תיבת דו-שיח היא חלון קטן שמבקש מהמשתמש לקבל החלטה או להזין מידע נוסף. תיבת דו-שיח לא ממלאת את המסך, ובדרך כלל משמשת לאירועים מודליים שבהם המשתמשים צריכים לבצע פעולה כדי להמשיך.
המחלקה Dialog היא מחלקת הבסיס של תיבות דו-שיח, אבל לא יוצרת את Dialog ישירות. במקום זאת, צריך להשתמש באחת מהתת-הסוגים הבאים:
AlertDialog- תיבת דו-שיח שיכולה לכלול כותרת, עד שלושה לחצנים, רשימה של פריטים לבחירה או פריסה בהתאמה אישית.
DatePickerDialogאוTimePickerDialog- תיבת דו-שיח עם ממשק משתמש מוגדר מראש שמאפשרת למשתמש לבחור תאריך או שעה.
הכיתות האלה מגדירות את הסגנון והמבנה של תיבת הדו-שיח. צריך גם
DialogFragment
כקונטיינר לתיבת הדו-שיח. המחלקה DialogFragment מספקת את כל הפקדים הדרושים ליצירת תיבת דו-שיח ולניהול המראה שלה, במקום לשלוח קריאה ל-methods באובייקט Dialog.
השימוש ב-DialogFragment לניהול תיבת הדו-שיח מאפשר לטפל כראוי באירועים במחזור החיים, למשל כשהמשתמש מקיש על לחצן 'הקודם' או מסובב את המסך. באמצעות הכיתה DialogFragment אפשר גם לעשות שימוש חוזר בממשק המשתמש של תיבת הדו-שיח כרכיב שניתן להטמיע בממשק משתמש גדול יותר – בדיוק כמו Fragment רגיל – למשל, אם רוצים שממשק המשתמש של תיבת הדו-שיח יופיע בצורה שונה במסכים גדולים וקטנים.
בקטעים הבאים במסמך מוסבר איך משתמשים ב-DialogFragment בשילוב עם אובייקט AlertDialog. כדי ליצור בורר תאריכים או שעות, קראו את המאמר הוספת בוררים לאפליקציה.
יצירת קטע של תיבת דו-שיח
תוכלו ליצור מגוון רחב של עיצובים של תיבות דו-שיח — כולל פריסות בהתאמה אישית וכאלה שמתוארות ב-Material Design
Dialogs — על ידי הרחבה של DialogFragment ויצירת AlertDialog בשיטת הקריאה החוזרת
onCreateDialog().
לדוגמה, הנה AlertDialog בסיסי שמנוהל בתוך DialogFragment:
Kotlin
class StartGameDialogFragment : DialogFragment() { override fun onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState: Bundle?): Dialog { return activity?.let { // Use the Builder class for convenient dialog construction. val builder = AlertDialog.Builder(it) builder.setMessage("Start game") .setPositiveButton("Start") { dialog, id -> // START THE GAME! } .setNegativeButton("Cancel") { dialog, id -> // User cancelled the dialog. } // Create the AlertDialog object and return it. builder.create() } ?: throw IllegalStateException("Activity cannot be null") } } class OldXmlActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_old_xml) StartGameDialogFragment().show(supportFragmentManager, "GAME_DIALOG") } }
Java
public class StartGameDialogFragment extends DialogFragment { @Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Use the Builder class for convenient dialog construction. AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_start_game) .setPositiveButton(R.string.start, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // START THE GAME! } }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // User cancels the dialog. } }); // Create the AlertDialog object and return it. return builder.create(); } } // ... StartGameDialogFragment().show(supportFragmentManager, "GAME_DIALOG");
כשיוצרים מופע של הכיתה הזו ומפעילים את show() על האובייקט הזה, תיבת הדו-שיח מופיעה כפי שמוצגת באיור הבא.
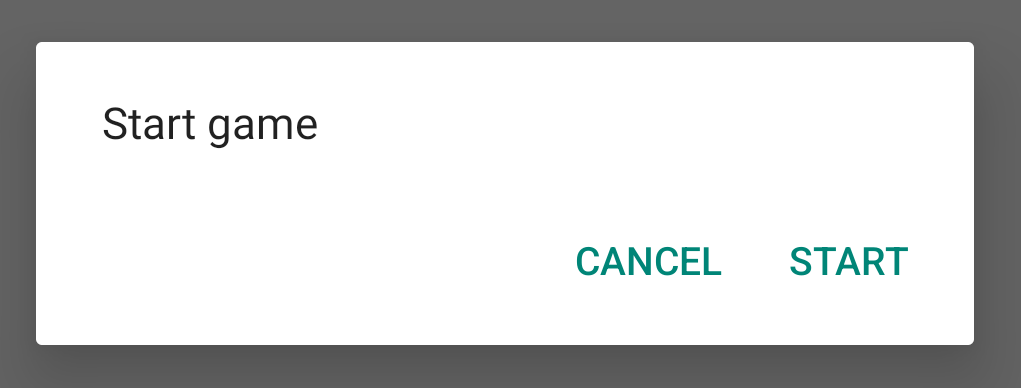
בקטע הבא מוסבר בפירוט נוסף איך משתמשים בממשקי ה-API של AlertDialog.Builder כדי ליצור את תיבת הדו-שיח.
בהתאם למורכבות תיבת הדו-שיח, אפשר להטמיע מגוון שיטות אחרות של קריאה חוזרת ב-DialogFragment, כולל כל ה-methods הבסיסיות של מחזור החיים של קטעים.
יצירת תיבת דו-שיח של התראה
בכיתה AlertDialog אפשר ליצור מגוון עיצובים של תיבת דו-שיח, ולרוב היא הכיתה היחידה של תיבת דו-שיח שנדרשת. כפי שמתואר באיור הבא, יש שלושה אזורים בתיבת הדו-שיח של ההתראה:
- כותרת: השדה הזה הוא אופציונלי, והוא משמש רק כשאזור התוכן מאוכלס בהודעה מפורטת, ברשימת פריטים או בפריסה מותאמת אישית. אם אתם רוצים לשלוח הודעה או שאלה פשוטה, אין צורך בשם.
- אזור תוכן: באזור הזה אפשר להציג הודעה, רשימה או פריסה מותאמת אישית אחרת.
- לחצני פעולה: בתיבת דו-שיח יכולים להיות עד שלושה לחצני פעולה.
בכיתה AlertDialog.Builder יש ממשקי API שמאפשרים ליצור AlertDialog עם סוגי התוכן האלה, כולל פריסה בהתאמה אישית.
כדי ליצור AlertDialog:
Kotlin
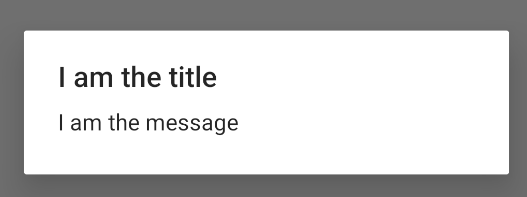
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setMessage("I am the message") .setTitle("I am the title") val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
// 1. Instantiate an AlertDialog.Builder with its constructor. AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); // 2. Chain together various setter methods to set the dialog characteristics. builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_message) .setTitle(R.string.dialog_title); // 3. Get the AlertDialog. AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();
קטע הקוד הקודם יוצר את תיבת הדו-שיח הבאה:
הוספת לחצנים
כדי להוסיף לחצני פעולה כמו אלה שמופיעים בתמונה השנייה, קוראים ל-methods setPositiveButton() ו-setNegativeButton():
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setMessage("I am the message") .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive") { dialog, which -> // Do something. } .setNegativeButton("Negative") { dialog, which -> // Do something else. } val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); // Add the buttons. builder.setPositiveButton(R.string.ok, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // User taps OK button. } }); builder.setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // User cancels the dialog. } }); // Set other dialog properties. ... // Create the AlertDialog. AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();
השיטות set...Button() מחייבות שם ללחצן – שמסופק על ידי משאב מחרוזת – ו-DialogInterface.OnClickListener שמגדיר את הפעולה שתתבצע כשהמשתמש מקייש על הלחצן.
יש שלושה לחצני פעולה שאפשר להוסיף:
- חיובי: משתמשים באפשרות הזו כדי לאשר את הפעולה ולהמשיך בה (פעולת 'אישור').
- שלילי: משתמשים באפשרות הזו כדי לבטל את הפעולה.
- ניטרלי: משתמשים באפשרות הזו כשהמשתמשים לא רוצים להמשיך בפעולה, אבל לא בהכרח רוצים לבטל אותה. הוא מופיע בין הלחצן החיובי ללחצן השלילי. לדוגמה, הפעולה יכולה להיות 'הזכיר לי מאוחר יותר'.
אפשר להוסיף רק לחצן אחד מכל סוג ל-AlertDialog. לדוגמה, אי אפשר להוסיף יותר מלחצן אחד עם משמעות חיובית.
קטע הקוד הקודם יוצר תיבת דו-שיח עם התראה כמו זו:
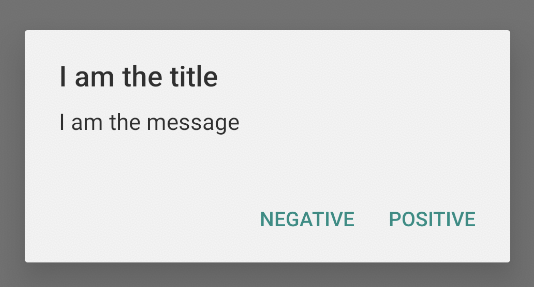
הוספת רשימה
יש שלושה סוגי רשימות זמינים בממשקי ה-API של AlertDialog:
- רשימה רגילה עם בחירת תשובה יחידה.
- רשימה קבועה עם אפשרות בחירה יחידה (לחצני בחירה).
- רשימה קבועה של אפשרויות בחירה (תיבות סימון).
כדי ליצור רשימה של בחירה יחידה, כמו זו שמופיעה באיור 5, משתמשים בשיטה setItems():
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive") { dialog, which -> // Do something. } .setNegativeButton("Negative") { dialog, which -> // Do something else. } .setItems(arrayOf("Item One", "Item Two", "Item Three")) { dialog, which -> // Do something on item tapped. } val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
@Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); builder.setTitle(R.string.pick_color) .setItems(R.array.colors_array, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { // The 'which' argument contains the index position of the selected item. } }); return builder.create(); }
קטע הקוד הזה יוצר תיבת דו-שיח כמו זו:
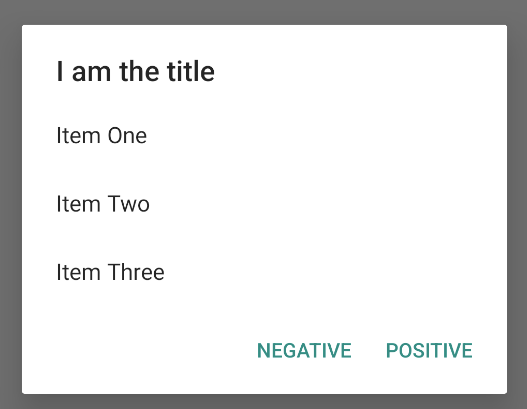
מכיוון שהרשימה מופיעה באזור התוכן של תיבת הדו-שיח, אי אפשר להציג בה גם הודעה וגם רשימה. מגדירים כותרת לתיבת הדו-שיח באמצעות setTitle().
כדי לציין את הפריטים ברשימה, צריך להפעיל את setItems() ולהעביר מערך. לחלופין, אפשר לציין רשימה באמצעות setAdapter().
כך אפשר לגבות את הרשימה עם נתונים דינמיים, כמו ממסד נתונים, באמצעות ListAdapter.
אם תשתמשו ב-ListAdapter כדי לגבות את הרשימה, תמיד צריך להשתמש ב-Loader כדי שהתוכן ייטען באופן אסינכרוני. מידע נוסף זמין במאמרים יצירת פריסות באמצעות מתאם ומערכי טעינה.
הוספת רשימה קבועה של אפשרויות בחירה מרובות או אפשרות בחירה יחידה
כדי להוסיף רשימה של פריטים עם אפשרויות בחירה מרובות (תיבות סימון) או פריטים עם אפשרות בחירה יחידה (לחצני רדיו), משתמשים ב-method setMultiChoiceItems() או ב-method setSingleChoiceItems(), בהתאמה.
לדוגמה, כך יוצרים רשימת תשובות אפשריות כמו זו שמוצגת באיור 6, שמשמרת את הפריטים שנבחרו ב-ArrayList:
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive") { dialog, which -> // Do something. } .setNegativeButton("Negative") { dialog, which -> // Do something else. } .setMultiChoiceItems( arrayOf("Item One", "Item Two", "Item Three"), null) { dialog, which, isChecked -> // Do something. } val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
@Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { selectedItems = new ArrayList(); // Where we track the selected items AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); // Set the dialog title. builder.setTitle(R.string.pick_toppings) // Specify the list array, the items to be selected by default (null for // none), and the listener through which to receive callbacks when items // are selected. .setMultiChoiceItems(R.array.toppings, null, new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which, boolean isChecked) { if (isChecked) { // If the user checks the item, add it to the selected // items. selectedItems.add(which); } else if (selectedItems.contains(which)) { // If the item is already in the array, remove it. selectedItems.remove(which); } } }) // Set the action buttons .setPositiveButton(R.string.ok, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // User taps OK, so save the selectedItems results // somewhere or return them to the component that opens the // dialog. ... } }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { ... } }); return builder.create(); }
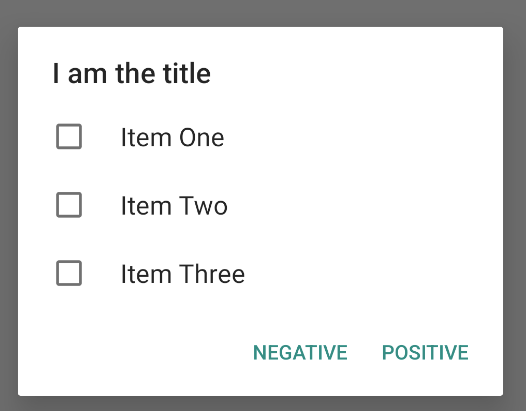
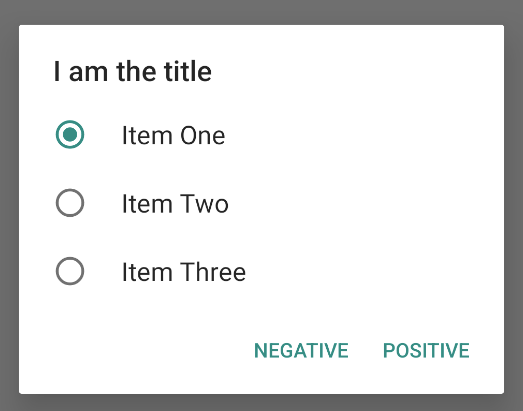
אפשר להציג תיבת דו-שיח עם התראה עם אפשרות בחירה אחת באופן הבא:
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive") { dialog, which -> // Do something. } .setNegativeButton("Negative") { dialog, which -> // Do something else. } .setSingleChoiceItems( arrayOf("Item One", "Item Two", "Item Three"), 0 ) { dialog, which -> // Do something. } val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
String[] choices = {"Item One", "Item Two", "Item Three"}; AlertDialog.Builder builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context); builder .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive", (dialog, which) -> { }) .setNegativeButton("Negative", (dialog, which) -> { }) .setSingleChoiceItems(choices, 0, (dialog, which) -> { }); AlertDialog dialog = builder.create(); dialog.show();
התוצאה היא הדוגמה הבאה:
יצירת פריסה בהתאמה אישית
אם רוצים להשתמש בפריסת מותאם אישית בתיבת דו-שיח, יוצרים פריסה ומוסיפים אותה ל-AlertDialog באמצעות קריאה ל-setView() באובייקט AlertDialog.Builder.
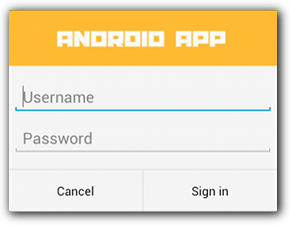
כברירת מחדל, הפריסה בהתאמה אישית ממלאת את חלון הדו-שיח, אבל עדיין אפשר להשתמש בשיטות AlertDialog.Builder כדי להוסיף לחצנים וכותרת.
לדוגמה, זהו קובץ הפריסה של פריסת תיבת הדו-שיח בהתאמה אישית שצוינה למעלה:
res/layout/dialog_signin.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <ImageView android:src="@drawable/header_logo" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="64dp" android:scaleType="center" android:background="#FFFFBB33" android:contentDescription="@string/app_name" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/username" android:inputType="textEmailAddress" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="16dp" android:layout_marginLeft="4dp" android:layout_marginRight="4dp" android:layout_marginBottom="4dp" android:hint="@string/username" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/password" android:inputType="textPassword" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="4dp" android:layout_marginLeft="4dp" android:layout_marginRight="4dp" android:layout_marginBottom="16dp" android:fontFamily="sans-serif" android:hint="@string/password"/> </LinearLayout>
כדי להרחיב את הפריסה ב-DialogFragment, מקבלים LayoutInflater באמצעות getLayoutInflater() ומפעילים את inflate().
הפרמטר הראשון הוא מזהה המשאב של הפריסה, והפרמטר השני הוא תצוגת הורה של הפריסה. לאחר מכן אפשר לקרוא ל-setView() כדי למקם את הפריסה בתיבת הדו-שיח. הדוגמה הבאה ממחישה זאת.
Kotlin
override fun onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState: Bundle?): Dialog { return activity?.let { val builder = AlertDialog.Builder(it) // Get the layout inflater. val inflater = requireActivity().layoutInflater; // Inflate and set the layout for the dialog. // Pass null as the parent view because it's going in the dialog // layout. builder.setView(inflater.inflate(R.layout.dialog_signin, null)) // Add action buttons. .setPositiveButton(R.string.signin, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, id -> // Sign in the user. }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, id -> getDialog().cancel() }) builder.create() } ?: throw IllegalStateException("Activity cannot be null") }
Java
@Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); // Get the layout inflater. LayoutInflater inflater = requireActivity().getLayoutInflater(); // Inflate and set the layout for the dialog. // Pass null as the parent view because it's going in the dialog layout. builder.setView(inflater.inflate(R.layout.dialog_signin, null)) // Add action buttons .setPositiveButton(R.string.signin, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // Sign in the user. } }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { LoginDialogFragment.this.getDialog().cancel(); } }); return builder.create(); }
אם רוצים תיבת דו-שיח בהתאמה אישית, אפשר להציג Activity כתיבת דו-שיח במקום להשתמש בממשקי ה-API של Dialog. יוצרים פעילות ומגדירים את העיצוב שלה כ-Theme.Holo.Dialog ברכיב המניפסט <activity>:
<activity android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Holo.Dialog" >
הפעילות תוצג עכשיו בחלון של תיבת דו-שיח במקום במסך מלא.
העברת האירועים בחזרה למארח של תיבת הדו-שיח
כשהמשתמש מקייש על אחד מלחצני הפעולה של תיבת הדו-שיח או בוחר פריט מהרשימה שלה, ייתכן ש-DialogFragment יבצע את הפעולה הנדרשת בעצמו, אבל בדרך כלל כדאי להעביר את האירוע לפעילות או לקטע שמפתחים את תיבת הדו-שיח. כדי לעשות זאת, מגדירים ממשק עם שיטה לכל סוג של אירוע קליק. לאחר מכן, מטמיעים את הממשק הזה ברכיב המארח שמקבל את אירועי הפעולה מתיבת הדו-שיח.
לדוגמה, הנה DialogFragment שמגדיר ממשק שבו הוא מעביר את האירועים חזרה לפעילות המארחת:
Kotlin
class NoticeDialogFragment : DialogFragment() { // Use this instance of the interface to deliver action events. internal lateinit var listener: NoticeDialogListener // The activity that creates an instance of this dialog fragment must // implement this interface to receive event callbacks. Each method passes // the DialogFragment in case the host needs to query it. interface NoticeDialogListener { fun onDialogPositiveClick(dialog: DialogFragment) fun onDialogNegativeClick(dialog: DialogFragment) } // Override the Fragment.onAttach() method to instantiate the // NoticeDialogListener. override fun onAttach(context: Context) { super.onAttach(context) // Verify that the host activity implements the callback interface. try { // Instantiate the NoticeDialogListener so you can send events to // the host. listener = context as NoticeDialogListener } catch (e: ClassCastException) { // The activity doesn't implement the interface. Throw exception. throw ClassCastException((context.toString() + " must implement NoticeDialogListener")) } } }
Java
public class NoticeDialogFragment extends DialogFragment { // The activity that creates an instance of this dialog fragment must // implement this interface to receive event callbacks. Each method passes // the DialogFragment in case the host needs to query it. public interface NoticeDialogListener { public void onDialogPositiveClick(DialogFragment dialog); public void onDialogNegativeClick(DialogFragment dialog); } // Use this instance of the interface to deliver action events. NoticeDialogListener listener; // Override the Fragment.onAttach() method to instantiate the // NoticeDialogListener. @Override public void onAttach(Context context) { super.onAttach(context); // Verify that the host activity implements the callback interface. try { // Instantiate the NoticeDialogListener so you can send events to // the host. listener = (NoticeDialogListener) context; } catch (ClassCastException e) { // The activity doesn't implement the interface. Throw exception. throw new ClassCastException(activity.toString() + " must implement NoticeDialogListener"); } } ... }
הפעילות שמארחת את תיבת הדו-שיח יוצרת מופע של תיבת הדו-שיח באמצעות ה-constructor של קטע תיבת הדו-שיח, ומקבלת את האירועים של תיבת הדו-שיח באמצעות הטמעה של הממשק NoticeDialogListener:
Kotlin
class MainActivity : FragmentActivity(), NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener { fun showNoticeDialog() { // Create an instance of the dialog fragment and show it. val dialog = NoticeDialogFragment() dialog.show(supportFragmentManager, "NoticeDialogFragment") } // The dialog fragment receives a reference to this Activity through the // Fragment.onAttach() callback, which it uses to call the following // methods defined by the NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener // interface. override fun onDialogPositiveClick(dialog: DialogFragment) { // User taps the dialog's positive button. } override fun onDialogNegativeClick(dialog: DialogFragment) { // User taps the dialog's negative button. } }
Java
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity implements NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener{ ... public void showNoticeDialog() { // Create an instance of the dialog fragment and show it. DialogFragment dialog = new NoticeDialogFragment(); dialog.show(getSupportFragmentManager(), "NoticeDialogFragment"); } // The dialog fragment receives a reference to this Activity through the // Fragment.onAttach() callback, which it uses to call the following // methods defined by the NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener // interface. @Override public void onDialogPositiveClick(DialogFragment dialog) { // User taps the dialog's positive button. ... } @Override public void onDialogNegativeClick(DialogFragment dialog) { // User taps the dialog's negative button. ... } }
מכיוון שפעילות המארח מטמיעה את NoticeDialogListener, שנאכפת על ידי שיטת הקריאה החוזרת onAttach() שמוצגת בדוגמה הקודמת, הקטע של תיבת הדו-שיח יכול להשתמש ב-methods של קריאה חוזרת בממשק כדי לספק אירועי קליקים לפעילות:
Kotlin
override fun onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState: Bundle): Dialog { return activity?.let { // Build the dialog and set up the button click handlers. val builder = AlertDialog.Builder(it) builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_start_game) .setPositiveButton(R.string.start, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, id -> // Send the positive button event back to the // host activity. listener.onDialogPositiveClick(this) }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, id -> // Send the negative button event back to the // host activity. listener.onDialogNegativeClick(this) }) builder.create() } ?: throw IllegalStateException("Activity cannot be null") }
Java
public class NoticeDialogFragment extends DialogFragment { ... @Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Build the dialog and set up the button click handlers. AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_start_game) .setPositiveButton(R.string.start, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // Send the positive button event back to the host activity. listener.onDialogPositiveClick(NoticeDialogFragment.this); } }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // Send the negative button event back to the host activity. listener.onDialogNegativeClick(NoticeDialogFragment.this); } }); return builder.create(); } }
הצגת תיבת דו-שיח
כשרוצים להציג את תיבת הדו-שיח, יוצרים מופע של DialogFragment ומפעילים את show(), מעבירים את FragmentManager ושם תג של קטע הקוד של תיבת הדו-שיח.
אפשר לקבל את FragmentManager על ידי קריאה ל-getSupportFragmentManager() מה-FragmentActivity או על ידי קריאה ל-getParentFragmentManager() מה-Fragment. דוגמה:
Kotlin
fun confirmStartGame() { val newFragment = StartGameDialogFragment() newFragment.show(supportFragmentManager, "game") }
Java
public void confirmStartGame() { DialogFragment newFragment = new StartGameDialogFragment(); newFragment.show(getSupportFragmentManager(), "game"); }
הארגומנט השני, "game", הוא שם תג ייחודי שבו המערכת משתמשת כדי לשמור ולשחזר את מצב הקטעים לפי הצורך. התג מאפשר גם לקבל כינוי לקטע באמצעות קריאה ל-findFragmentByTag().
הצגת תיבת דו-שיח במסך מלא או כקטע מוטמע
יכול להיות שתרצו שחלק מעיצוב ממשק המשתמש יופיע כתיבת דו-שיח במצבים מסוימים, וכקטע מוטמע או במסך מלא במצבים אחרים. יכול להיות שתרצו גם שהיא תופיע בצורה שונה בהתאם לגודל המסך של המכשיר. המחלקה DialogFragment מציעה גמישות לביצוע הפעולה הזו, כי היא יכולה להתנהג כמו Fragment שניתן להטמעה.
עם זאת, במקרה הזה אי אפשר להשתמש ב-AlertDialog.Builder או באובייקטים אחרים מסוג Dialog כדי ליצור את תיבת הדו-שיח. אם רוצים שאפשר יהיה להטמיע את DialogFragment, צריך להגדיר את ממשק המשתמש של תיבת הדו-שיח בפריסה, ואז לטעון את הפריסה ב-callback של onCreateView().
הנה דוגמה DialogFragment שיכול להופיע בתור תיבת דו-שיח או מקטע שניתן להטמעה, באמצעות פריסה בשם purchase_items.xml:
Kotlin
class CustomDialogFragment : DialogFragment() { // The system calls this to get the DialogFragment's layout, regardless of // whether it's being displayed as a dialog or an embedded fragment. override fun onCreateView( inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle? ): View { // Inflate the layout to use as a dialog or embedded fragment. return inflater.inflate(R.layout.purchase_items, container, false) } // The system calls this only when creating the layout in a dialog. override fun onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState: Bundle): Dialog { // The only reason you might override this method when using // onCreateView() is to modify the dialog characteristics. For example, // the dialog includes a title by default, but your custom layout might // not need it. Here, you can remove the dialog title, but you must // call the superclass to get the Dialog. val dialog = super.onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState) dialog.requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE) return dialog } }
Java
public class CustomDialogFragment extends DialogFragment { // The system calls this to get the DialogFragment's layout, regardless of // whether it's being displayed as a dialog or an embedded fragment. @Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Inflate the layout to use as a dialog or embedded fragment. return inflater.inflate(R.layout.purchase_items, container, false); } // The system calls this only when creating the layout in a dialog. @Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // The only reason you might override this method when using // onCreateView() is to modify the dialog characteristics. For example, // the dialog includes a title by default, but your custom layout might // not need it. Here, you can remove the dialog title, but you must // call the superclass to get the Dialog. Dialog dialog = super.onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState); dialog.requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE); return dialog; } }
בדוגמה הבאה נקבע אם להציג את הקטע כתיבת דו-שיח או כממשק משתמש במסך מלא, על סמך גודל המסך:
Kotlin
fun showDialog() { val fragmentManager = supportFragmentManager val newFragment = CustomDialogFragment() if (isLargeLayout) { // The device is using a large layout, so show the fragment as a // dialog. newFragment.show(fragmentManager, "dialog") } else { // The device is smaller, so show the fragment fullscreen. val transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction() // For a polished look, specify a transition animation. transaction.setTransition(FragmentTransaction.TRANSIT_FRAGMENT_OPEN) // To make it fullscreen, use the 'content' root view as the container // for the fragment, which is always the root view for the activity. transaction .add(android.R.id.content, newFragment) .addToBackStack(null) .commit() } }
Java
public void showDialog() { FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager(); CustomDialogFragment newFragment = new CustomDialogFragment(); if (isLargeLayout) { // The device is using a large layout, so show the fragment as a // dialog. newFragment.show(fragmentManager, "dialog"); } else { // The device is smaller, so show the fragment fullscreen. FragmentTransaction transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction(); // For a polished look, specify a transition animation. transaction.setTransition(FragmentTransaction.TRANSIT_FRAGMENT_OPEN); // To make it fullscreen, use the 'content' root view as the container // for the fragment, which is always the root view for the activity. transaction.add(android.R.id.content, newFragment) .addToBackStack(null).commit(); } }
מידע נוסף על ביצוע עסקאות של קטעי קוד זמין במאמר קטעי קוד.
בדוגמה הזו, הערך הבוליאני mIsLargeLayout מציין אם המכשיר הנוכחי צריך להשתמש בפריסה הגדולה של האפליקציה, וכך להציג את הקטע הזה כתיבת דו-שיח במקום במסך מלא. הדרך הטובה ביותר להגדיר ערך בוליאני כזה היא להצהיר על ערך בוליאני של משאב עם ערך של משאב חלופי למסכים בגדלים שונים. לדוגמה, אלה שתי גרסאות של משאב ה-bool לגדלים שונים של מסכים:
res/values/bools.xml
<!-- Default boolean values --> <resources> <bool name="large_layout">false</bool> </resources>
res/values-large/bools.xml
<!-- Large screen boolean values --> <resources> <bool name="large_layout">true</bool> </resources>
לאחר מכן אפשר לאתחל את הערך mIsLargeLayout במהלך ה-method onCreate() של הפעילות, כמו בדוגמה הבאה:
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) isLargeLayout = resources.getBoolean(R.bool.large_layout) }
Java
boolean isLargeLayout; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); isLargeLayout = getResources().getBoolean(R.bool.large_layout); }
הצגת פעילות כתיבת תיבת דו-שיח במסכים גדולים
במקום להציג תיבת דו-שיח כממשק משתמש במסך מלא במסכים קטנים, אפשר לקבל את אותה תוצאה על ידי הצגת Activity כתיבת דו-שיח במסכים גדולים. הגישה שבוחרים תלויה בעיצוב האפליקציה, אבל הצגת פעילות כתיבת תיבת דו-שיח שימושית בדרך כלל כשהאפליקציה מיועדת למסכים קטנים, ואתם רוצים לשפר את חוויית השימוש בטאבלטים על ידי הצגת פעילות לטווח קצר כתיבת תיבת דו-שיח.
כדי להציג פעילות כתיבת תיבת דו-שיח רק במסכים גדולים, מחילים את העיצוב Theme.Holo.DialogWhenLarge על רכיב המניפסט <activity>:
<activity android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Holo.DialogWhenLarge" >
מידע נוסף על עיצוב הפעילויות בעזרת עיצובים זמין במאמר סגנונות ועיצובים.
סגירת תיבת דו-שיח
כשהמשתמש מקשיב על לחצן פעולה שנוצר באמצעות AlertDialog.Builder, המערכת סוגרת את תיבת הדו-שיח בשבילכם.
המערכת גם סוגרת את תיבת הדו-שיח כשהמשתמש מקיש על פריט ברשימת דו-שיח, חוץ מאשר במקרים שבהם ברשימה נעשה שימוש בלחצני בחירה או בתיבות סימון. אחרת, אפשר לסגור את תיבת הדו-שיח באופן ידני על ידי קריאה ל-dismiss() ב-DialogFragment.
אם צריך לבצע פעולות מסוימות כשתיבת הדו-שיח נעלמת, אפשר להטמיע את ה-method onDismiss() ב-DialogFragment.
אפשר גם לבטל תיבת דו-שיח. זהו אירוע מיוחד שמציין שהמשתמש עוזב את תיבת הדו-שיח בלי להשלים את המשימה. המצב הזה מתרחש אם המשתמש מקשיב על לחצן החזרה או מקשיב על המסך מחוץ לאזור של תיבת הדו-שיח, או אם מפעילים את cancel() באופן מפורש ב-Dialog, למשל בתגובה ללחצן 'ביטול' בתיבת הדו-שיח.
כמו בדוגמה הקודמת, אפשר להגיב לאירוע הביטול על ידי הטמעה של onCancel() בכיתה DialogFragment.

