اگر از یک طرحبندی مبتنی بر View استفاده میکنید، سه انتخاب اصلی برای اجرای ضامنها وجود دارد. توصیه می کنیم از مؤلفه SwitchMaterial از کتابخانه Material Components استفاده کنید:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<com.google.android.material.switchmaterial.SwitchMaterial
android:id="@+id/material_switch"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/material_switch"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
همانطور که در مثال زیر نشان داده شده است، برنامه های قدیمی ممکن است همچنان از مؤلفه قدیمی SwitchCompat AppCompat استفاده کنند:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.SwitchCompat
android:id="@+id/switchcompat"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/switchcompat"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
مثال زیر AppCompatToggleButton را نشان میدهد که یکی دیگر از مؤلفههای قدیمی است که رابط کاربری متفاوتی دارد:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/toggle_button_label"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/toggle"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="packed"
app:layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf="@id/toggle"
android:text="@string/toggle_button" />
<androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatToggleButton
android:id="@+id/toggle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/toggle_button_label"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
این سه مولفه رفتار یکسانی را ارائه می دهند اما متفاوت به نظر می رسند. تفاوت بین SwitchMaterial و SwitchCompat ظریف است، اما AppCompatToggleButton به طور قابل توجهی متفاوت است:
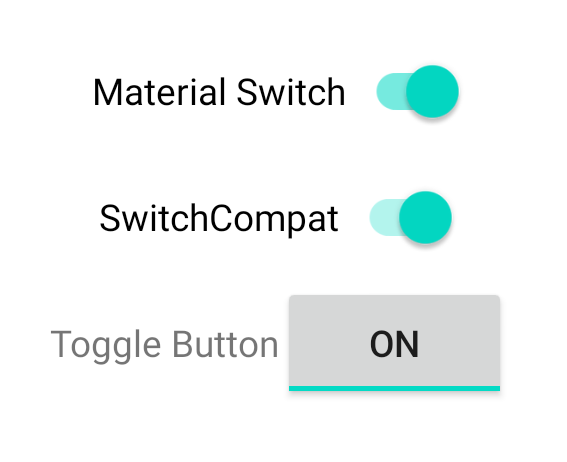
کنترل تغییرات حالت
SwitchMaterial ، SwitchCompat و AppCompatToggleButton همگی زیرمجموعه های CompoundButton هستند که به آنها مکانیزم مشترکی برای مدیریت تغییرات وضعیت بررسی شده می دهد. شما یک نمونه از CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener را پیاده سازی می کنید و آن را به دکمه اضافه می کنید، همانطور که در مثال زیر نشان داده شده است:
کاتلین
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) val binding: SwitchLayoutBinding = SwitchLayoutBinding.inflate(layoutInflater) setContentView(binding.root) binding.materialSwitch.setOnCheckedChangeListener { _, isChecked -> if (isChecked) { // The switch is checked. } else { // The switch isn't checked. } } } }
جاوا
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); SwitchLayoutBinding binding = SwitchLayoutBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater()); setContentView(binding.getRoot()); binding.materialSwitch.setOnCheckedChangeListener((buttonView, isChecked) -> { if (isChecked) { // The switch is checked. } else { // The switch isn't checked. } }); } }
CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener یک رابط روش انتزاعی منفرد (یا رابط SAM ) است، بنابراین می توانید آن را به صورت لامبدا پیاده سازی کنید. هر زمان که حالت چک شده تغییر کند، لامبدا فراخوانی میشود و مقدار بولی isChecked که به لامبدا ارسال میشود، وضعیت چک شده جدید را نشان میدهد.


