Mit Tabs können Sie Gruppen verwandter Inhalte organisieren. Es gibt zwei Arten von Tabs:
- Primäre Tabs: Sie befinden sich oben im Inhaltsbereich unter einer oberen App-Leiste. Sie zeigen die wichtigsten Inhaltsziele an und sollten verwendet werden, wenn nur ein Satz von Tabs erforderlich ist.
- Sekundäre Tabs: Werden in einem Inhaltsbereich verwendet, um zusammengehörige Inhalte weiter zu trennen und eine Hierarchie zu schaffen. Sie sind erforderlich, wenn für einen Bildschirm mehr als eine Tabulatortastebene benötigt wird.
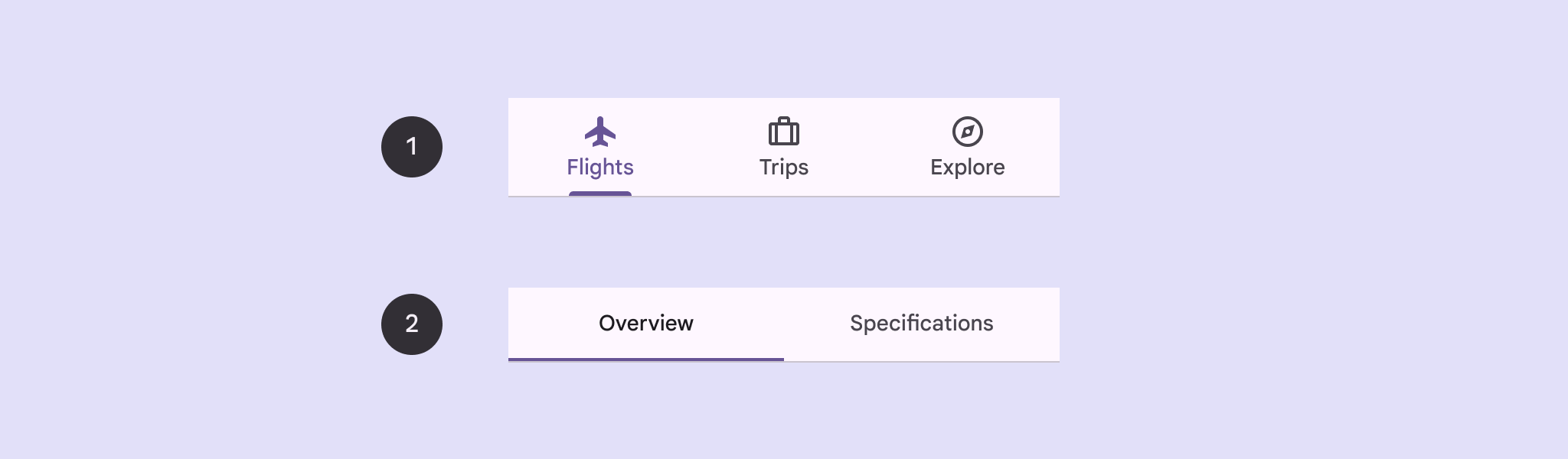
Auf dieser Seite wird beschrieben, wie Sie primäre Tabs in Ihrer App mit zugehörigen Bildschirmen und grundlegender Navigation anzeigen.
API-Oberfläche
Verwenden Sie die Composables Tab, PrimaryTabRow und SecondaryTabRow, um Tabs zu implementieren. Die zusammensetzbare Funktion Tab stellt einen einzelnen Tab in der Zeile dar und wird in der Regel in einem PrimaryTabRow (für Tabs mit primären Indikatoren) oder SecondaryTabRow (für Tabs mit sekundären Indikatoren) verwendet.
Tab umfasst die folgenden wichtigen Parameter:
selected: Gibt an, ob der aktuelle Tab visuell hervorgehoben wird.onClick(): Eine erforderliche Lambda-Funktion, die die Aktion definiert, die ausgeführt werden soll, wenn der Nutzer auf den Tab klickt. Hier werden in der Regel Navigationsereignisse verarbeitet, der Status des ausgewählten Tabs aktualisiert oder entsprechende Inhalte geladen.text: Zeigt Text auf dem Tab an. Optional.iconzeigt ein Symbol auf dem Tab an. Optional.enabled: Steuert, ob der Tab aktiviert ist und mit ihm interagiert werden kann. Wenn der Wert auf „false“ gesetzt ist, wird der Tab deaktiviert angezeigt und reagiert nicht auf Klicks.
Beispiel: Tab-basierte Navigation
Im folgenden Snippet wird eine obere Navigationsleiste mit Tabs zum Navigieren zwischen verschiedenen Bildschirmen in einer App implementiert:
@Composable fun NavigationTabExample(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) { val navController = rememberNavController() val startDestination = Destination.SONGS var selectedDestination by rememberSaveable { mutableIntStateOf(startDestination.ordinal) } Scaffold(modifier = modifier) { contentPadding -> PrimaryTabRow(selectedTabIndex = selectedDestination, modifier = Modifier.padding(contentPadding)) { Destination.entries.forEachIndexed { index, destination -> Tab( selected = selectedDestination == index, onClick = { navController.navigate(route = destination.route) selectedDestination = index }, text = { Text( text = destination.label, maxLines = 2, overflow = TextOverflow.Ellipsis ) } ) } } AppNavHost(navController, startDestination) } }
Wichtige Fakten
PrimaryTabRowzeigt eine horizontale Zeile mit Tabs an, wobei jeder Tab einemDestinationentspricht.val navController = rememberNavController()erstellt und speichert eine Instanz vonNavHostController, die die Navigation in einemNavHostverwaltet.var selectedDestination by rememberSaveable { mutableIntStateOf(startDestination.ordinal) }verwaltet den Status des ausgewählten Tabs.startDestination.ordinalruft den numerischen Index (die Position) desDestination.SONGS-Enum-Eintrags ab.
- Wenn Sie auf einen Tab klicken, werden die
onClick-Lambda-AufrufenavController.navigate(route = destination.route)verwendet, um zum entsprechenden Bildschirm zu wechseln. - Die
onClick-Lambda-Funktion vonTabaktualisiert denselectedDestination-Status, um den angeklickten Tab visuell hervorzuheben. - Dazu wird die kombinierbare Funktion
AppNavHostaufgerufen undnavControllerundstartDestinationübergeben, um den tatsächlichen Inhalt des ausgewählten Bildschirms anzuzeigen.
Ergebnis
Das folgende Bild zeigt das Ergebnis des vorherigen Snippets:
.png?authuser=7&hl=de)
