בדיקות של ממשק המשתמש ב-Compose משתמשות בסמנטיקה כדי ליצור אינטראקציה עם ההיררכיה של ממשק המשתמש. סמנטיקה, כפי שהשם מרמז, נותנת משמעות לחלק בממשק המשתמש. בהקשר הזה, 'חלק מממשק המשתמש' (או רכיב) יכול להיות כל דבר, החל מרכיב אחד שאפשר להרכיב ועד מסך מלא. עץ הסמנטיקה נוצר לצד ההיררכיה של ממשק המשתמש ומתאר את ההיררכיה.
מידע נוסף על סמנטיקה באופן כללי זמין במאמר סמנטיקה בכתיבה.
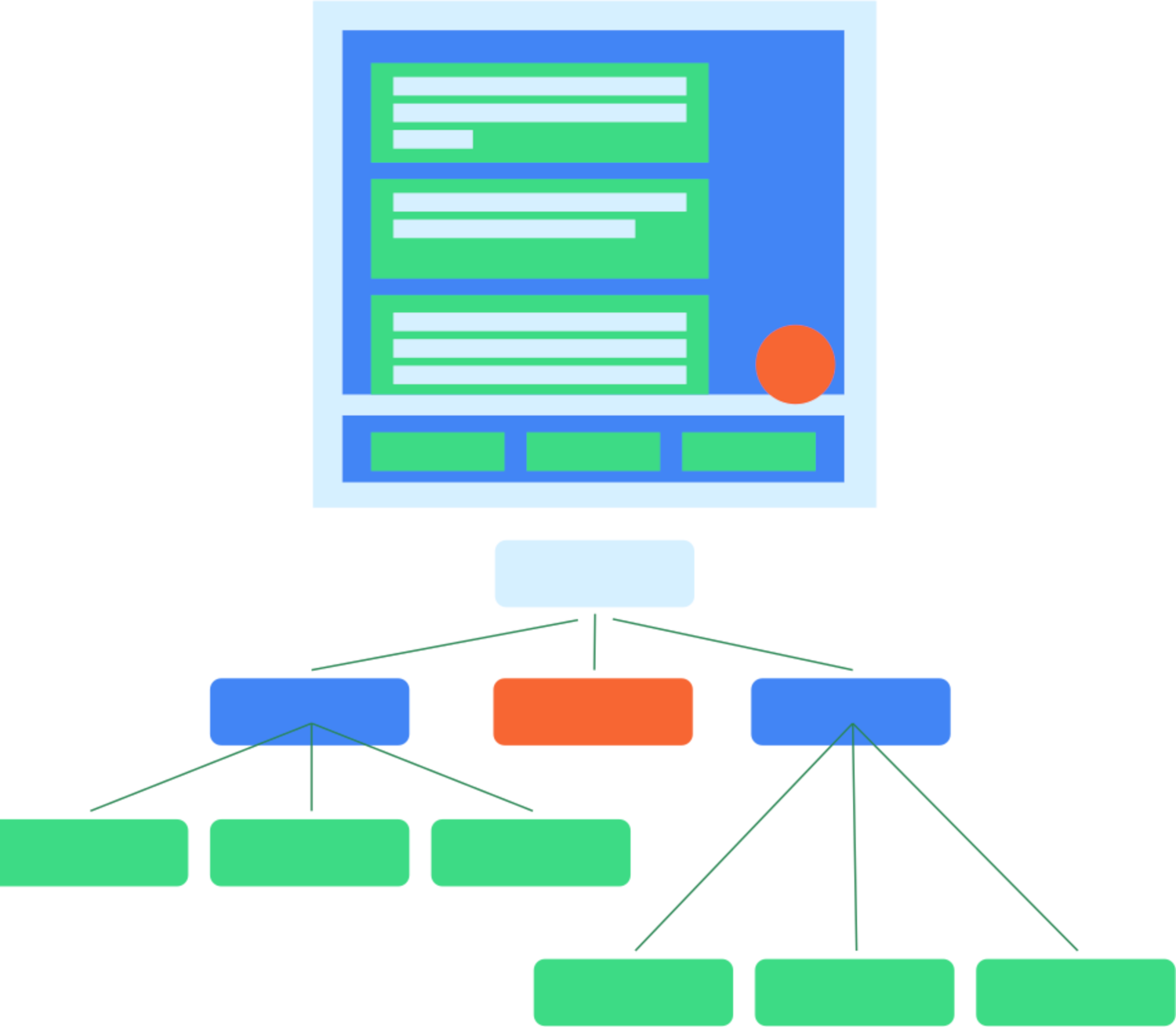
איור 1. היררכיה טיפוסית של ממשק משתמש ועץ סמנטיקה.
מסגרת הסמנטיקה משמשת בעיקר לנגישות, ולכן הבדיקות מנצלות את המידע שסמנטיקה חושפת לגבי היררכיית ממשק המשתמש. המפתחים מחליטים מה וכמה לחשוף.

איור 2. לחצן טיפוסי שמכיל סמל וטקסט.
לדוגמה, אם יש לחצן כזה שמורכב מסמל ומרכיב טקסט, עץ הסמנטיקה שמוגדר כברירת מחדל מכיל רק את תווית הטקסט 'לייק'. הסיבה לכך היא שחלק מהתכנים הקומפוזביליים, כמו Text, כבר חושפים חלק מהמאפיינים לעץ הסמנטיקה. אפשר להוסיף מאפיינים לעץ הסמנטי באמצעות Modifier.
MyButton(
modifier = Modifier.semantics { contentDescription = "Add to favorites" }
)
מקורות מידע נוספים
- בדיקת אפליקציות ב-Android: דף הנחיתה הראשי בנושא בדיקות ב-Android מספק סקירה רחבה יותר של עקרונות וטכניקות בדיקה.
- היסודות של בדיקות: מידע נוסף על המושגים הבסיסיים שמאחורי בדיקת אפליקציית Android.
- בדיקות מקומיות: אתם יכולים להריץ כמה בדיקות באופן מקומי, בתחנת העבודה שלכם.
- בדיקות עם מכשור: מומלץ להריץ גם בדיקות עם מכשור. כלומר, בדיקות שמופעלות ישירות במכשיר.
- אינטגרציה רציפה (CI): אינטגרציה רציפה מאפשרת לכם לשלב את הבדיקות בצינור הפריסה.
- בדיקה של גדלי מסך שונים: יש למשתמשים הרבה מכשירים שונים, ולכן כדאי לבדוק גדלים שונים של מסכים.
- Espresso: למרות שהכלי מיועד לממשקי משתמש מבוססי-View, הידע ב-Espresso יכול להיות שימושי גם לבדיקה של חלק מההיבטים ב-Compose.
