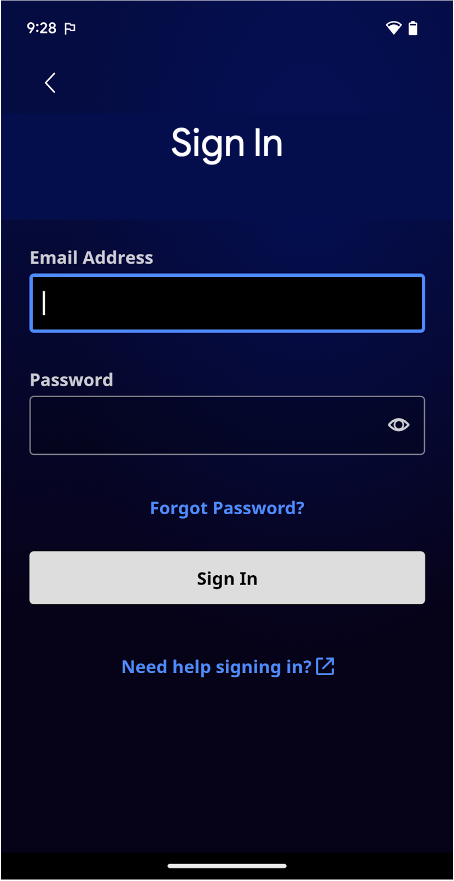
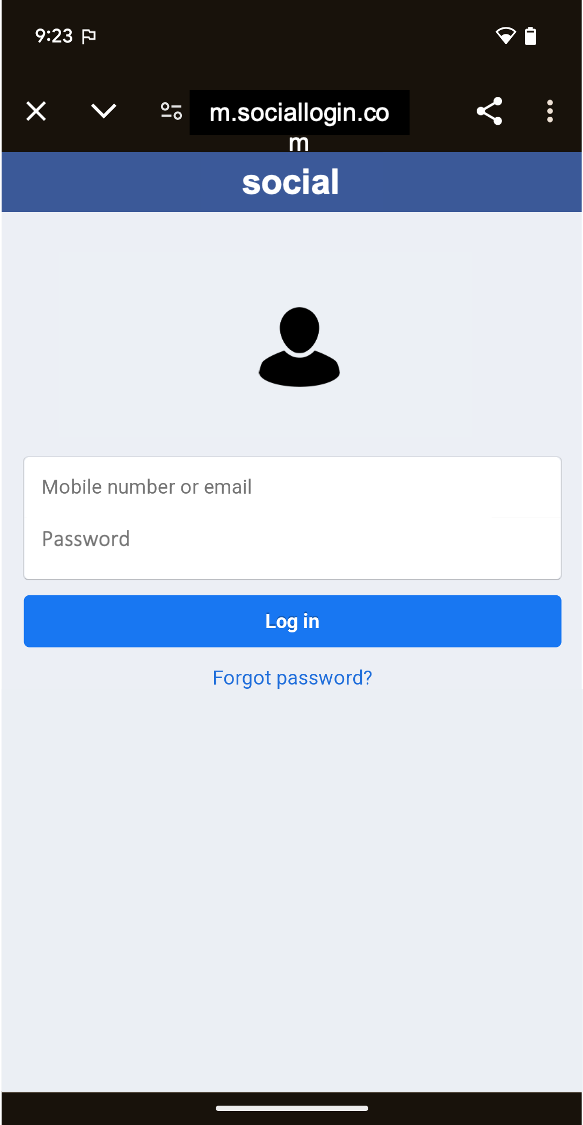
Android lets you build on the power of the web within your apps. So, you can benefit from the flexibility and efficiency of being able to display certain types of content.
This lets you seamlessly integrate existing web content into your Android app, such as to display a news feed, show interactive tutorials, display ads, or even host a mini-game without building everything from scratch. Think of it as a window to the internet, from within your app. There are two ways to embed web content into your app:
WebView: It displays web content you control inline where you want a high degree of flexibility in customizing or updating the UI.Custom Tabs: A full in-app browsing experience powered by the user's default browser (see browser support) for when users click a link and you want to keep them in the app, instead of leaving to an external browser, with much of the browsing experience out-of-the-box.

Why embed web content?
There are several benefits to embedding web content in your app:
- Efficiency: Reuse existing code from your website. Build on existing web technologies and content.
- Integration: Use external content from third-party providers, such as media and ads, within your app.
- Flexibility: Update content dynamically without being constrained to predefined UIs, or without releasing app updates.
When to use web content?
There are three primary uses cases for using the Web in your Android app:
1. Embedding web content into your app as primary or supporting content:
Use WebView
- Display your own web content inline as a primary experience where you want a high degree of flexibility in customizing or updating the UI.
- Display other content such as ads, legal terms and regulations, or other third-party content inline, or as a window within your app experience.

2. In-app browsing using Custom Tabs, or WebView for more advanced
use cases
- Have a full in-app browsing experience for when users click a link and you
want to keep them in the app, instead of leaving to an external browser.
- Note: For large screen devices such as tablets and foldables, there are additional options to help apps take advantage of additional space:
- Apps can open weblinks in split screen using launch an adjacent multi-window experience. This enables users to multitask between your app and a browser at the same time. OR
Custom Tabshave a side panel option that can open in the same task, but next to your existing app content.
- The
Custom Tabis powered by the user's default browser, for browsers which supportCustom Tabs.- While it's possible to use a
WebViewand provide a highly customizable in-app browsing experience, we recommendCustom Tabsfor an out-of-the-box browser experience and seamless transition for when a user wants to open a web link in the browser.
- While it's possible to use a
3. Login or Authentication flows within your app
Android's suggested approach is to build your login or authentication flows using Credential Manager. If you find you still need to use Embedded Web for these experiences, use the following guidance:
- Some apps use
WebViews to provide sign-in flows for their users, including using a username and passkey (or password) specific to your app. This enables developers to unify the authentication flows across platforms. - When linking out to a third-party identity provider or login experience, such
as "Sign in with…",
Custom Tabsare the way to go. Launching aCustom Tabhelps protect the user's credential by keeping it isolated to the third-party site.
For more information about using WebViews for authentication,
see Authenticate users with WebView.
For launching a Custom Tab, see Overview of Android Custom Tabs.