Android 스튜디오 3.0 이상에서는 Android 스튜디오 프로젝트에서 빌드하지 않고도 디버깅이 사용 설정된 APK를 프로파일링하고 디버그할 수 있습니다.
APK 디버깅을 시작하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
Android 스튜디오 시작 화면에서 Profile or debug APK를 클릭합니다.
프로젝트가 이미 열려 있다면 메뉴 바에서 File > Profile or Debug APK를 클릭합니다.
대화상자가 열리면 Android 스튜디오로 가져오려는 APK를 선택합니다.
OK(확인)을 클릭합니다.
이 옵션이 표시되지 않으면 'Android APK 지원' 플러그인이 사용 설정되어 있는지 확인하세요.
그러면 그림 1처럼 Android 스튜디오에 압축해제된 APK 파일이 표시됩니다. 이 파일은 DEX 파일의 보다 읽기 쉬운 버전인 SMALI 파일을 제공하지만 완전히 디컴파일된 파일 세트는 아닙니다.
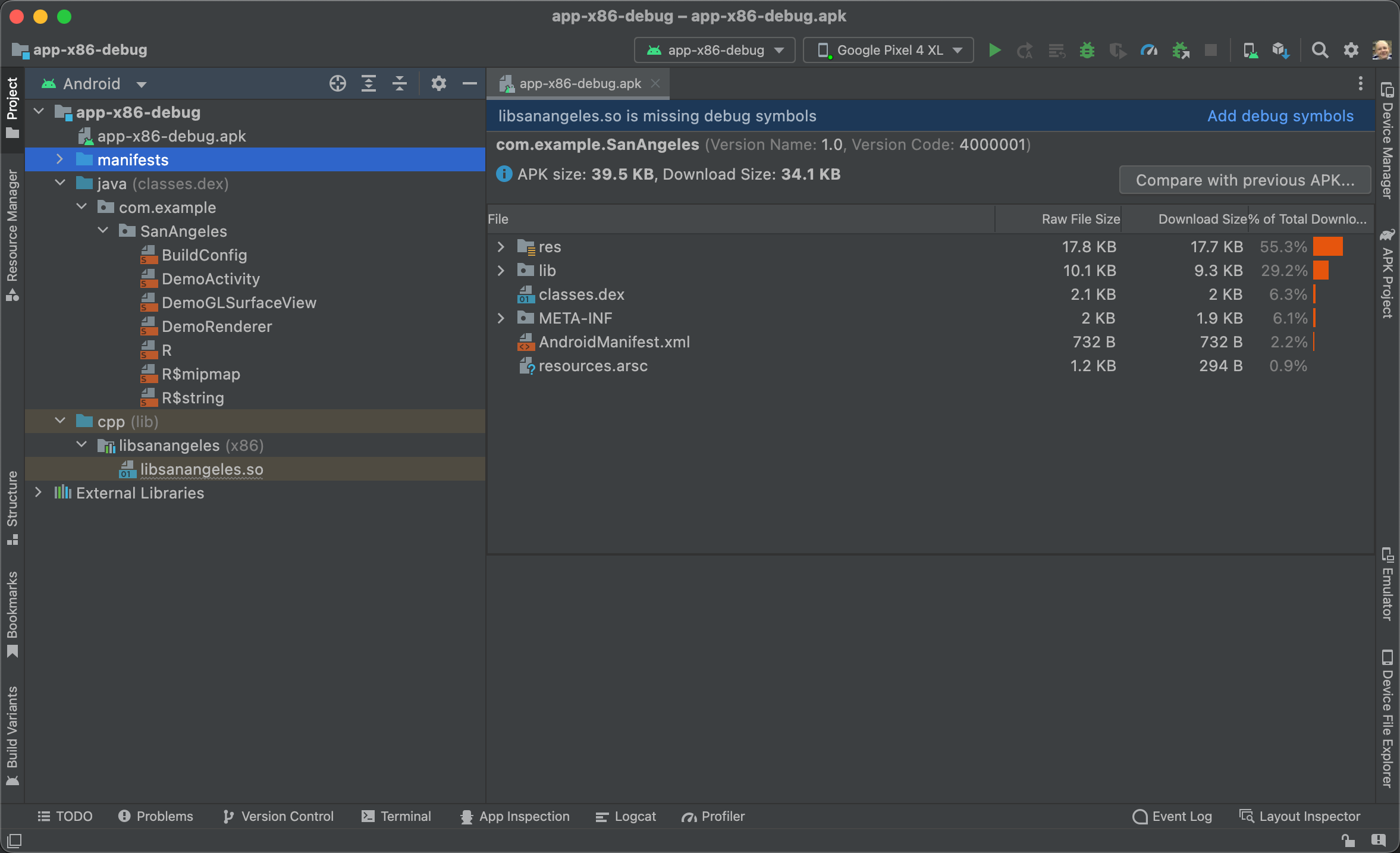
그림 1. Android 스튜디오에 사전 빌드된 APK 가져오기
Project 창의 Android 뷰에서는 APK의 다음과 같은 내용을 검사할 수 있습니다.
- APK 파일: APK를 더블클릭하여 APK Analyzer를 엽니다.
- 매니페스트: APK에서 추출한 앱 매니페스트가 포함됩니다.
- Java: Android 스튜디오가 APK의 DEX 파일에서 SMALI 파일로 분해하는 Kotlin 코드 또는 Java 코드가 포함됩니다. 이 디렉터리의 각 SMALI 파일이 하나의 Kotlin 클래스 또는 Java 클래스에 해당합니다.
- cpp: 앱에 네이티브 코드가 포함된 경우, 이 디렉터리에는 APK의 네이티브 라이브러리(SO 파일)가 포함됩니다.
- 외부 라이브러리: Android SDK가 포함됩니다.
Android 프로파일러를 사용하여 앱의 성능 테스트를 시작할 수 있습니다.
앱의 Kotlin 코드나 Java 코드를 디버그하려면 Kotlin 또는 Java 소스를 연결하고 Kotlin 또는 Java 소스 파일에 중단점을 추가해야 합니다. 마찬가지로, 네이티브 코드를 디버그하려면 네이티브 디버그 기호를 연결해야 합니다.
Kotlin 또는 Java 소스 연결
기본적으로 Android 스튜디오는 APK에서 Kotlin 코드 또는 Java 코드를 추출하고 SMALI 파일로 저장합니다. 중단점을 사용하여 Kotlin 코드 또는 Java 코드를 디버그하려면 디버그할 SMALI 파일에 해당하는 Kotlin 또는 Java 소스 파일로 IDE를 가리켜야 합니다.
Kotlin 또는 Java 소스를 연결하려면 다음 단계를 진행하세요.
- Android 뷰의 Project 창에서 SMALI 파일을 더블클릭합니다.
파일을 열면 Kotlin 또는 Java 소스를 선택하라는 배너가 편집기에 표시됩니다.

- 편집기 창의 배너에서 Attach Kotlin/Java Sources...를 클릭합니다.
- 앱의 Kotlin 또는 Java 소스 파일이 있는 디렉터리로 이동한 다음 Open을 클릭합니다.
Project 창에서 Android 스튜디오가 SMALI 파일을 해당하는 Kotlin 또는 Java 소스 파일로 바꿉니다. Android 스튜디오에는 내부 클래스도 자동으로 포함됩니다. 이제 중단점을 추가하고 앱을 디버그할 수 있습니다.
네이티브 디버그 기호 연결하기
APK에 디버그 기호를 포함하지 않는 네이티브 라이브러리(SO 파일)가 포함된 경우 그림 1에 나온 것처럼 Android 스튜디오가 배너를 표시합니다. 디버그 가능한 네이티브 라이브러리를 연결해야만 APK의 네이티브 코드를 디버그하거나 중단점을 사용할 수 있습니다.
디버그 가능한 네이티브 라이브러리를 연결하려면 다음 단계를 진행하세요.
- 아직 NDK 및 도구를 다운로드하지 않았다면 다운로드합니다.
Android 뷰의 Project 창에 있는 cpp 디렉터리 아래에서 디버그 기호가 포함되지 않은 네이티브 라이브러리 파일을 더블클릭합니다.
APK가 지원하는 모든 ABI가 편집기에 테이블로 나타납니다.
편집기 창 오른쪽 상단에서 Add를 클릭합니다.
연결하려는 디버그 가능한 네이티브 라이브러리가 포함된 디렉터리로 이동하여 OK를 클릭합니다.
APK와 디버그 가능한 네이티브 라이브러리가 서로 다른 워크스테이션을 사용하여 빌드된 경우 다음 단계에 따라 디버그 기호의 로컬 경로도 지정해야 합니다.
누락된 디버그 기호의 로컬 경로를 추가하려면 편집기 창의 Path Mappings 섹션에 있는 Local Paths 열 아래의 필드를 수정합니다(그림 2 참고).
대부분의 경우 루트 폴더 경로를 제공하기만 하면 됩니다. 그러면 Android 스튜디오가 자동으로 하위 디렉터리를 검사하여 추가 소스를 매핑합니다. 또한 Android 스튜디오는 자동으로 원격 NDK 경로를 로컬 NDK 다운로드에 매핑합니다.
편집기 창의 Path Mappings 섹션에 있는 Apply Changes를 클릭합니다.
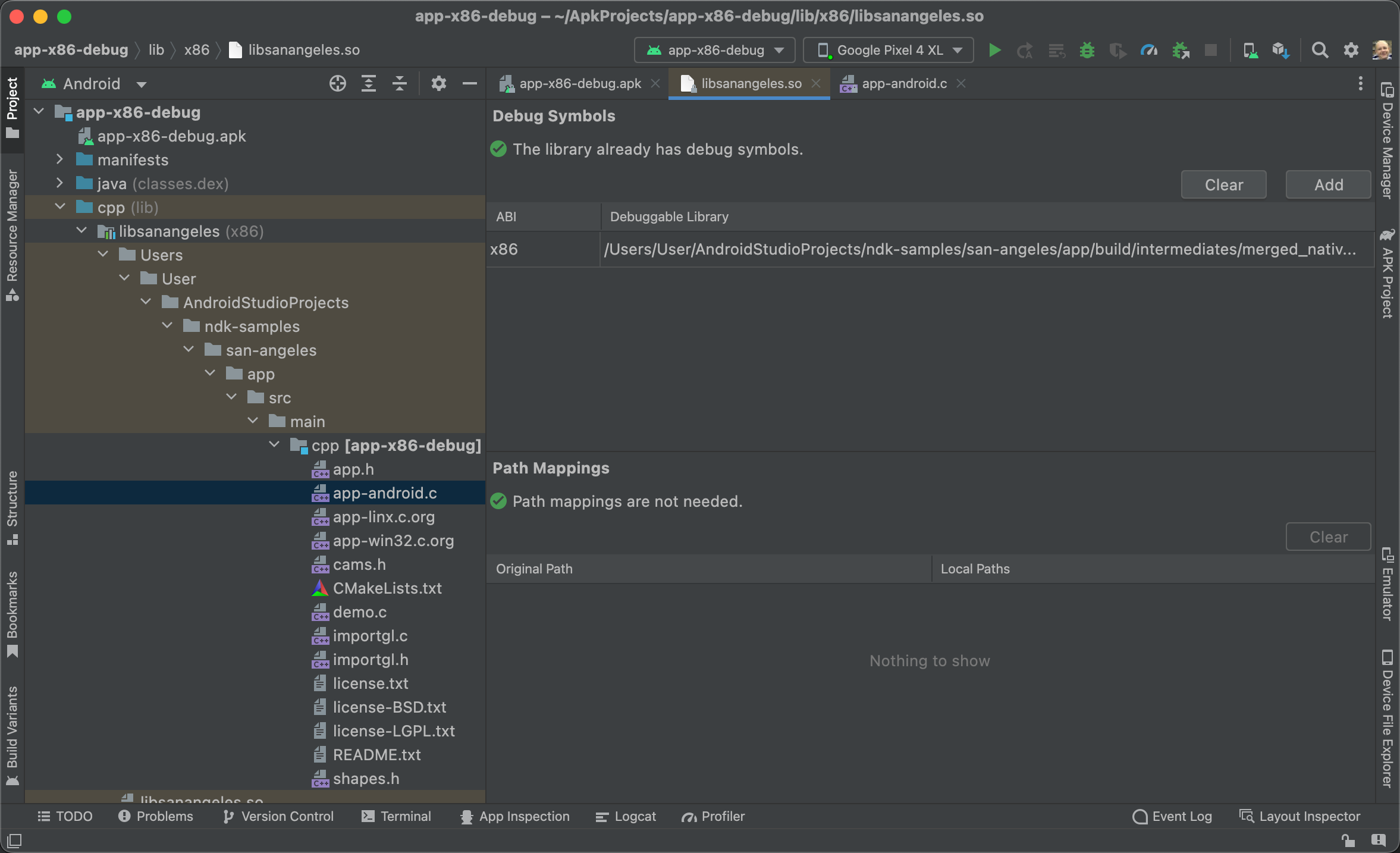
그림 2. 디버그 기호 로컬 경로
네이티브 소스 파일이 Project 창에 나타납니다. 네이티브 소스 파일을 열고 중단점을 추가하고 앱을 디버그합니다. 매핑을 삭제하려면 편집기 창의 Path Mappings 섹션에서 Clear를 클릭합니다.
알려진 문제: 디버그 기호를 APK에 연결할 때 APK와 디버그 가능한 SO 파일은 모두 동일한 워크스테이션이나 빌드 서버를 사용하여 빌드해야 합니다.
Android 스튜디오 3.6 이상에서는 APK를 IDE 외부에서 업데이트할 때 새 프로젝트를 만들 필요가 없습니다. Android 스튜디오에서는 APK의 변경사항을 감지하고 다시 가져올 수 있는 옵션을 제공합니다.

그림 3. Android 스튜디오 외부에서 업데이트된 APK 다시 가져오기
