如果您遇到因不必要或過度重組而導致的效能問題,請對應用程式的穩定性進行偵錯。本指南將說明幾種偵錯方法。
版面配置檢查器
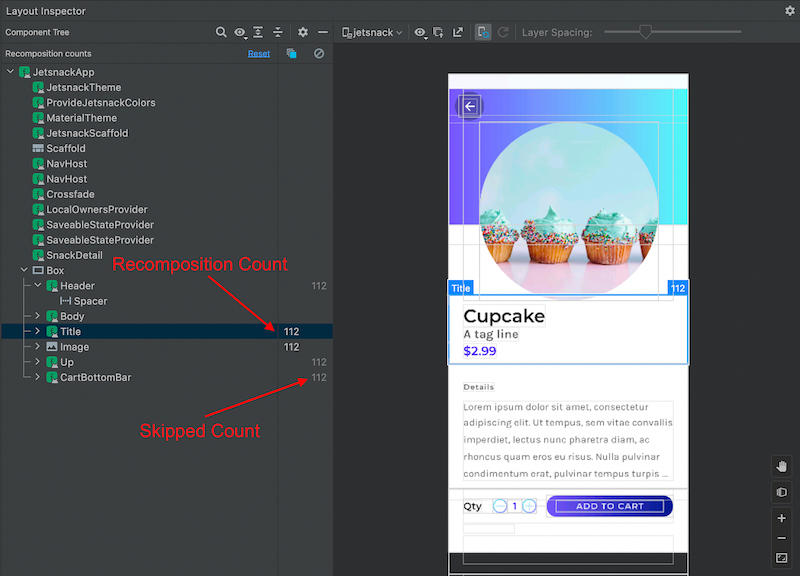
您可以使用 Android Studio 的版面配置檢查器,查看應用程式中重組的可組合項,並顯示 Compose 重組或略過元件的次數。
Compose 編譯器報告
Compose 編譯器可以輸出穩定性推斷結果,供您檢查。您可以根據這項輸出內容,判斷哪些可組合函式可略過,哪些則否。以下小節會簡要說明如何使用這些報表,如需更詳細的資訊,請參閱技術文件。
設定
根據預設,系統不會啟用 Compose 編譯器報告。您可以使用編譯器標記啟用這些功能。確切設定會因專案而異,但如果是使用 Compose 編譯器 Gradle 外掛程式的專案,您可以在每個模組的 build.gradle 檔案中新增下列項目。
android { ... }
composeCompiler {
reportsDestination = layout.buildDirectory.dir("compose_compiler")
metricsDestination = layout.buildDirectory.dir("compose_compiler")
}
建構專案時,系統現在會產生 Compose 編譯器報告。
輸出範例
reportsDestination 會輸出三個檔案。以下是 JetSnack 的輸出範例。
<modulename>-classes.txt:這個模組中類別穩定性的報告。範例。<modulename>-composables.txt:模組中可重新啟動和可略過的可組合函式報表。範例。<modulename>-composables.csv:可組合函式報表的CSV版本,可匯入試算表或使用指令碼處理。範例
可組合項報表
composables.txt 檔案會詳細說明指定模組的每個可組合函式,包括參數的穩定性,以及是否可重新啟動或略過。以下是 JetSnack 的假設範例:
restartable skippable scheme("[androidx.compose.ui.UiComposable]") fun SnackCollection(
stable snackCollection: SnackCollection
stable onSnackClick: Function1<Long, Unit>
stable modifier: Modifier? = @static Companion
stable index: Int = @static 0
stable highlight: Boolean = @static true
)
這個 SnackCollection 可組合函式完全可重新啟動、略過及穩定。雖然這並非必要條件,但一般來說,我們建議採用這種做法。
另一方面,我們來看看另一個例子。
restartable scheme("[androidx.compose.ui.UiComposable]") fun HighlightedSnacks(
stable index: Int
unstable snacks: List<Snack>
stable onSnackClick: Function1<Long, Unit>
stable modifier: Modifier? = @static Companion
)
HighlightedSnacks 可組合函式無法略過。Compose 絕不會在重組期間略過這項作業。即使參數沒有任何變更,也會發生這種情況。這是因為 unstable 參數 snacks。
課程報表
檔案 classes.txt 包含指定模組中類別的類似報表。以下程式碼片段是類別 Snack 的輸出內容:
unstable class Snack {
stable val id: Long
stable val name: String
stable val imageUrl: String
stable val price: Long
stable val tagline: String
unstable val tags: Set<String>
<runtime stability> = Unstable
}
如要參考,以下是 Snack 的定義:
data class Snack(
val id: Long,
val name: String,
val imageUrl: String,
val price: Long,
val tagline: String = "",
val tags: Set<String> = emptySet()
)
Compose 編譯器已將 Snack 標示為不穩定。這是因為 tags 參數的類型為 Set<String>。由於不是 MutableSet,因此這是不可變動的型別。不過,Set、List 和 Map 等標準集合類別最終都是介面。因此,基礎實作可能仍可變動。
例如,您可以輸入 val set: Set<String> = mutableSetOf("foo")。變數是常數,且宣告的型別不可變動,但實作仍可變動。Compose 編譯器只能看到宣告的型別,因此無法確定這個類別是否不可變動。因此會將 tags 標示為不穩定。
