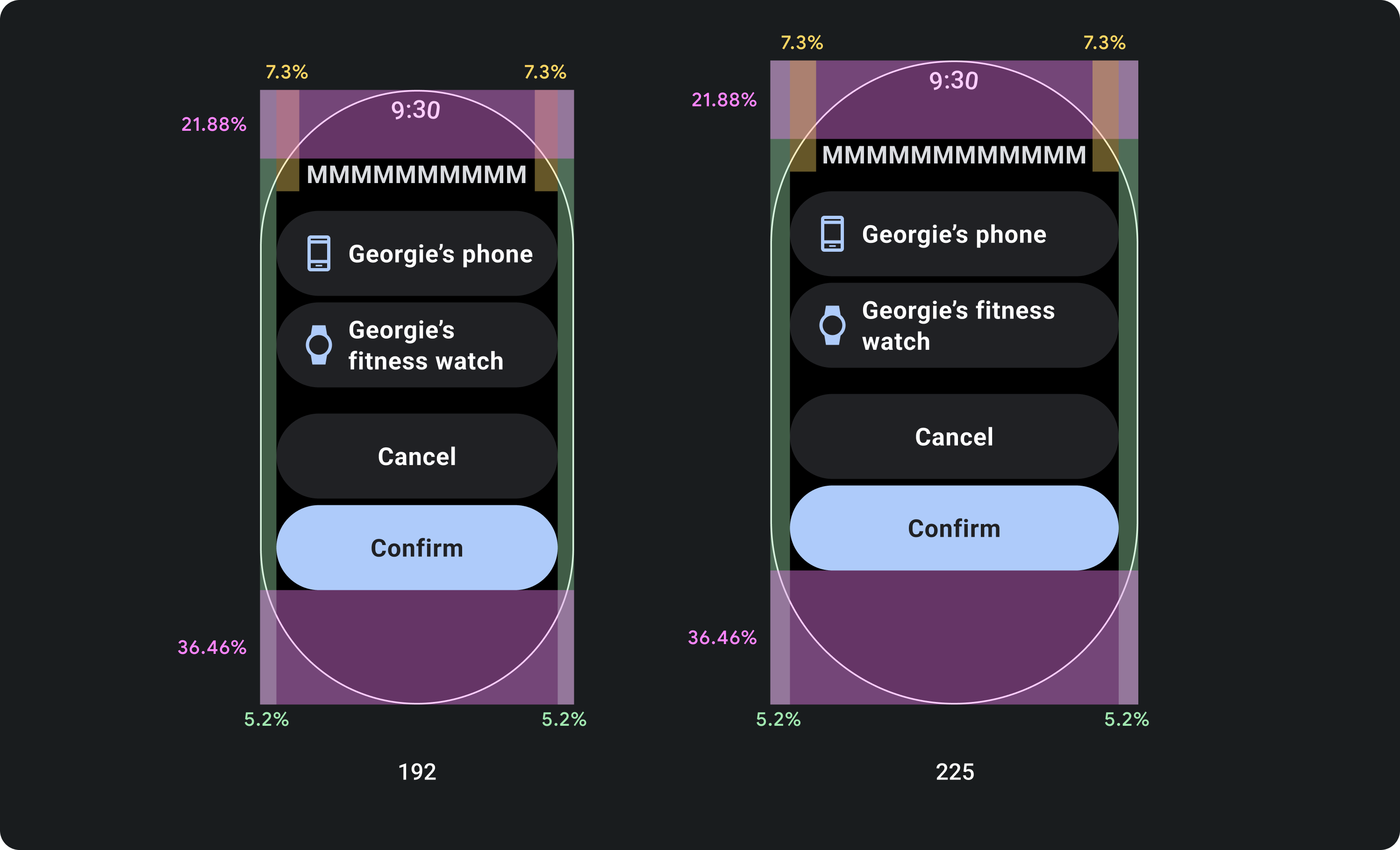
设计时应采用百分比利润率,而非固定利润率
若要创建可响应 Wear OS 设备的屏幕尺寸的内容,请应用百分比外边距,其中每个外边距的大小都相对于屏幕尺寸。如果项目位于屏幕的顶部或底部,请应用额外的内内边距,以最大限度地减少从屏幕的曲边裁剪的内容。相比之下,当一组内容足够小,足以放在一个屏幕上时,顶部和底部的空间会增加。
check_circle
正确做法
组件必须遵循百分比外边距,以便其尺寸随屏幕尺寸而缩放。这样,屏幕内容会始终填充可用空间,不会被屏幕边缘剪裁。
cancel
错误做法
不要将最大的空间用于文本,而不考虑文本在较小的屏幕上可能会如何被截断并影响设计的功能。
遵循较小的屏幕要求的字符数限制
在大多数情况下,较大的屏幕可以在截断之前显示更多文本和内容。不过,即使可能会提供更多水平空间,也应始终针对最小的屏幕尺寸进行设计,以便在各种设备上打造一致的体验。
例如,在截断之前,在较大的屏幕上,按钮可以容纳更多字符,但如果是对用户体验至关重要的号召性用语,则应使用足够短的文本,使其能够在小设备的屏幕上完整显示而不会被截断。
或者,如果功能块显示可变内容(例如从服务器提取的文本),请做好规划,避免此文本在较小的屏幕上被截断。

check_circle
正确做法
影响设计功能的文本(如号召性用语按钮)在设计时考虑到最小的屏幕。在较大的屏幕上,额外的空间可以在断点后显示额外的文本行。文本行数取决于组件和上下文。

cancel
错误做法
编写的文本会占据大屏幕的最大可用空间,而不考虑它在小屏幕上的显示效果可能会如何被截断并影响设计的功能。
本页面上的内容和代码示例受内容许可部分所述许可的限制。Java 和 OpenJDK 是 Oracle 和/或其关联公司的注册商标。
最后更新时间 (UTC):2025-07-27。
[[["易于理解","easyToUnderstand","thumb-up"],["解决了我的问题","solvedMyProblem","thumb-up"],["其他","otherUp","thumb-up"]],[["没有我需要的信息","missingTheInformationINeed","thumb-down"],["太复杂/步骤太多","tooComplicatedTooManySteps","thumb-down"],["内容需要更新","outOfDate","thumb-down"],["翻译问题","translationIssue","thumb-down"],["示例/代码问题","samplesCodeIssue","thumb-down"],["其他","otherDown","thumb-down"]],["最后更新时间 (UTC):2025-07-27。"],[],[],null,["# Prevent text truncation and content clipping\n\nSmartwatches have smaller screen sizes than handheld devices, so it's critical\nto arrange and display elements in a manner that users can access and that\nefficiently uses the available screen space. To help your items fit the screen,\nuse the correct amount of padding and margins as specified by the\n[Material guidelines](https://m3.material.io/foundations/layout/understanding-layout/spacing).\n\nEven when your design fits the screen, elements of your interface may be\ntruncated or clipped when the user does one of the following:\n\n- Changes the display language.\n- Changes the text size.\n- Enables the **Bold text** system setting.\n\nIt's crucial to test your designs with these considerations in mind to ensure\nthey adapt seamlessly to different user environments.\n\nKeep interactive elements fully visible\n---------------------------------------\n\nIf your interface includes interactive elements, check that users can scroll\nthese elements fully into view, especially if these elements are placed at the\nedges of a page. If your app uses the [Horologist](https://github.com/google/horologist) library, use the\n[`responsive()` layout factory](https://github.com/google/horologist/blob/main/docs/compose-layout.md). Otherwise, use spacers and add margins to\nthe top and bottom of a [`ScalingLazyColumn`](/reference/kotlin/androidx/wear/compose/foundation/lazy/package-summary#ScalingLazyColumn%28androidx.compose.ui.Modifier,androidx.wear.compose.foundation.lazy.ScalingLazyListState,androidx.compose.foundation.layout.PaddingValues,kotlin.Boolean,androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Arrangement.Vertical,androidx.compose.ui.Alignment.Horizontal,androidx.compose.foundation.gestures.FlingBehavior,kotlin.Boolean,androidx.wear.compose.foundation.lazy.ScalingParams,androidx.wear.compose.foundation.lazy.ScalingLazyListAnchorType,androidx.wear.compose.foundation.lazy.AutoCenteringParams,kotlin.Function1%29) object to prevent the first and\nlast list items from always being clipped.\n\nUse chips instead of cards for dense layouts\n--------------------------------------------\n\nIf you need a denser layout, use [`CompactChip`](/reference/kotlin/androidx/wear/compose/material/package-summary#CompactChip(kotlin.Function0,androidx.compose.ui.Modifier,kotlin.Function1,kotlin.Function1,androidx.wear.compose.material.ChipColors,kotlin.Boolean,androidx.compose.foundation.interaction.MutableInteractionSource,androidx.compose.foundation.layout.PaddingValues,androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Shape,androidx.wear.compose.material.ChipBorder)) instead of cards. The larger\nsurface area of cards makes it much more difficult to prevent text truncation\nand content clipping.\n\nConsider screen size effects on truncation and clipping\n-------------------------------------------------------\n\nDepending on the Wear OS device's screen size, you have a smaller or larger\nspace for additional text and buttons to be visible:\n\n### Design for percentage margins, not fixed margins\n\nTo create content that adapts responsively to the Wear OS device's screen size,\napply percentage margins, where the size of each margin is relative to the\nscreen size. In cases where items sit on the top or bottom of the screen, apply\nadditional inner padding to minimize content clipping from the screen's curved\nedge. In contrast, the space at the top and bottom increases when a group of\ncontent is small enough to fit on one screen.\n\ncheck_circle\n\n### Do\n\nComponents must adhere to the percentage margins so that their size scales with the screen's size. This way, the content of your screen always fills the space available and isn't cropped by the screen's edges.\n\ncancel\n\n### Don't\n\nDon't use the maximum space available for text without considering how it may truncate on smaller screens and affect the functionality of your design.\n\n### Use the character limits required by smaller screens\n\nIn most cases, larger screens can show more text and content before truncation.\nEven though more horizontal space might be available, however, always design for\nthe smallest screen size to create a consistent experience across devices.\n\nFor example, a button may have space for more characters on a larger screen\nbefore truncation, but if it's an important call to action that is vital to the\nuser experience, then use text that's short enough to appear entirely, without\ntruncating, on a small device's screen.\n\nAlternatively, if the tile shows variable content, such as text fetched from a\nserver, plan for the possibility that this text is truncated on smaller screens.\n\ncheck_circle\n\n### Do\n\nText which affects the functionality of your design, like call-to-action buttons, is designed with the smallest screen in mind. The additional space on larger screens can show additional lines of text after the breakpoint. The number of lines of text depends on the component and context.\n\ncancel\n\n### Don't\n\nDon't write text that consumes the maximum space available on a larger screen without considering how it may appear truncated on smaller screens and affect the functionality of your design."]]





