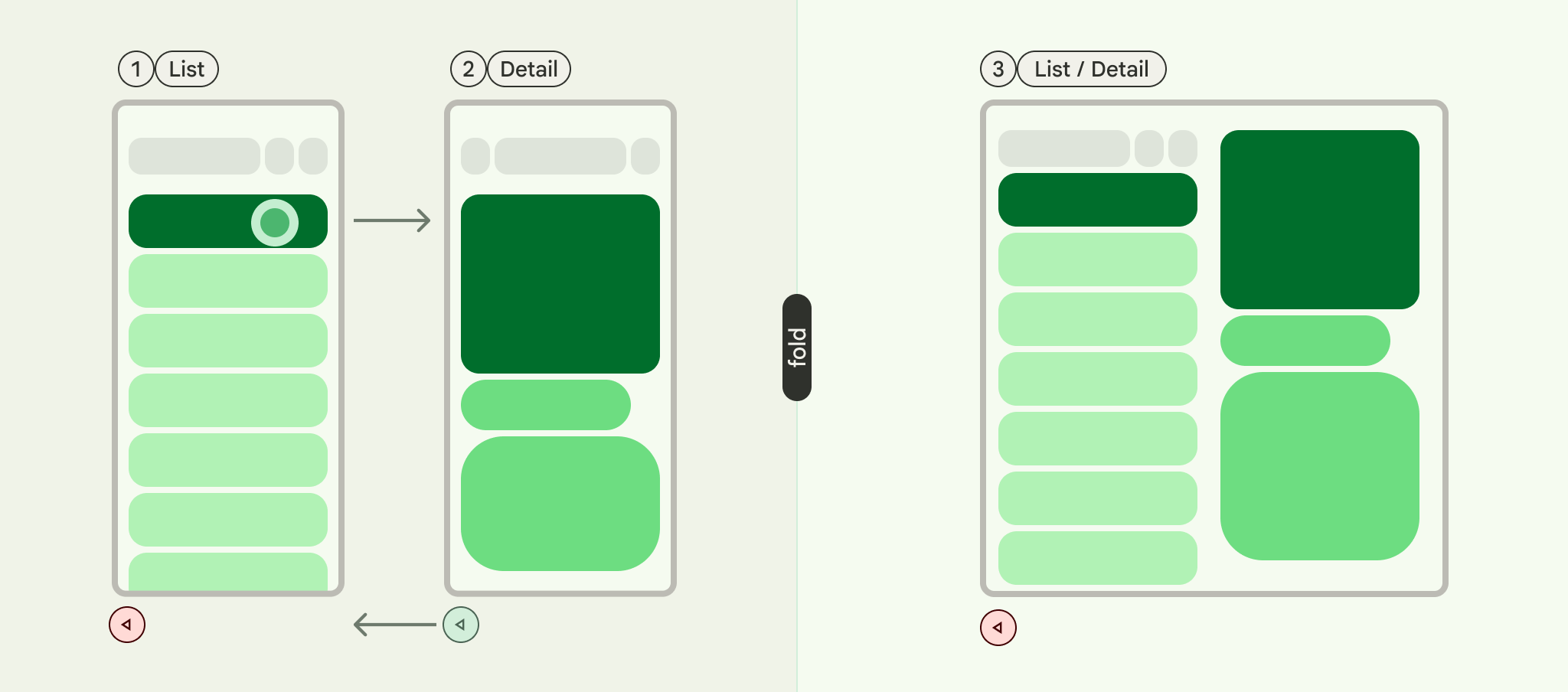
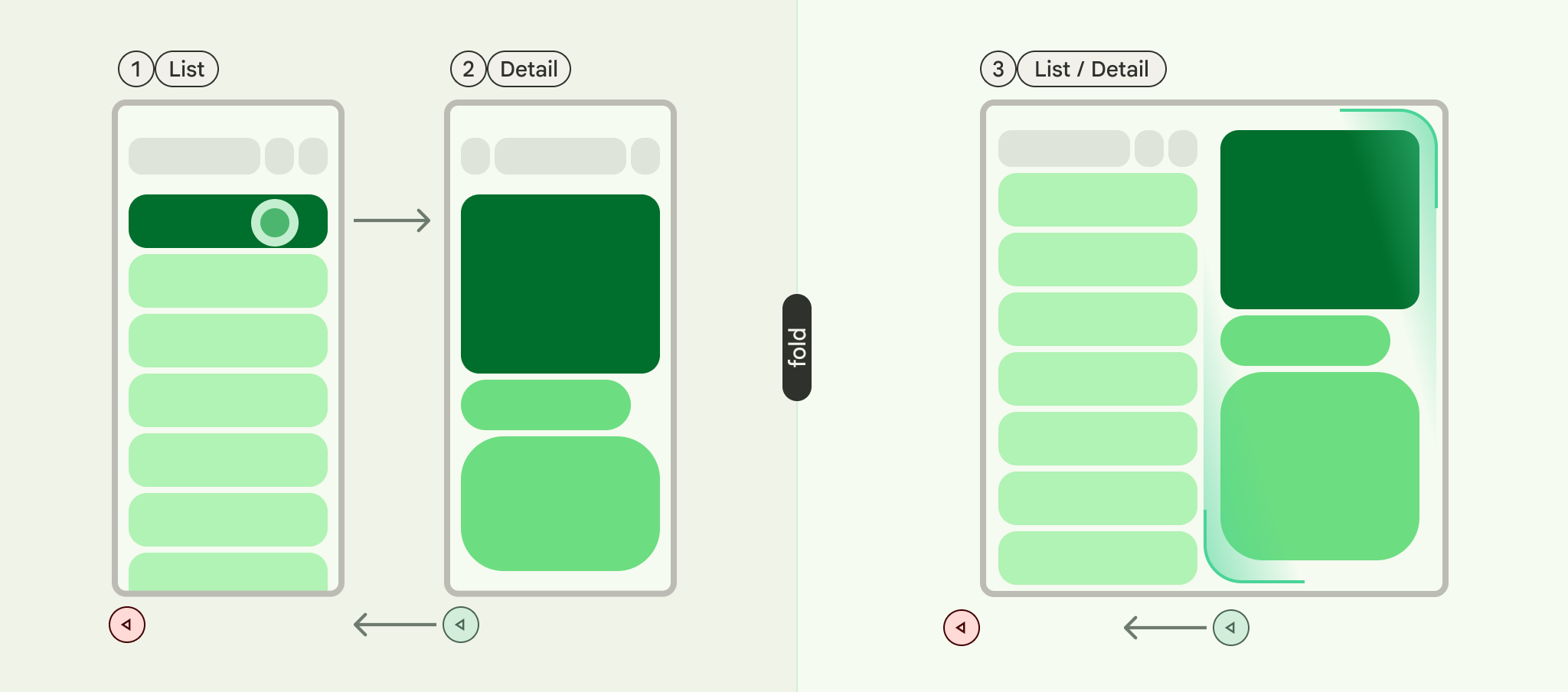
목록-세부정보는 하나의 창에 항목 목록을 표시하고 다른 창에 목록에서 선택한 항목의 세부정보를 표시하는 이중 창 레이아웃으로 구성된 UI 패턴입니다.
이 패턴은 대규모 컬렉션의 요소에 관한 자세한 정보를 제공하는 애플리케이션에 특히 유용합니다. 예를 들어 이메일 목록과 각 이메일 메시지의 세부 콘텐츠가 있는 이메일 클라이언트가 있습니다. 목록-세부정보는 앱 환경설정을 세부정보 창에 있는 각 카테고리의 환경설정과 함께 카테고리 목록으로 나누는 등 덜 중요한 경로에도 사용할 수 있습니다.
NavigableListDetailPaneScaffold로 목록-세부정보 패턴 구현
NavigableListDetailPaneScaffold는 Jetpack Compose에서 목록-세부정보 레이아웃을 간편하게 구현할 수 있는 컴포저블입니다. ListDetailPaneScaffold를 래핑하고 내장 탐색 및 뒤로 탐색 예측 애니메이션을 추가합니다.
목록 세부정보 스캐폴드는 최대 3개의 창을 지원합니다.
- 목록 창: 항목 모음을 표시합니다.
- 세부정보 창: 선택한 항목의 세부정보를 표시합니다.
- 추가 창 (선택사항): 필요한 경우 추가 컨텍스트를 제공합니다.
스캐폴드는 창 크기에 따라 적응합니다.
- 큰 창에서는 목록 창과 세부정보 창이 나란히 표시됩니다.
- 작은 창에서는 한 번에 하나의 창만 표시되며 사용자가 탐색할 때 전환됩니다.
종속 항목 선언
NavigableListDetailPaneScaffold은 Material 3 적응형 탐색 라이브러리의 일부입니다.
앱 또는 모듈의 build.gradle 파일에 다음 세 가지 관련 종속 항목을 추가합니다.
Kotlin
implementation("androidx.compose.material3.adaptive:adaptive") implementation("androidx.compose.material3.adaptive:adaptive-layout") implementation("androidx.compose.material3.adaptive:adaptive-navigation")
Groovy
implementation 'androidx.compose.material3.adaptive:adaptive' implementation 'androidx.compose.material3.adaptive:adaptive-layout' implementation 'androidx.compose.material3.adaptive:adaptive-navigation'
- 적응형:
HingeInfo및Posture과 같은 하위 수준 빌딩 블록 - adaptive-layout:
ListDetailPaneScaffold,SupportingPaneScaffold과 같은 적응형 레이아웃 - adaptive-navigation: 창 내부와 창 간에 탐색하는 컴포저블과 기본적으로 탐색을 지원하는 적응형 레이아웃(예:
NavigableListDetailPaneScaffold,NavigableSupportingPaneScaffold)
프로젝트에 compose-material3-adaptive 버전 1.1.0-beta1 이상이 포함되어 있는지 확인합니다.
뒤로 탐색 예측 동작 선택
Android 15 이하에서 뒤로 탐색 예측 애니메이션을 사용 설정하려면 뒤로 탐색 예측 동작을 지원하도록 선택해야 합니다. 선택하려면 AndroidManifest.xml 파일의 <application> 태그 또는 개별 <activity> 태그에 android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback="true"를 추가합니다. 자세한 내용은 뒤로 탐색 예측 동작 선택을 참고하세요.
앱이 Android 16 (API 수준 36) 이상을 타겟팅하면 기본적으로 뒤로 탐색 예측이 사용 설정됩니다.
기본 사용법
다음과 같이 NavigableListDetailPaneScaffold을 구현합니다.
- 선택한 콘텐츠를 나타내는 클래스를 사용합니다. 선택한 목록 항목의 저장 및 복원을 지원하려면
Parcelable클래스를 사용합니다. kotlin-parcelize 플러그인을 사용하여 코드를 생성합니다. rememberListDetailPaneScaffoldNavigator로ThreePaneScaffoldNavigator를 만듭니다.
이 탐색기는 목록, 세부정보, 추가 창 간에 이동하는 데 사용됩니다. 일반 유형을 선언하면 탐색기는 스캐폴드의 상태(즉, 표시되는 MyItem)도 추적합니다. 이 유형은 parcelable이므로 상태는 탐색기에서 저장하고 복원하여 구성 변경을 자동으로 처리할 수 있습니다.
탐색기를
NavigableListDetailPaneScaffold컴포저블에 전달합니다.목록 창 구현을
NavigableListDetailPaneScaffold에 제공합니다. 탐색 중에 기본 창 애니메이션을 적용하려면AnimatedPane을 사용합니다. 그런 다음ThreePaneScaffoldNavigator를 사용하여 세부정보 창ListDetailPaneScaffoldRole.Detail으로 이동하고 전달된 항목을 표시합니다.NavigableListDetailPaneScaffold에 세부정보 창 구현을 포함합니다.
탐색이 완료되면 currentDestination에는 앱이 탐색한 창이 포함되며, 여기에는 창에 표시된 콘텐츠도 포함됩니다. contentKey 속성은 원래 호출에 지정된 것과 동일한 유형이므로 표시해야 하는 데이터에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
- 필요한 경우
NavigableListDetailPaneScaffold에서defaultBackBehavior을 변경합니다. 기본적으로NavigableListDetailPaneScaffold는defaultBackBehavior에PopUntilScaffoldValueChange를 사용합니다.
앱에 다른 뒤로 탐색 패턴이 필요한 경우 다른 BackNavigationBehavior 옵션을 지정하여 이 동작을 재정의할 수 있습니다.
옵션 BackNavigationBehavior개
다음 섹션에서는 한 창에 이메일 목록이 있고 다른 창에 세부정보 뷰가 있는 이메일 앱의 예를 사용합니다.
PopUntilScaffoldValueChange (대부분의 경우 기본값으로 권장됨)
이 동작은 전체 레이아웃 구조의 변경에 중점을 둡니다. 다중 창 설정에서 세부정보 창의 이메일 콘텐츠를 변경해도 기본 레이아웃 구조는 변경되지 않습니다. 따라서 현재 컨텍스트 내에서 되돌릴 레이아웃 변경사항이 없으므로 뒤로 버튼을 누르면 앱이나 현재 탐색 그래프가 종료될 수 있습니다. 단일 창 레이아웃에서는 뒤로 버튼을 누르면 세부정보 뷰 내의 콘텐츠 변경사항을 건너뛰고 목록 뷰로 돌아갑니다. 이는 명확한 레이아웃 변경을 나타내기 때문입니다.
다음 예를 고려하세요.
- 다중 창: 세부정보 창에서 이메일 (항목 1)을 보고 있습니다. 다른 이메일 (항목 2)을 클릭하면 세부정보 창이 업데이트되지만 목록 창과 세부정보 창은 계속 표시됩니다. 뒤로 버튼을 누르면 앱이나 현재 탐색 흐름이 종료될 수 있습니다.
- 단일 창: 항목 1을 본 후 항목 2를 보면 뒤로 버튼을 눌렀을 때 이메일 목록 창으로 바로 돌아갑니다.
사용자가 각 뒤로 작업으로 명확한 레이아웃 전환을 인식하도록 하려면 이를 사용하세요.
PopUntilContentChange
이 동작은 표시되는 콘텐츠에 우선순위를 부여합니다. 항목 1을 본 다음 항목 2를 보면 레이아웃에 관계없이 뒤로 버튼을 누르면 항목 1로 돌아갑니다.
다음 예를 고려하세요.
- 다중 창: 세부정보 창에서 항목 1을 본 다음 목록에서 항목 2를 클릭합니다. 세부정보 창이 업데이트됩니다. 뒤로를 누르면 세부정보 창이 Item 1로 복원됩니다.
- 단일 창: 동일한 콘텐츠 되돌리기가 발생합니다.
사용자가 뒤로 작업으로 이전에 본 콘텐츠로 돌아갈 것으로 예상하는 경우에 사용합니다.
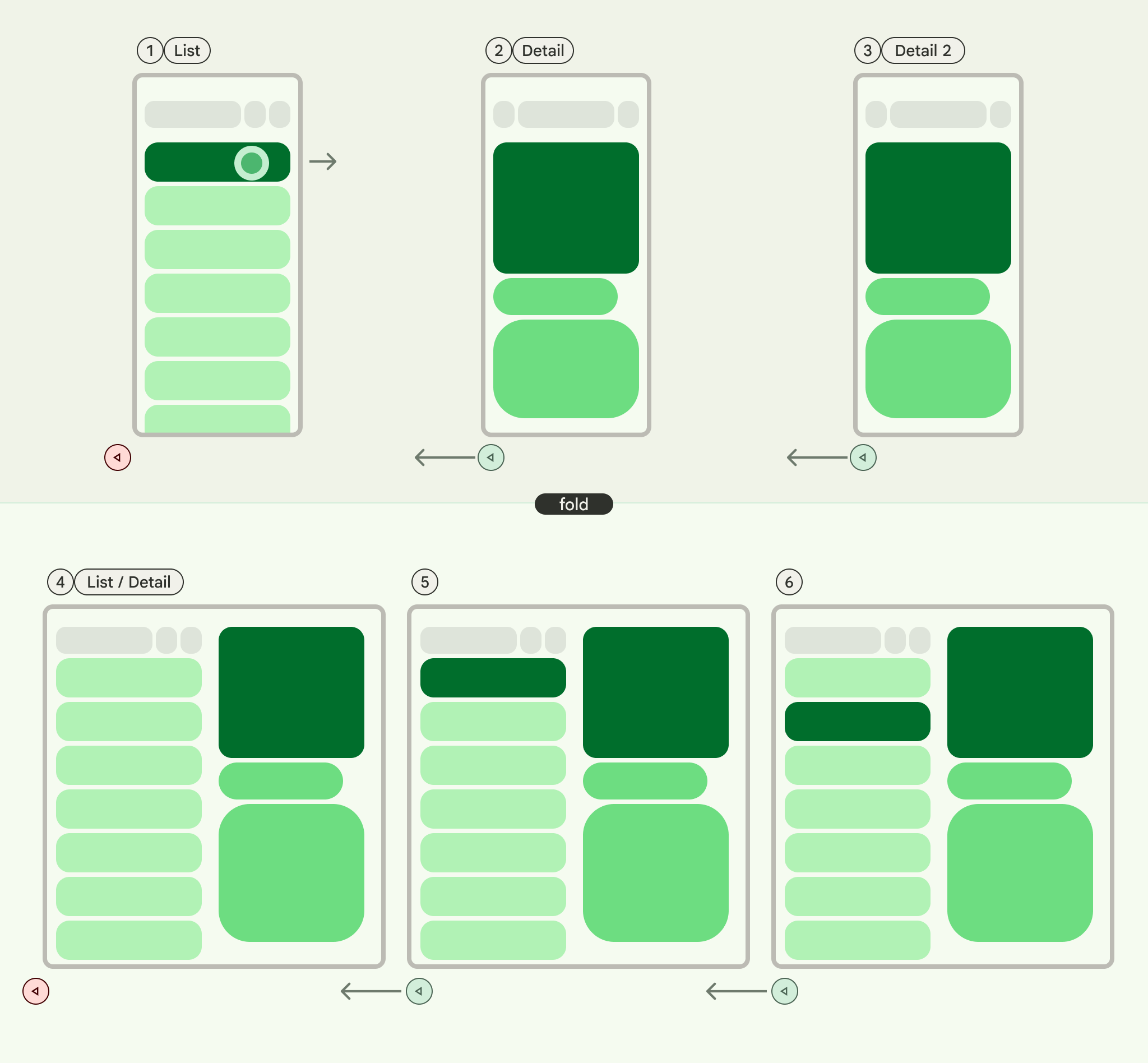
PopUntilCurrentDestinationChange
이 동작은 현재 탐색 대상이 변경될 때까지 백 스택을 팝합니다. 이는 단일 창 레이아웃과 다중 창 레이아웃에 동일하게 적용됩니다.
다음 예를 고려하세요.
단일 또는 다중 창 레이아웃에 관계없이 뒤로 버튼을 누르면 항상 강조 표시된 탐색 요소에서 이전 대상으로 포커스가 이동합니다. 이메일 앱에서는 선택한 창의 시각적 표시가 이동합니다.
현재 탐색의 명확한 시각적 표시를 유지하는 것이 사용자 환경에 중요한 경우에 사용합니다.
PopLatest
이 옵션은 백 스택에서 가장 최근의 대상만 삭제합니다. 중간 상태를 건너뛰지 않고 뒤로 탐색하려면 이 옵션을 사용하세요.
이 단계를 구현하면 코드가 다음과 같아집니다.
val scaffoldNavigator = rememberListDetailPaneScaffoldNavigator<MyItem>() val scope = rememberCoroutineScope() val backNavigationBehavior = BackNavigationBehavior.PopUntilScaffoldValueChange NavigableListDetailPaneScaffold( navigator = scaffoldNavigator, listPane = { AnimatedPane { MyList( onItemClick = { item -> // Navigate to the detail pane with the passed item scope.launch { scaffoldNavigator.navigateTo( ListDetailPaneScaffoldRole.Detail, item ) } }, ) } }, detailPane = { AnimatedPane { // Show the detail pane content if selected item is available scaffoldNavigator.currentDestination?.contentKey?.let { Column { // Allow users to dismiss the detail pane. Use back navigation to // hide an expanded detail pane. if (scaffoldNavigator.scaffoldValue[ListDetailPaneScaffoldRole.Detail] == PaneAdaptedValue.Expanded) { // Material design principles promote the usage of a right-aligned // close (X) button. IconButton( modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.End).padding(16.dp), onClick = { scope.launch { scaffoldNavigator.navigateBack(backNavigationBehavior) } } ) { Icon(Icons.Default.Close, contentDescription = "Close") } } MyDetails(it) } } } }, )
