Thanh điều hướng cung cấp quyền truy cập vào các đích đến trong những ứng dụng chạy trên thiết bị có màn hình lớn. Bạn nên sử dụng thanh điều hướng cho:
- Đích đến cấp cao nhất cần truy cập được ở mọi nơi trong ứng dụng
- Từ 3 đến 7 điểm đến chính
- Bố cục dành cho máy tính bảng hoặc máy tính
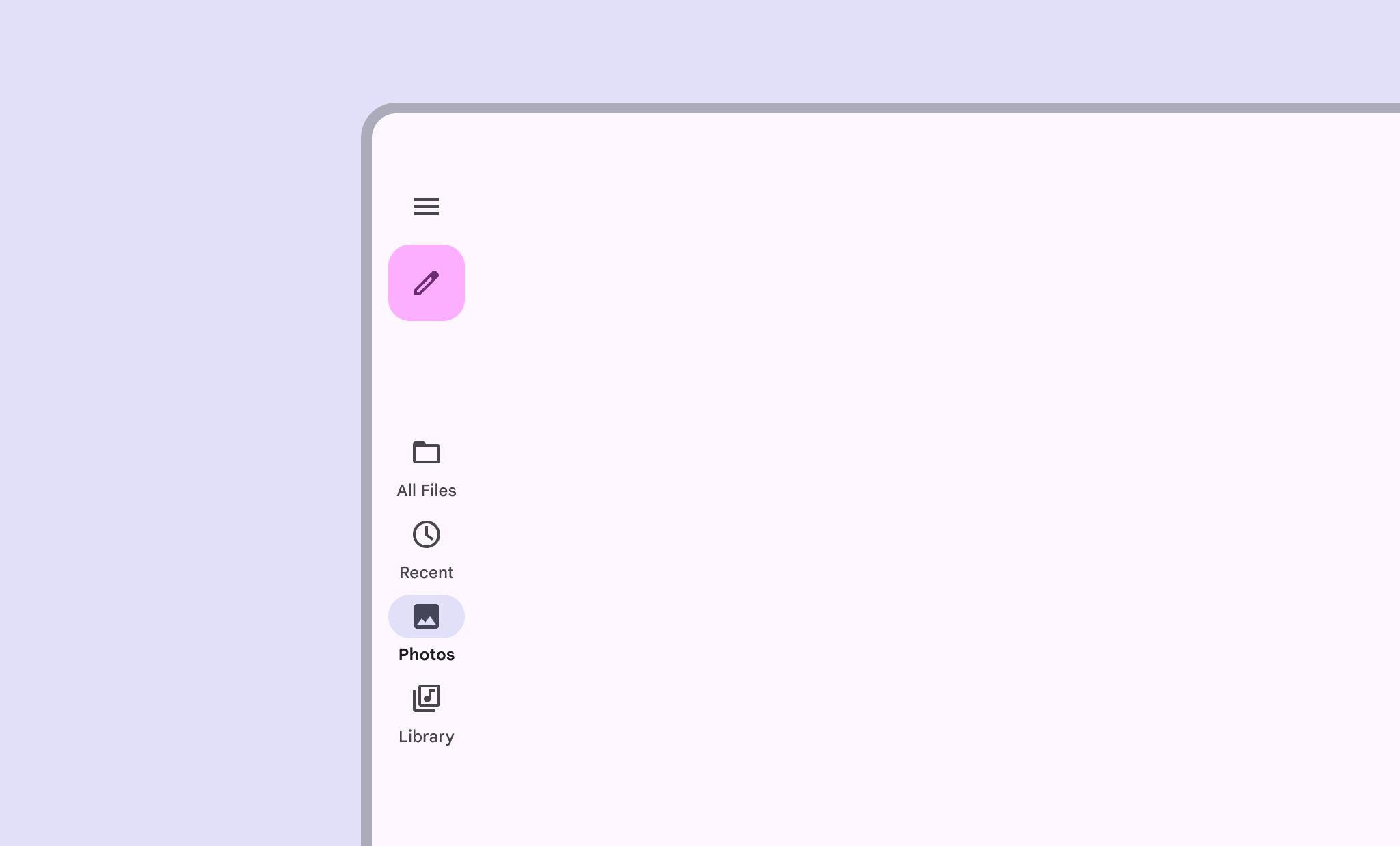
Trang này hướng dẫn bạn cách hiển thị các thanh điều hướng trong ứng dụng bằng các màn hình liên quan và chế độ điều hướng cơ bản.
Nền tảng API
Sử dụng thành phần kết hợp NavigationRail với NavigationRailItem để triển khai một thanh điều hướng dọc trong ứng dụng của bạn. NavigationRailItem biểu thị một mục riêng lẻ trong cột đường ray.
NavigationRailItem bao gồm các thông số chính sau:
selected: Xác định xem mục trong danh sách phát hiện tại có được làm nổi bật bằng hình ảnh hay không.onClick(): Một hàm lambda bắt buộc xác định hành động sẽ được thực hiện khi người dùng nhấp vào mục trên thanh điều hướng. Đây là nơi bạn thường xử lý các sự kiện điều hướng, cập nhật trạng thái của mục trong thanh bên đã chọn hoặc tải nội dung tương ứng.label: Hiển thị văn bản trong mục đường ray. Không bắt buộc.icon: Hiển thị một biểu tượng trong mục thanh điều hướng. Không bắt buộc.
Ví dụ: Hệ thống điều hướng dựa trên thanh điều hướng dọc
Đoạn mã sau đây triển khai một dải điều hướng để người dùng có thể di chuyển giữa các màn hình khác nhau trong một ứng dụng:
@Composable fun NavigationRailExample(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) { val navController = rememberNavController() val startDestination = Destination.SONGS var selectedDestination by rememberSaveable { mutableIntStateOf(startDestination.ordinal) } Scaffold(modifier = modifier) { contentPadding -> NavigationRail(modifier = Modifier.padding(contentPadding)) { Destination.entries.forEachIndexed { index, destination -> NavigationRailItem( selected = selectedDestination == index, onClick = { navController.navigate(route = destination.route) selectedDestination = index }, icon = { Icon( destination.icon, contentDescription = destination.contentDescription ) }, label = { Text(destination.label) } ) } } AppNavHost(navController, startDestination) } }
Điểm chính
NavigationRailhiển thị một cột dọc gồm các mục trên thanh, trong đó mỗi mục tương ứng với mộtDestination.val navController = rememberNavController()tạo và ghi nhớ một thực thể củaNavHostController, đối tượng này quản lý hoạt động điều hướng trong mộtNavHost.var selectedDestination by rememberSaveable { mutableIntStateOf(startDestination.ordinal) }quản lý trạng thái của mục đường ray hiện được chọn.startDestination.ordinallấy chỉ mục số (vị trí) của mục nhập enumDestination.SONGS.
- Khi người dùng nhấp vào một mục trên thanh điều hướng,
navController.navigate(route = destination.route)sẽ được gọi để chuyển đến màn hình tương ứng. - Hàm lambda
onClickcủaNavigationRailItemsẽ cập nhật trạng tháiselectedDestinationđể làm nổi bật trực quan mục đường ray được nhấp vào. - Thao tác này gọi thành phần kết hợp
AppNavHost, truyềnnavControllervàstartDestinationđể hiển thị nội dung thực tế của màn hình đã chọn.
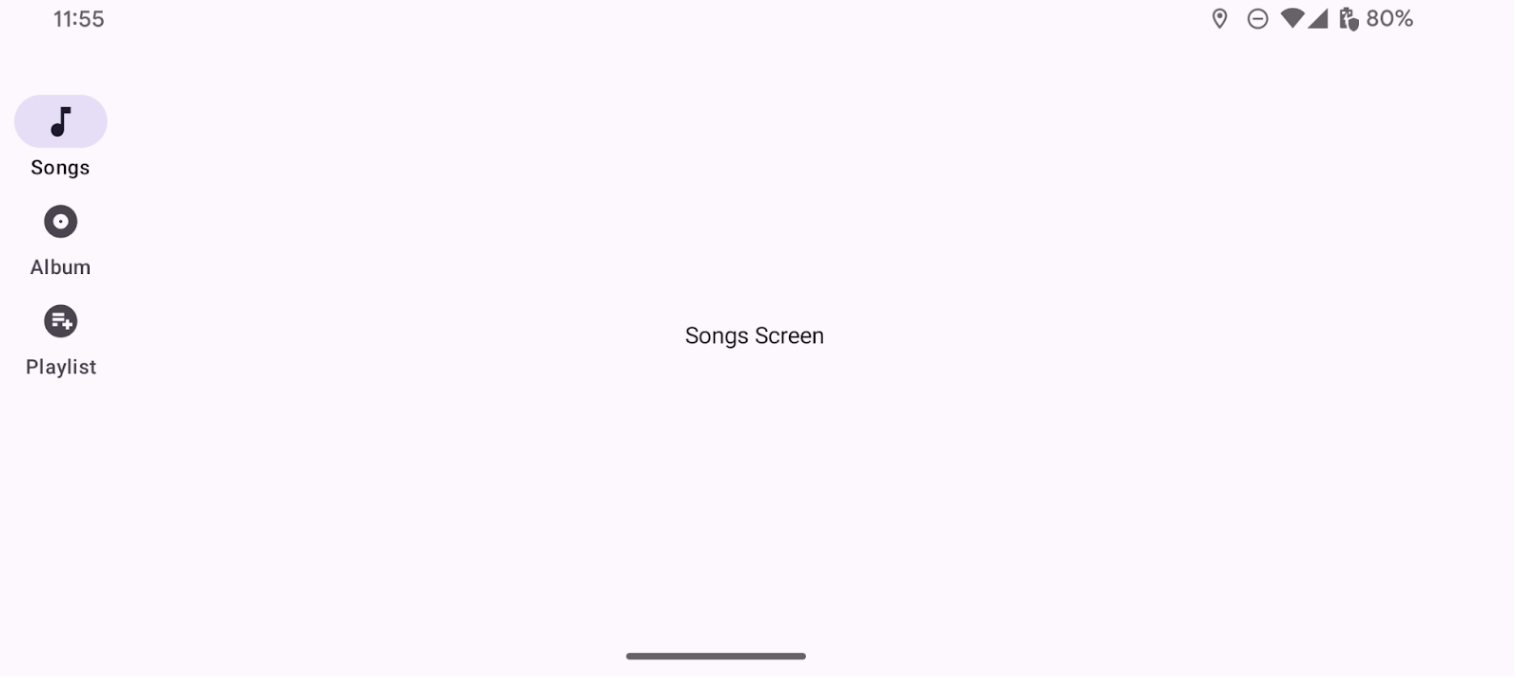
Kết quả
Hình ảnh sau đây cho thấy kết quả của đoạn mã trước: