تستهای رابط کاربری در Compose از معناشناسی برای تعامل با سلسله مراتب رابط کاربری استفاده میکنند. معناشناسی، همانطور که از نامش پیداست، به یک قطعه از رابط کاربری معنا میدهد. در این زمینه، یک "قطعه از رابط کاربری" (یا عنصر) میتواند به معنای هر چیزی از یک عنصر قابل ترکیب تا یک صفحه کامل باشد. درخت معناشناسی در کنار سلسله مراتب رابط کاربری ایجاد میشود و سلسله مراتب را توصیف میکند.
شما میتوانید اطلاعات بیشتری در مورد معناشناسی را به طور کلی در Semantics in Compose بیاموزید.
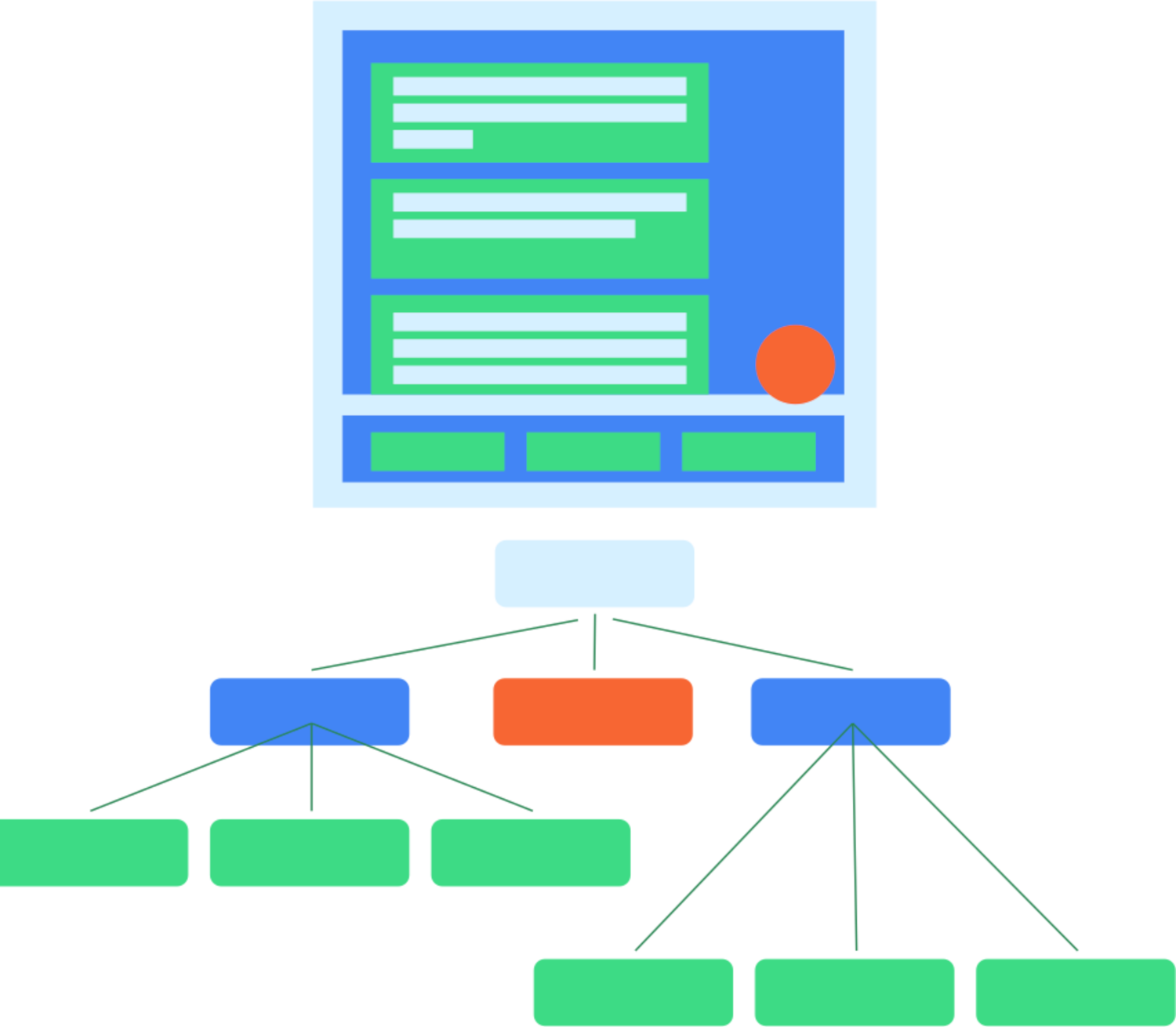
شکل ۱. یک سلسله مراتب رابط کاربری معمولی و درخت معنایی آن.
چارچوب معنایی در درجه اول برای دسترسیپذیری استفاده میشود، بنابراین تستها از اطلاعات افشا شده توسط معنایی در مورد سلسله مراتب رابط کاربری بهره میبرند. توسعهدهندگان تصمیم میگیرند چه چیزی و چه مقدار را افشا کنند.

شکل ۲. یک دکمه معمولی حاوی یک آیکون و متن.
برای مثال، با توجه به دکمهای مانند این که شامل یک آیکون و یک عنصر متنی است، درخت معنایی پیشفرض فقط شامل برچسب متنی "Like" است. دلیل این امر این است که برخی از composableها، مانند Text ، از قبل برخی از ویژگیها را در درخت معنایی نمایش میدهند. میتوانید با استفاده از یک Modifier ، ویژگیها را به درخت معنایی اضافه کنید.
MyButton(
modifier = Modifier.semantics { contentDescription = "Add to favorites" }
)
منابع اضافی
- تست برنامهها در اندروید : صفحه اصلی تست اندروید، نمای وسیعتری از اصول و تکنیکهای تست ارائه میدهد.
- اصول اولیه تست : درباره مفاهیم اصلی پشت تست یک برنامه اندروید بیشتر بدانید.
- تستهای محلی : شما میتوانید برخی از تستها را به صورت محلی، روی ایستگاه کاری خودتان اجرا کنید.
- تستهای ابزاری : اجرای تستهای ابزاری نیز روش خوبی است. یعنی تستهایی که مستقیماً روی دستگاه اجرا میشوند.
- ادغام مداوم : ادغام مداوم به شما امکان میدهد تستهای خود را در خط تولید خود ادغام کنید.
- آزمایش اندازههای مختلف صفحه نمایش : با توجه به اینکه دستگاههای زیادی در دسترس کاربران است، باید اندازههای مختلف صفحه نمایش را آزمایش کنید.
- Espresso : اگرچه برای رابطهای کاربری مبتنی بر View در نظر گرفته شده است، اما دانش Espresso همچنان میتواند برای برخی از جنبههای تست Compose مفید باشد.

