Compose의 UI 테스트는 시맨틱을 사용하여 UI 계층 구조와 상호작용합니다. 이름에서 알 수 있듯이 시맨틱은 UI 요소에 의미를 부여합니다. 이 컨텍스트에서 'UI 조각' (또는 요소)은 단일 컴포저블에서 전체 화면에 이르기까지의 어떤 것을 의미할 수 있습니다. 시맨틱 트리는 UI 계층 구조와 함께 생성되고 계층 구조를 설명합니다.
일반적인 시맨틱에 관한 자세한 내용은 Compose의 시맨틱을 참고하세요.
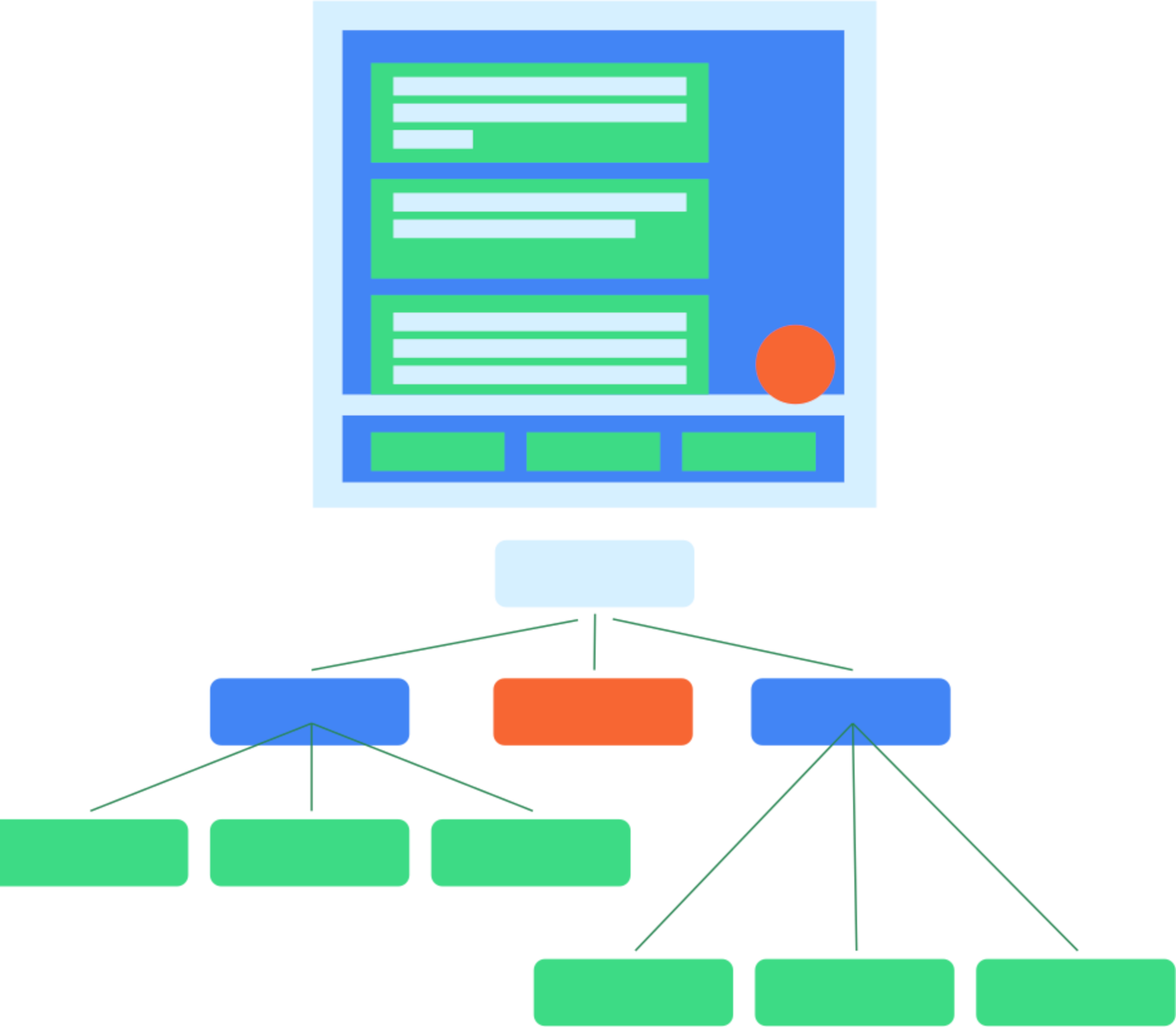
그림 1. 일반적인 UI 계층 구조 및 시맨틱 트리
시맨틱 프레임워크는 주로 접근성에 사용되므로 테스트는 시맨틱에 의해 노출되는 UI 계층 구조 관련 정보를 활용합니다. 개발자는 노출할 내용과 양을 결정합니다.

그림 2. 아이콘 및 텍스트가 포함된 일반적인 버튼
예를 들어 아이콘과 텍스트 요소로 구성된 이 같은 버튼의 경우 기본 시맨틱 트리에는 '좋아요'라는 텍스트 라벨만 포함됩니다. Text와 같은 일부 컴포저블이 일부 속성을 이미 시맨틱 트리에 노출하기 때문입니다. Modifier를 사용하여 시맨틱 트리에 속성을 추가할 수 있습니다.
MyButton(
modifier = Modifier.semantics { contentDescription = "Add to favorites" }
)
추가 리소스
- Android에서 앱 테스트: Android 테스트 기본사항 및 기법에 관한 광범위한 정보를 제공하는 기본 Android 테스트 방문 페이지입니다.
- 테스트 기본사항: Android 앱 테스트의 핵심 개념을 자세히 알아봅니다.
- 로컬 테스트: 일부 테스트는 자체 워크스테이션에서 로컬로 실행할 수 있습니다.
- 계측 테스트: 계측 테스트도 실행하는 것이 좋습니다. 즉, 기기에서 직접 실행되는 테스트입니다.
- 지속적 통합: 지속적 통합을 사용하면 테스트를 배포 파이프라인에 통합할 수 있습니다.
- 다양한 화면 크기 테스트: 사용자가 사용할 수 있는 기기가 많으므로 다양한 화면 크기를 테스트해야 합니다.
- Espresso: Espresso는 뷰 기반 UI를 위해 설계되었지만 Compose 테스트의 일부 측면에서는 여전히 유용할 수 있습니다.
