将 C 和 C++ 代码置于项目模块的 cpp 目录中,以将其添加到您的 Android 项目中。在您构建项目时,这些代码会编译到一个可由 Gradle 与您的应用打包在一起的原生库中。然后,Java 或 Kotlin 代码即可通过 Java 原生接口 (JNI) 调用原生库中的函数。如需详细了解如何使用 JNI 框架,请参阅 Android 的 JNI 提示。
Android Studio 支持适用于跨平台项目的 CMake。Android Studio 还支持 ndk-build,它比 CMake 速度更快,但仅支持 Android。目前不支持在同一模块中同时使用 CMake 和 ndk-build。
如需将现有的 ndk-build 库导入您的 Android Studio 项目,请了解如何将 Gradle 关联到原生库项目。
本页将向您介绍如何设置 Android Studio 以支持必要的构建工具、如何创建新项目并让其支持 C/C++,以及如何向您的项目添加新的 C/C++ 文件。
如果您想要将原生代码添加到现有项目,请按以下步骤操作:
-
创建新的原生源代码文件,并将这些文件添加到您的 Android Studio 项目中。
- 如果您已经拥有原生代码或想要导入预构建原生库,请跳过此步骤。
-
配置 CMake 以将原生源代码构建入库。如果您要导入并关联预构建库或平台库,则必须使用此构建脚本。
- 如果现有的原生库已有
CMakeLists.txt构建脚本,或者使用ndk-build并包含Android.mk构建脚本,请跳过此步骤。
- 如果现有的原生库已有
-
提供 CMake 或
ndk-build脚本文件的路径,以配置 Gradle。Gradle 使用构建脚本将源代码导入您的 Android Studio 项目并将原生库打包到应用中。
配置完项目后,使用 JNI 框架通过 Java 或 Kotlin 代码访问原生函数。如需构建和运行应用,请点击 Run 图标  。
。
注意:如果现有项目使用的是已废弃的 ndkCompile 工具,请改为使用 CMake 或 ndk-build。
下载 NDK 和构建工具
如需为您的应用编译和调试原生代码,您需要以下组件:
- Android 原生开发套件 (NDK):一个工具集,让您能够在 Android 应用中使用 C 和 C++ 代码。NDK 会提供平台库,让您能够管理原生 activity 和访问实体设备组件,例如传感器和触控输入。
-
CMake:一款外部构建工具,可与 Gradle 搭配使用来构建原生库。如果您只计划使用
ndk-build,则无需此组件。 - LLDB:Android Studio 中用于调试原生代码的调试程序。
如需了解如何安装这些组件,请参阅安装及配置 NDK 和 CMake。
创建支持 C/C++ 的新项目
创建支持原生代码的新项目的流程与创建任何其他 Android Studio 项目的流程类似,但需要执行一个额外的步骤:
- 在向导的 Choose your project 部分中,选择 Native C++ 项目类型。
- 点击 Next。
- 填写向导下一部分中的所有其他字段。
- 点击 Next。
-
在向导的 Customize C++ Support 部分中,您可以使用 C++ Standard 字段自定义项目。
- 使用下拉列表选择您想要使用哪种 C++ 标准化。选择 Toolchain Default,将使用默认的 CMake 设置。
- 点击 Finish。
在 Android Studio 完成新项目的创建后,请从 Android Studio 左侧打开 Project 窗格,然后从菜单中选择 Android 视图。如图 1 所示,Android Studio 会添加 cpp 组:
图 1. 原生源代码和外部构建脚本的 Android 视图组。
注意:此视图并未反映磁盘上的实际文件层次结构,而是将相似的文件归为一组,以便简化项目导航。
在 cpp 组中,您可以找到项目中的所有原生源代码文件、头文件、CMake 或 ndk-build 的构建脚本,以及项目中的预构建库。对于新项目,Android Studio 会创建一个示例 C++ 源代码文件 native-lib.cpp,并将其置于应用模块的 src/main/cpp/ 目录中。此示例代码提供了一个简单的 C++ 函数 stringFromJNI(),它会返回字符串 "Hello from C++"。如需了解如何向项目添加其他源代码文件,请参阅介绍如何创建新的原生源代码文件的部分。
与 build.gradle 文件指示 Gradle 如何构建应用一样,CMake 和 ndk-build 需要构建脚本才能确定如何构建您的原生库。对于新项目,Android Studio 会创建 CMake 构建脚本 CMakeLists.txt,并将其置于模块的根目录中。如需详细了解此构建脚本的内容,请参阅配置 CMake。
构建和运行示例应用
点击 Run 图标  后,Android Studio 会构建并启动一个应用,此应用会在您的 Android 设备或模拟器上显示文字“Hello from C++”。下面的概览介绍了在构建和运行示例应用时会发生的事件:
后,Android Studio 会构建并启动一个应用,此应用会在您的 Android 设备或模拟器上显示文字“Hello from C++”。下面的概览介绍了在构建和运行示例应用时会发生的事件:
- Gradle 调用您的外部构建脚本
CMakeLists.txt。 - CMake 按照构建脚本中的命令将 C++ 源代码文件
native-lib.cpp编译到共享对象库中,并将其命名为libnative-lib.so。Gradle 随后会将其打包到应用中。 - 在运行时,应用的
MainActivity会使用System.loadLibrary()加载原生库。现在,应用就可以使用库的原生函数stringFromJNI()了。 -
MainActivity.onCreate()调用stringFromJNI(),后者会返回"Hello from C++",并使用它来更新TextView。
如需验证 Gradle 是否会将原生库打包到应用中,请使用 APK 分析器:
- 依次选择 Build > Build Bundles(s) / APK(s) > Build APK(s)。
- 依次选择 Build > Analyze APK。
- 从
app/build/outputs/目录中选择 APK 或 AAB,然后点击 OK。 - 如图 2 所示,您可以在 APK 分析器窗口中的
lib/<ABI>/下看到libnative-lib.so。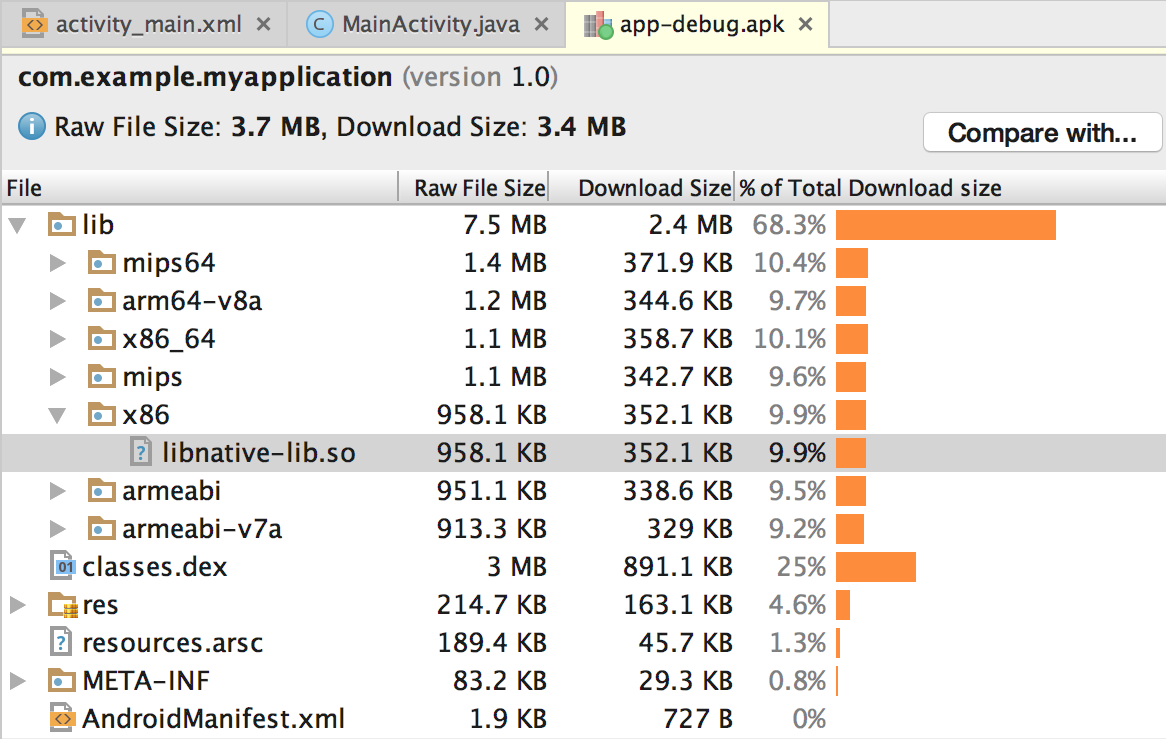
图 2. 使用 APK 分析器查找原生库。
提示:如果您想要利用其他使用了原生代码的 Android 应用进行实验,请依次点击 File > New > Import Sample,然后从 Ndk 列表中选择一个示例项目。
创建新的 C/C++ 源代码文件
如需将新的 C/C++ 源代码文件添加到现有项目,请按以下步骤操作:
- 如果您的应用的主源代码集内还没有
cpp/目录,请按如下所示的方法创建一个: - 打开 Android Studio 左侧的 Project 窗格,然后从菜单中选择 Project 视图。
- 依次选择 your-module > src。
- 右键点击 main 目录,然后依次选择 New > Directory。
- 输入
cpp作为目录名称,然后点击 OK。 - 右键点击
cpp/目录,然后依次选择 New > C/C++ Source File。 - 为您的源代码文件输入一个名称,例如
native-lib。 - 从 Type 菜单中,选择源代码文件的文件扩展名,例如
.cpp。- 点击 Edit File Types 图标
 ,向菜单中添加其他文件类型,例如
,向菜单中添加其他文件类型,例如 .cxx或.hxx。在弹出的 New File Extensions 对话框中,从 Source Extension 和 Header Extension 菜单中选择其他文件扩展名,然后点击 OK。
- 点击 Edit File Types 图标
- 如需创建头文件,请勾选 Create an relevantheader 复选框。
- 点击 OK。
向项目中添加新的 C/C++ 文件后,您仍需要配置 CMake 以将这些文件包含在原生库中。
其他资源
如需详细了解如何在应用中支持 C/C++ 代码,请使用以下资源。
Codelab
- 使用 Android Studio 创建 Hello-CMake 此 Codelab 将向您介绍如何使用 Android Studio CMake 模板开始开发 Android NDK 项目。
